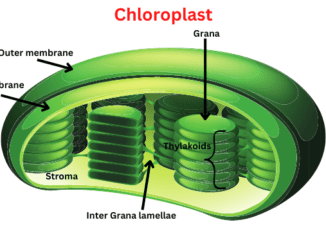
Where do light-dependent reactions occur?
Where do light-dependent reactions occur? The light reactions occur in the grana or thylakoid membrane of chloroplast and Involve processes that resemble mitochondrial electron Transport […]

Where do light-dependent reactions occur? The light reactions occur in the grana or thylakoid membrane of chloroplast and Involve processes that resemble mitochondrial electron Transport […]
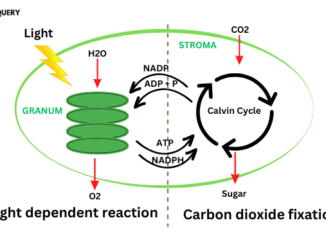
What are the products of light-dependent reactions? NADPH+H and ATP are products of light-dependent reactions. This energy is used in dark reactions to produce carbohydrates. […]
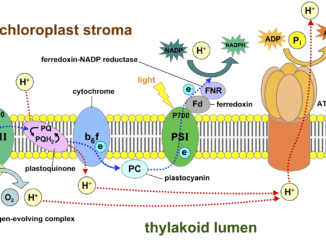
Let us get a better understanding of what is a photosystem and how they are so important for plants and other organisms. show the organisms […]

Introduction Strong acids are substances that on dissociation release a vast number of hydronium cations ( H+or H3O+). Strong acids also have a large value […]

Introduction Acetyl CoA is a vital compound in cellular respiration. It is produced from carbohydrates, protein or amino acids, and lipids. It is a key […]
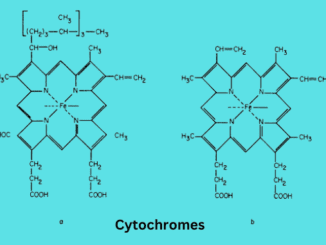
Definition Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with the central Fe (iron) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the […]
Alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is present in the outer layer of the cell membrane. They are present in different body tissues and have […]
Flavoproteins Flavoproteins are made of a polypeptide bound tightly to one of two related prosthetic groups either flavin mononucleotide called FMN or flavin adenine dinucleotide […]

Some readers might be in doubt that why Acetic acid is a weak electrolyte. In this section of the article, we will discuss the same […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes