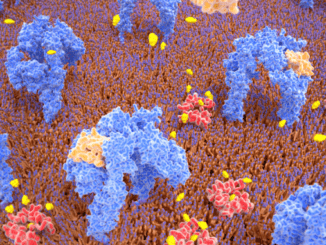
Enzyme activity: Definition, types and factors
Enzymes: An introduction Enzymes are biological catalysts that help in speeding up a chemical reaction without altering itself. All the enzymes are protein in nature […]

Enzymes: An introduction Enzymes are biological catalysts that help in speeding up a chemical reaction without altering itself. All the enzymes are protein in nature […]
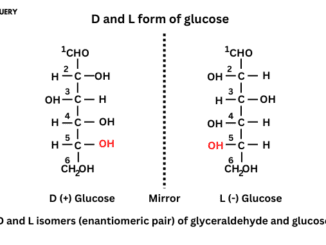
Introduction The following topic is about enantiomers vs diastereomers and their definition and structure with a simple basic difference. Enantiomers and diastereomers are both optically […]
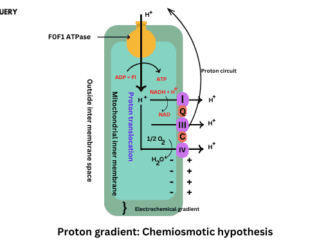
Know in one minute about the Chemiosmotic hypothesis The chemiosmotic hypothesis explains the mechanism of ATP Synthesis by a proton gradient. Lumen has low pH […]
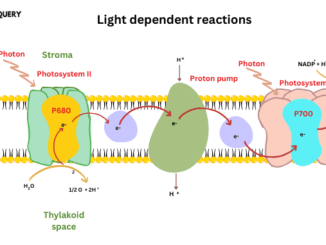
Know in one minute about light-dependent reactions Light-dependent reactions produced ATP and NADP + H, in the presence of light. Take place on the grana […]
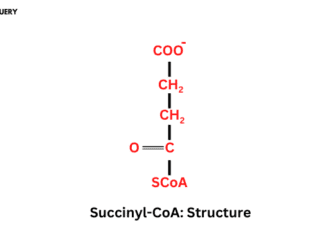
Know in one minute about Succinyl CoA Succinyl-CoA is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle. It is formed by propionyl-CoA during the beta Oxidation […]
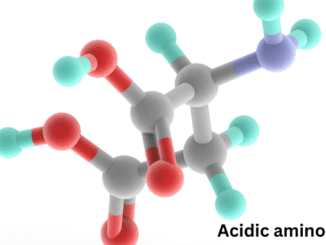
Know in one minute about acidic amino acids Acidic amino acids have more than the number of negatively charged groups in comparison to positively charged […]
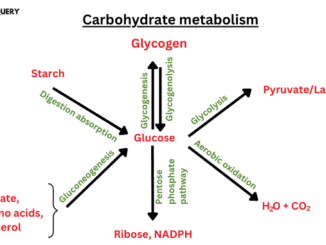
Know in one minute about carbohydrate metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is a process that degrades glucose into simpler compounds and produces energy. This energy is used […]
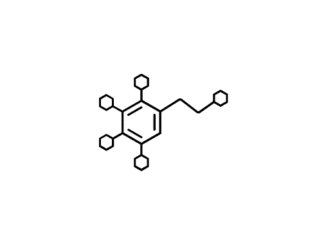
Primary metabolites Primary metabolites like carbohydrates, amino acids, peptides, and proteins can be found in all plants. They are responsible for basic physiological functions. Are […]

Know in one minute about the Regulation of Glycolysis Glycolysis is a control metabolic pathway. It is a sequenced reaction converting glucose to pyruvate or […]
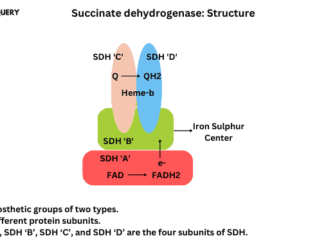
Know in one minute about Succinate dehydrogenase Succinate dehydrogenase is a complex structure enzyme, found in the inner membrane of mitochondria. It is the only […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes