Introduction
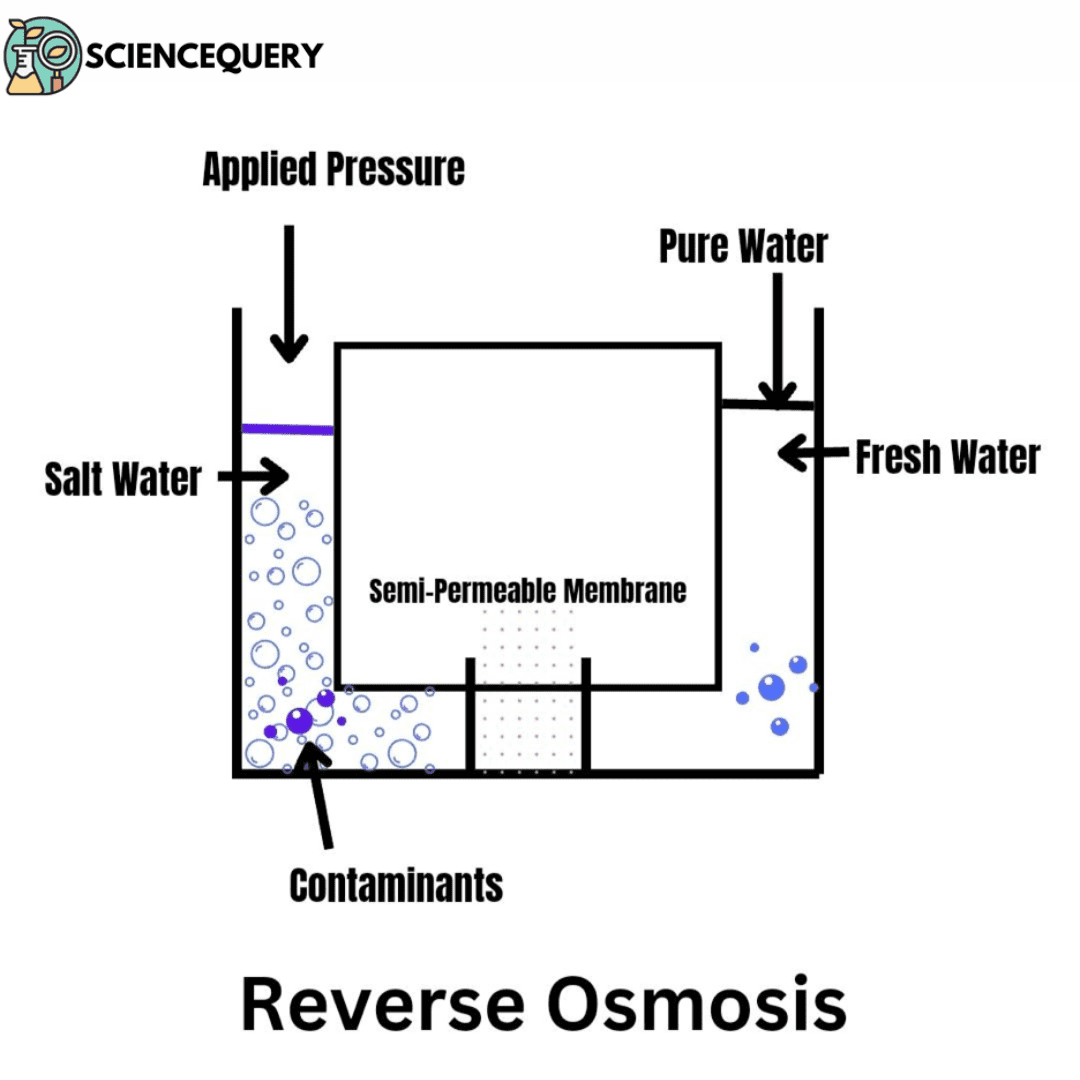
Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution. The membranes act as selectively permeable barriers that allow selective elements to pass through them. RO method helps in eliminating the dissolved solids as well as the suspended solids.
Osmosis is a process where water flows through a semipermeable membrane. The flow of solution ranges from low to high concentrations of dissolved solids. This semipermeable membrane allows water and the flow of some ions only. The water flow will be continued until the concentration is balanced on both sides.
Principles of osmosis
The basic principle of osmosis is that water will continue to flow from low to high concentrations of dissolved solids. This process continues until equilibrium is attained on both sides of the membrane. When at equilibrium, the solution is the same and there is no net flow of contents between the compartments.
Fundamental of reverse osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a pressure-driven process that uses a synthesized semi-permeable membrane made from cellulose acetate and polyamide to separate two mediums. This is a basic demineralization process that involves the separation of dissolved solids from liquid. Cellular acetate and linear aromatic polyamide membranes are widely used for this process.
Semi-permeable membrane and its role
Semipermeable Membranes allow the diffusion of only selective molecules across them. In turn, this process helps in removing salts and harmful bacteria from the water. Reverse osmosis relies on pressure differentials to push water molecules through it. This in turn leaves behind larger particles and impurities.
The asymmetric cellulose acetate made RO commercially viable due to improved flux systems. Advanced membranes called- FT30 are the commercially available semipermeable membranes used today.
Key components of reverse osmosis
key components of reverse osmosis include the following:
- Pre-filters: To ensure the removal of large particles and sediments from the water before it enter the reverse osmosis system.
- RO Membrane: It consists of a cellulose acetate membrane with tiny pores that allow only selective molecules to pass through it.
- Pressure Pump: A pump is needed to create pressure for the water to flow through the membrane at uniform speeds.
- Post-filters: After passing the membrane filters, suspended impurities require post-filtration for further purification.
- Storage Tank: Once filtered, potable water is stored in a tank until it’s ready for use.
- Flow Restrictor: Reverse osmosis produces wastewater that needs to be drained out while maintaining a proper flow rate within the system.
Role of pre-filter membrane
The role of prefiltration can be considered coarse filtration where the membranes are designed to remove impurities. The impurities are larger particles, removed from the feed before it enters the reverse osmosis system. Hence, it protects the membranes of reverse osmosis from clogging and fouling, thus increasing its life span.
Role of post-filter
Post filters are designed in a way to remove the remaining impurities after filtration. Post filters are highly used in this process as they target the processing of ultra-pure and clean water. Hence, the filtration technique is highly implemented in this process due to its effectiveness and efficiency in producing pure water.
Pressure in the RO process
Pressure is a key factor in reverse osmosis. It allows the flow of water through the membrane while maintaining a uniform pressure. It is applied on one side of the membrane for the water to pass through and separate from other substances.
Applications of reverse osmosis
It includes various applications such as:
- Desalination of seawater and brackish water for potable use. To convert this saline water for drinking purposes. This method is widely practiced in areas where water supply is scarce.
- Generation of distilled water that can be used extensively in pharmaceuticals and medical laboratories.
- Requirement of processed water for beverages that are used for beverage industry purposes.
- Reverse osmosis technology is also used in the processing of dairy products.
- This process is widely used in water reclamation of municipal and industrial wastewater. For example- Wastewater in Singapore is treated by reverse osmosis process.
- Waste treatment for the recovery of process materials like dyes, used in the manufacture of textiles.
Advantages of reverse osmosis
- In water treatment- Reverse Osmosis has become highly popular due to its effectiveness in removing impurities from water. It is efficient in removing bacteria, and suspended impurities from the water. Hence, it is a widely used method used in water treatment plants. The removal of impurities through RO results in improved taste and odor of the treated water.
- In removing various contaminants like salt, minerals, and impurities- Reverse osmosis technology is highly efficient in removing suspended impurities like salt, minerals, and other contaminants. It is capable of eliminating 99% of bacteria and solid particles from water by the use of filters.
The Reverse Osmosis method is also used for the desalination of salt water thus making it potable for drinking. This technique is widely used in areas of water scarcity. Sewage water is also treated in areas of less water supply by reverse osmosis process. Many countries including Southeast Asia have already adopted this technique of water purification.
Difference between reverse osmosis vs Forward Osmosis
Features |
Reverse Osmosis |
Forward Osmosis |
| Definition | Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution. | In forward osmosis, water will continue to flow from low to high concentrations of dissolved solids. |
| Gradient System | This process occurs against the potential gradient. This gradient system contributes a lot regarding desalination in wastewater treatment plants. | It occurs through a gradient system. |
| Applications | It is widely used in wastewater treatment plants as it is cost-effective and environmentally friendly. | In the human body, osmosis plays a crucial role in the transportation of nutrients in our cells.
Dried raisins when kept in water get puffed up due to the result of osmosis. |
Q&A
1. Is it healthy to drink reverse osmosis water?
Yes, RO water is completely safe for consumption. Modern water purifications consist of RO filters to remove harmful impurities.
2. What are the disadvantages of reverse osmosis?
The RO system eliminates about 99% of dissolved salt, minerals, and harmful contaminants. But the major concern is it also removes beneficial minerals along it, that are necessary for the human body. It ultimately deprives the body of the necessary vitamins and minerals.
3. Why is it called reverse osmosis?
The process of reverse osmosis is named as such because it involves the opposite direction of regular osmosis. Additionally, In reverse osmosis, a pressure-driven force is applied to water molecules. The water flows through the membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
4. What is reverse osmosis in the human body?
The main function of reverse osmosis in the human body is to filter excess water, electrolytes, and other substances from the blood through specialized structures called nephrons located in the kidneys.
Summary
- Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution.
- The membranes act as selectively permeable barriers that allow selective elements to pass through them.
- RO method helps in eliminating the dissolved solids as well as the suspended solids.
- It is a pressure-driven process that uses a synthesized semi-permeable membrane made from cellulose acetate and polyamide to separate two mediums.
- This is a basic demineralization process that involves the separation of dissolved solids from liquid.
- Cellular acetate and linear aromatic polyamide membranes are widely used for this process.
- Advanced membranes called- FT30 are the commercially available semipermeable membranes used today.
- Reverse osmosis technology is also used in the processing of dairy products.
- This process is widely used in water reclamation of municipal and industrial wastewater.The
- The Reverse Osmosis method is also used for the desalination of salt water thus making it potable for drinking. This technique is widely used in areas of water scarcity.
- It is capable of eliminating 99% of bacteria and solid particles from water by the use of filters.
- This process occurs against the potential gradient. This gradient system contributes a lot regarding desalination in wastewater treatment plants.
- This process is highly cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
- The main function of reverse osmosis in the human body is to filtration of excess water, electrolytes, and other substances from the blood through specialized structures called nephrons located in the kidneys.
References
- https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=h0jpDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=reverse+osmosis+wastewater&ots=wQc76TaKwG&sig=29ztfAFpCjC6R0IknknCYVhcwhU
- http://www.environmentaljournal.org/1-3/ujert-1-3-2.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0043135409001547
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0011916498001027
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0011916415301454
Written By: Sushmita Mukhopadhyay
