Reverse osmosis
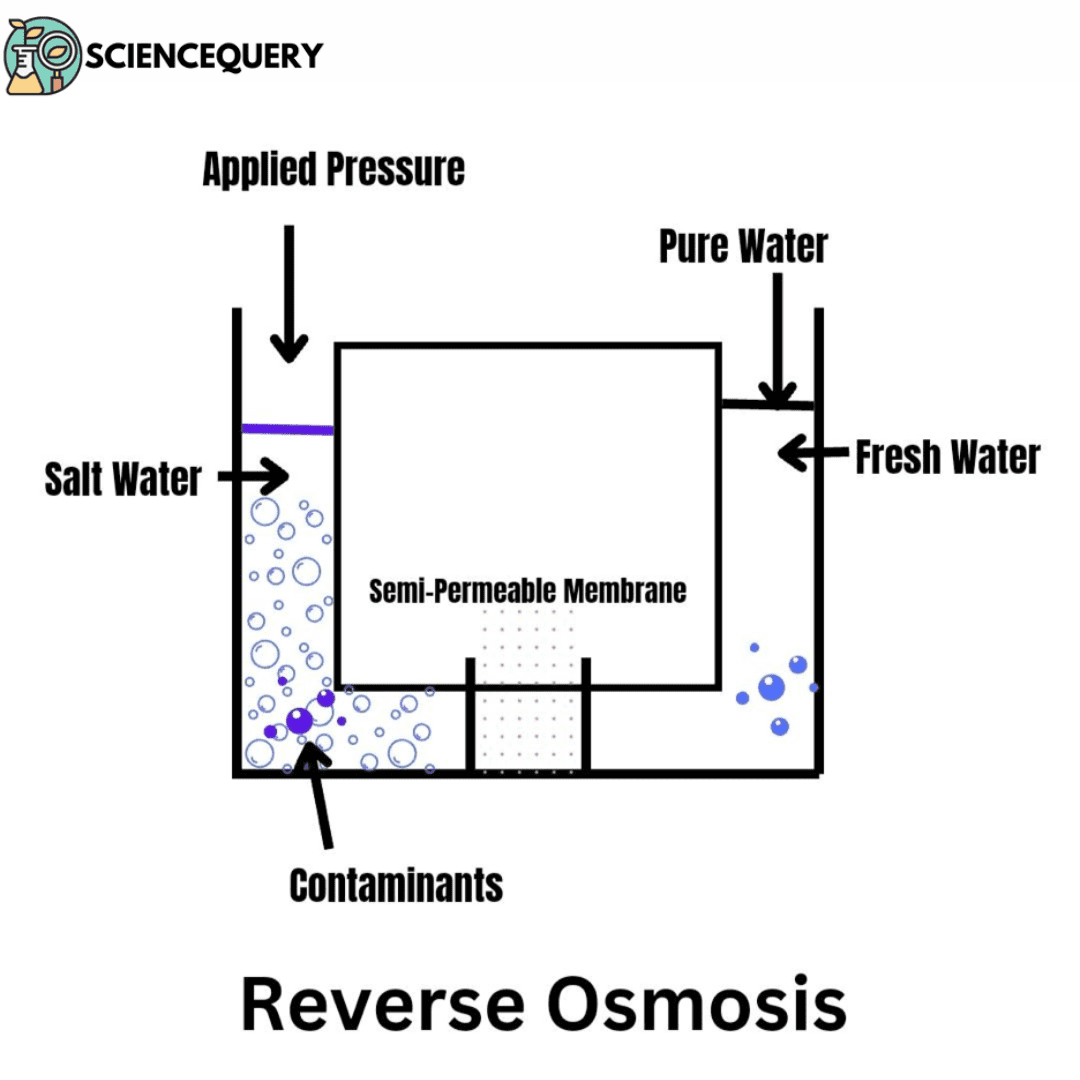
Introduction Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution. The membranes act […]

Introduction Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution. The membranes act […]
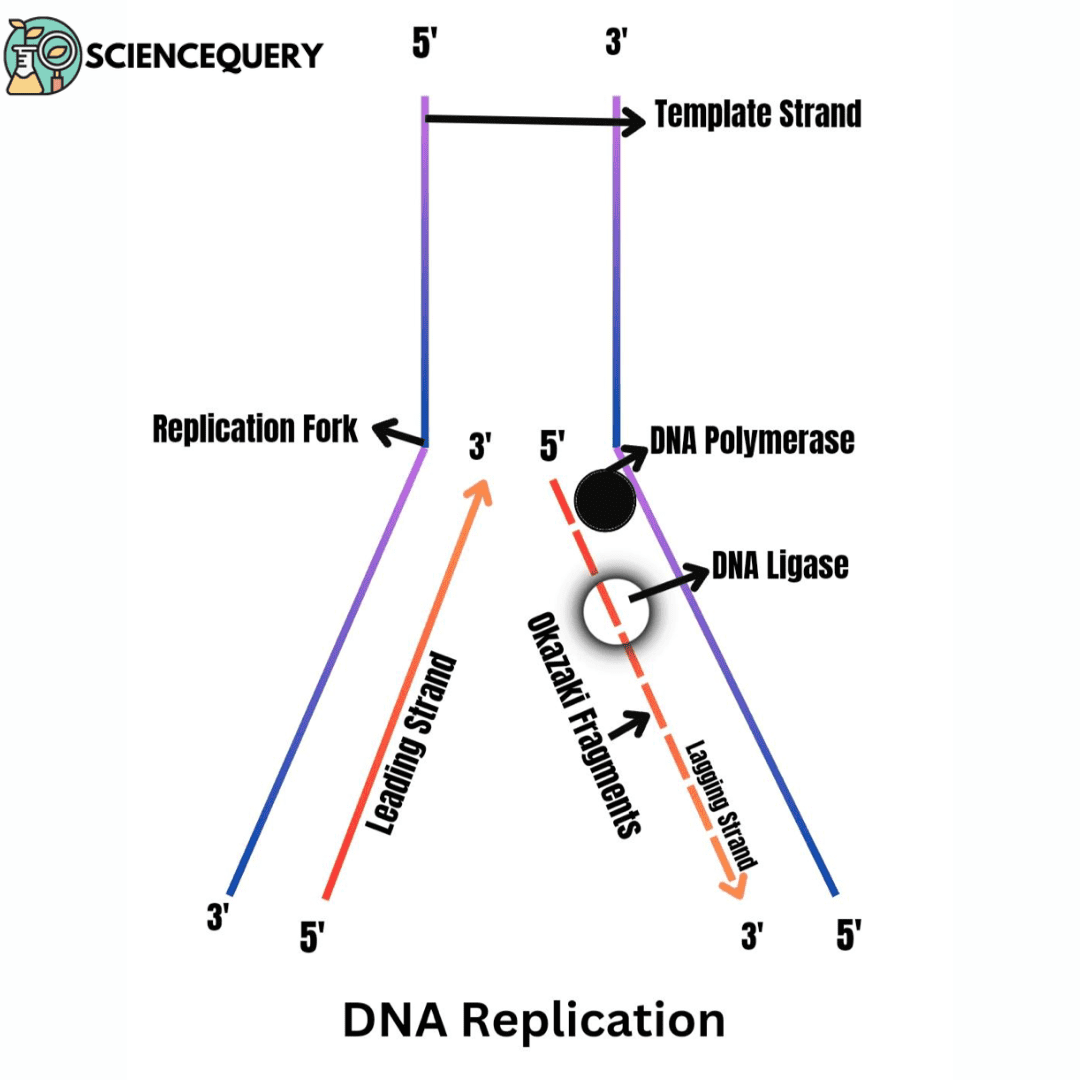
Introduction DNA is the fundamental building block of an organism’s genetic information. It consists of two long strands made up of four different nucleotide bases […]
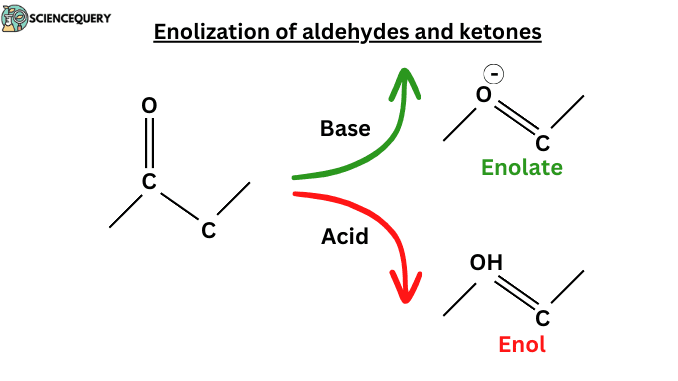
Introduction The enol is formed by the transfer of a proton from the central CH2 group of the Keto form to one of the OH […]

Introduction Soap and detergent both are cleaning agents that are essential for removing dirt, any contaminants that cannot be removed only with water. They are […]

Introduction Definition of Disaccharides is a compound that consists of two units of monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, galactose, and mannose. Disaccharides are generally formed in […]
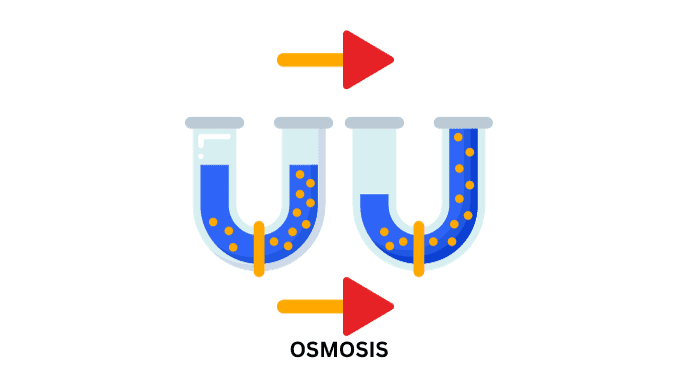
Introduction Definition Osmosis is the net diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution when the two are separated by means […]
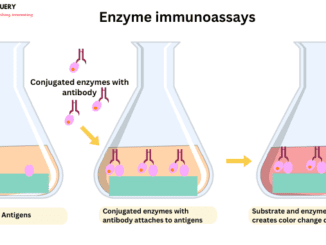
Know in one minute about Enzyme immunoassay Enzyme immunoassay is an important technique for the detection of proteins, hormones, peptides, etc. EIA determines the sample […]
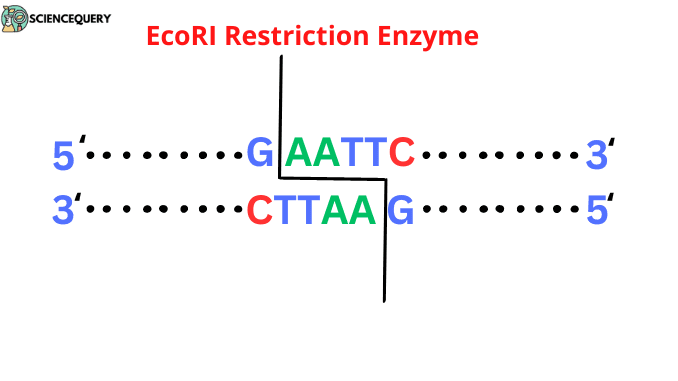
Know in one minute about EcoRI Restriction Enzyme EcoRI Restriction Enzyme is a type II restriction endonuclease. It was derived from the bacteria Escherichia coli […]
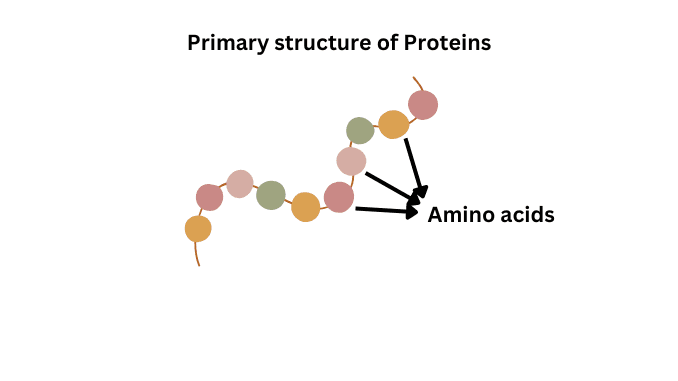
Introduction Protein is an essential part of our diet, consisting of long chains of amino acids called polypeptides. It plays a crucial role in building, […]
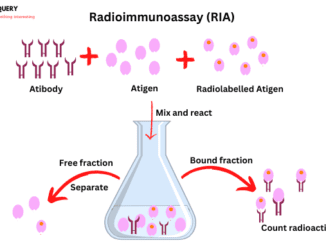
Know in one minute about Radioimmunoassay Radioimmunoassay is used to determine the concentration of Ag present in the patient sample. It utilizes the radioactive isotopes […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes