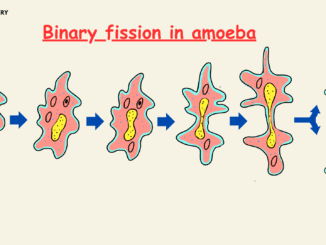
Binary Fission in Amoeba
Introduction Amoeba a simple unicellular organisms or single-cell organisms that can change their shape and move freely as it does not have any cell walls. […]

Introduction Amoeba a simple unicellular organisms or single-cell organisms that can change their shape and move freely as it does not have any cell walls. […]
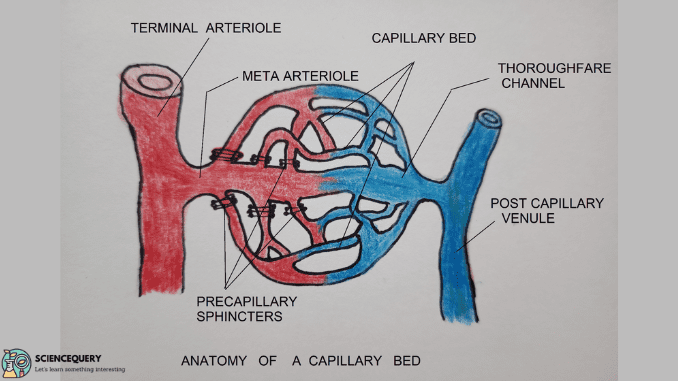
Capillaries Introduction Capillaries are the smallest and the most numerous of the blood vessels. They connect arteries and veins. The primary function is to exchange […]

What are vectors? and draw a simple diagram with a short note. Click here to download: What are vectors?

Introduction Greenhouse gases are those gasses present in the earth’s atmosphere that help to trap the heat received by the sun. The greenhouse effect is […]

Introduction The flow of energy in an ecosystem through various plants and organisms is known as the food chain. The tundra biome has a unique […]
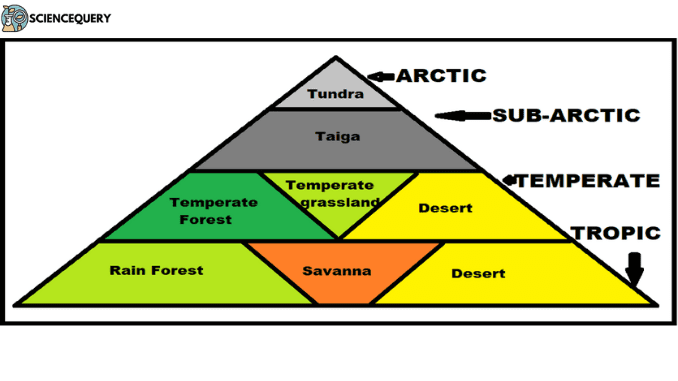
Introduction Biome is a major climax community of plants and animals. It generally corresponds to a climatic region. According to F.E Clements and V.S.Shelford, “ […]

Introduction A food web is the representation of the interconnected feeding relationship among various components of an ecosystem. It transfers energy through various producers, consumers, […]
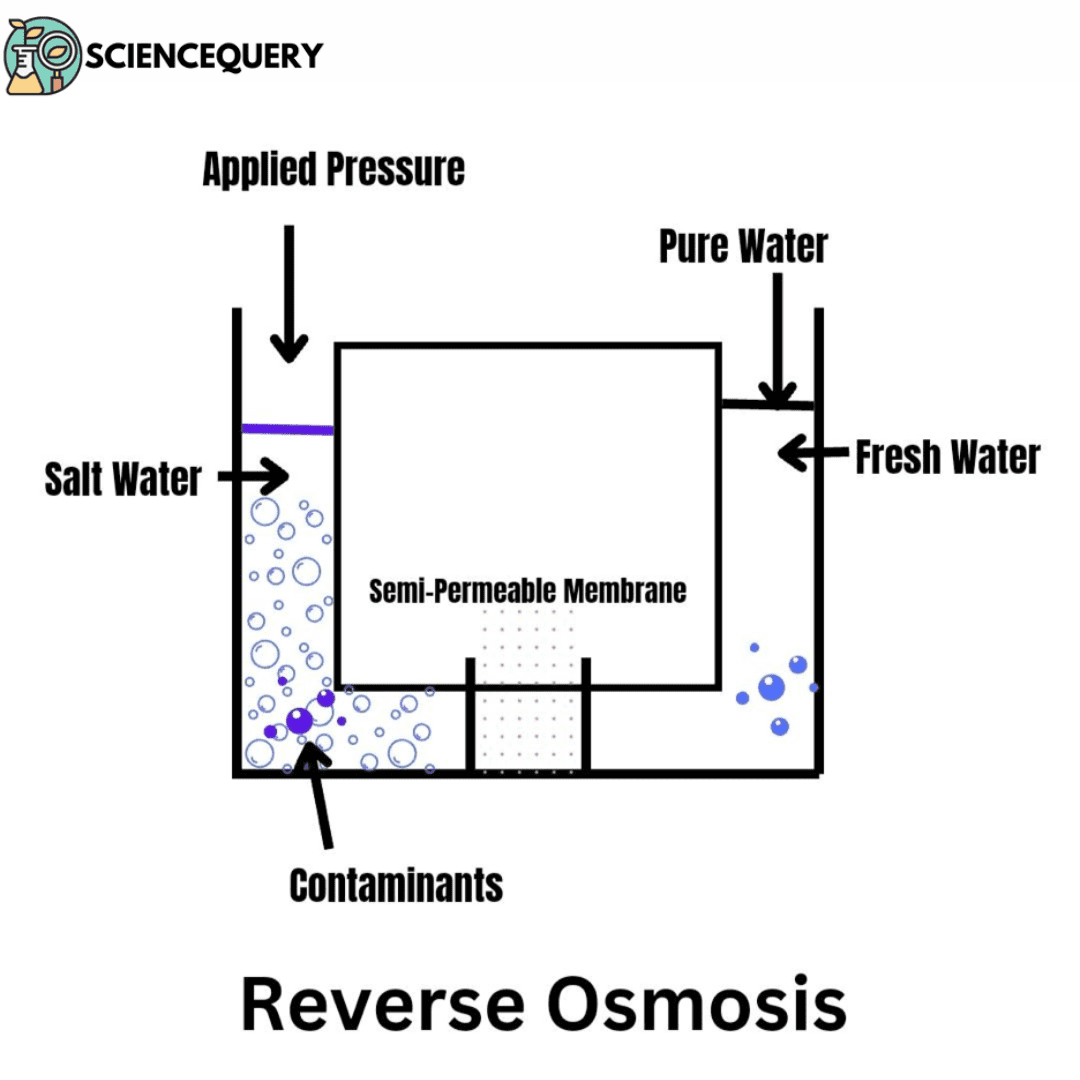
Introduction Reverse Osmosis is a membrane-based demineralized technique that is used to separate the dissolved solids such as ions from the solution. The membranes act […]
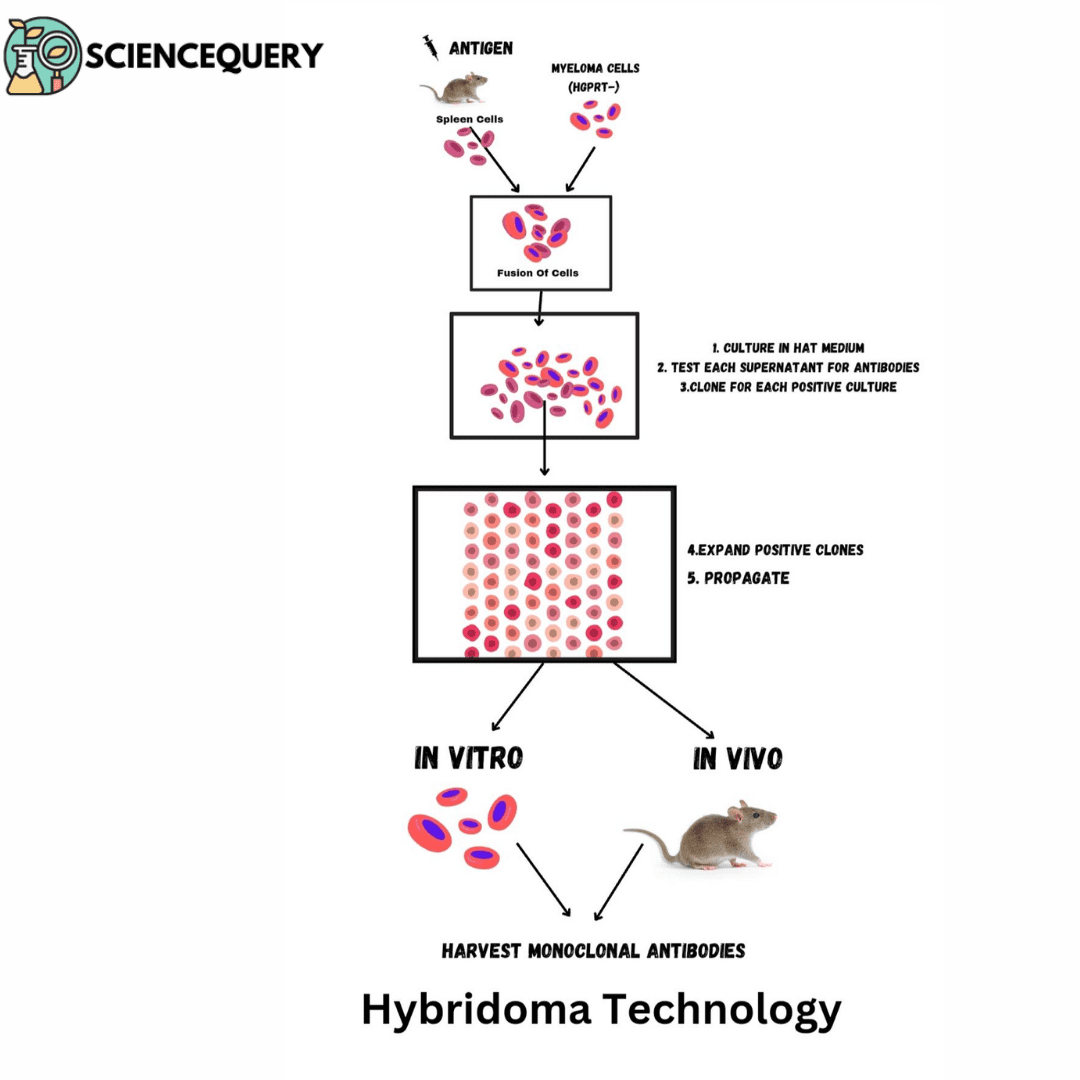
Introduction When two non-identical cells are brought into close contact and their membranes are allowed to fuse, the resulting product contains both nuclei. The fusion […]
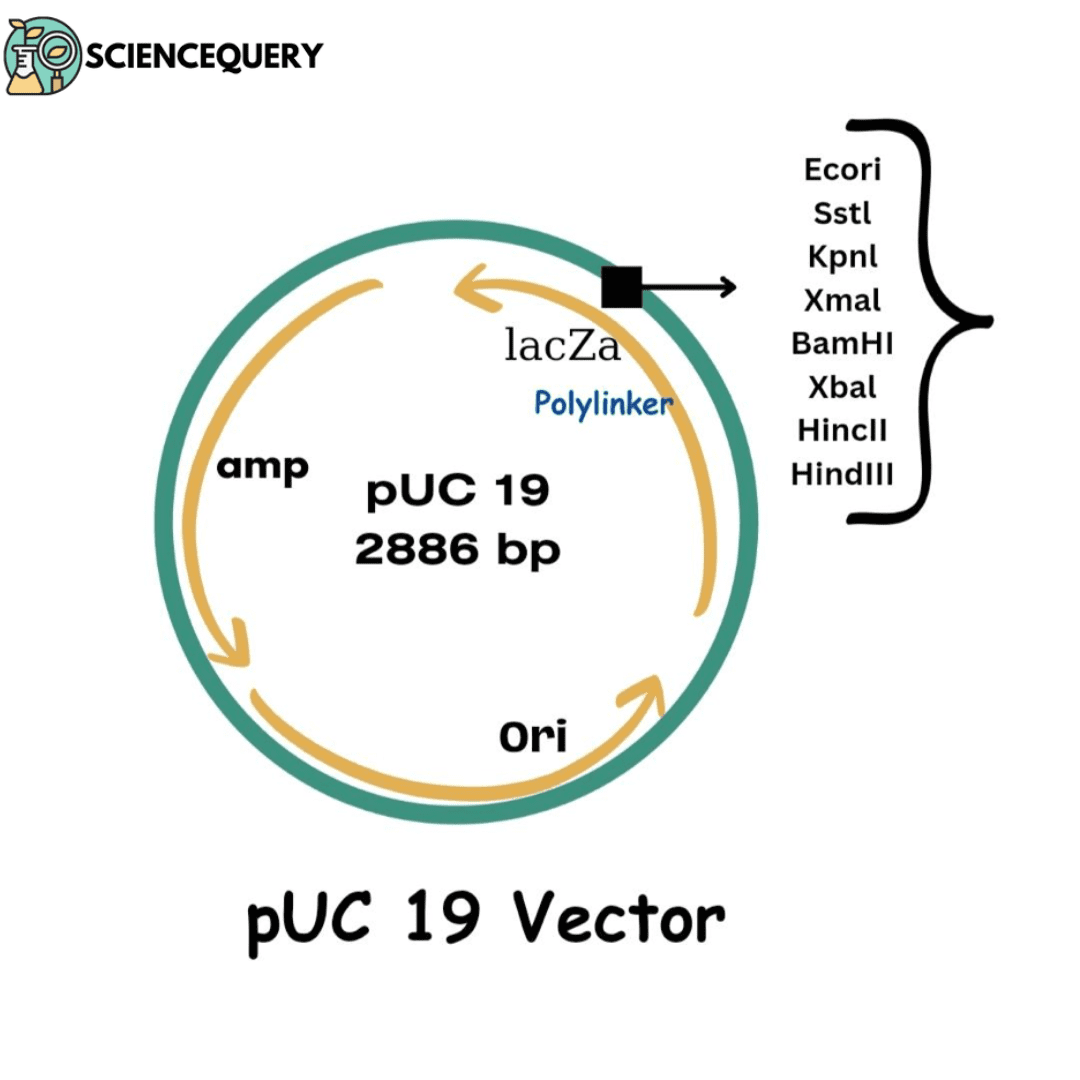
Introduction Vectors and their importance Vectors are the major component required to make an rDNA molecule for gene cloning. They act as a vehicle for […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes