Introduction
Soap and detergent both are cleaning agents that are essential for removing dirt, any contaminants that cannot be removed only with water. They are used for mostly household things like cleaning clothes, dishwashing, mopping floors etc. and used as skin cleaners and important for hand washing. following is the article on the difference between soap and detergent as cleaning agents
Converts the insoluble contaminate to solubilized form then it’s easily eliminated by water. Are very important for protection against any infection because they dissolve the bilayer lipid membrane of micro-organisms. Hence handwashing is one of the most effective actions to reduce the spread of any infection caused by bacteria or viruses.
Significance and understanding the difference
- Based on cleaning property and hard water compatibility detergent is better than soap.
- Detergents are used in hard water but soap cannot be used in hard water because they produced scum with hard water.
- Detergent clean soft fabric without any damage because its aqueous solution is neutral in nature.
- Due to hydrolysis, the aqueous solution of soap is alkaline in nature hence soap damages the soft fabrics.
- Soaps made with natural fatty acid or detergents are salts of sulfonic acid or alkyl hydrogen sulphate that’s why soaps are easily biodegradable but detergents are not.
Composition and origin
- Soaps were first introduced by Greek physician Galenus for cleaning purposes.
- They are a mixture of sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids like stearic acid, palmitic acid, or oleic acid.
- Example is
- C15H31COONa – Sodium palmitate
- C17H35COONa – Sodium stearate
- C17H33COONa – Sodium Oleate
- They consist of saturated and unsaturated chains of carboxylic acids containing 12 to 18 carbon molecules. The bigger the hydrocarbon chain the better the soap.
- If soap contains a higher percentage of unsaturated fatty acids we get soft soap. Examples are Potassium soap, shaving cream liquid shampoo etc.
- If soap contains a higher percentage of saturated fatty acids we get hard soap.
Composition of detergent
Detergent also known as soapless soap that means they do not look like soap but is soap.
They are a mixture of salts of sulfonic acids or alkyl hydrogen sulphate.
Examples are
- Sodium n-dodecyl sulphate
- Sodium lauryl sulphate
- Sodium n-dodecyl benzene sulphonate
Natural soap: derived from fats or oil
- Natural soaps are derived from natural products like vegetable oil, plant and fruit extracts, animal fat or oil.
- These natural soaps are environment-friendly because they easily decompose and are also useful for our skin health.
Synthetic detergent
- Synthetic detergents are anion-active detergents. These are sulphate salts of long chains of hydrocarbons.
- The anion active part is the cleansing agent.
- One common example is sodium alkyl sulphate.
- The preparation involves treating a long-chain alcohol with concentrated sulphuric acid. It is neutralized by NaOH.
- They are used in household work, like washing clothes, mopping floors etc. Anionic detergents are also used in toothpaste.
Soap is a hairpin-shaped structure that consists of two parts
1. Hydrophobic tail
A long chain of hydrocarbons which is soluble in water and insoluble in water.
Solubility
Soluble in oil or fat and insoluble in water
Polar or non-polar
It is non-polar because they have no charges.
2. Hydrophilic head
COO- group attached in this region and metals like sodium or potassium attached
Solubility
Soluble in water and insoluble in oil or fat
Polar or nonpolar
It is polar because they have a negative charge.
Formula: RCOONa
Molecular structure of detergent
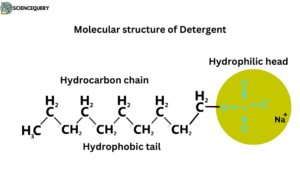 The detergent consists of two parts
The detergent consists of two parts
- A long chain of hydrocarbons which is hydrophobic.
- The short ionic chain is hydrophilic. Ionic chains generally contain sodium sulfonate (SO3–Na+) or sodium sulphate (SO4–Na+).
Formula: -R–SO3-Na
Soap
Manufacture of soap
- Generally, two ways are used for the manufacture of soap. First is Saponification and second is to directly neutralize the fatty acids by alkali.
- Saturated fatty acids like stearic acid, palmitic acid and caustic soda are used for producing hard soap.
- Unsaturated fatty acids like linolenic acid and caustic potash are used for producing soft soap.
Saponification
Soap is mainly made with vegetable oil or animal fat by heating with NaOH or KOH. This process is called saponification.
Fat or oil (triesters) + alkali (NaOH) → Soap (Sodium salts of fatty acids) + Glycerol
Soap interaction with hard water
- When soap is used in hard water, an insoluble solid substance is formed which is known as scum.
- The scum is composed of calcium and magnesium ions.
- When the calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water react with the hydrophobic head of soap molecules they form some insoluble substances which are responsible for the scum formation.
- This scum sticks to fabric or clothes resulting in dirt difficult to remove from clothes.
Detergent
- Detergents are generally sodium salts of sulfonic acids or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromides ions etc. Detergent and soap both have long hydrocarbon chains.
- They are not natural membrane constituents. They formed micelles in aqueous solutions.
- In water hydrophilic polar heads occur on the outside and the hydrophilic nonpolar tail inside.
- The bile acids and bile salts are naturally occurring detergents which are found in the digestive tract for emulsifying fats and they are also useful for the solubilization of membrane protein.
Detergents are classified into four types
- Anionic detergents
- Cationic detergents
- Nonionic detergents
- Amphoteric detergents
Detergent interaction with hard water
- The charged ends of these compounds do not form insoluble precipitates with calcium and magnesium ions in hard water. Thus they remain effective in hard water.
- Detergent contains SO3 instead of COO– groups. This SO3 does not actively react with calcium and magnesium ions in order to form the insoluble substances hence these insoluble substances are not formed.
- Soap and detergent have the ability to remove the dirt from the surface.
- Dirt is oily in nature so it does not dissolve in water. A soap molecule has two ends with different abilities.
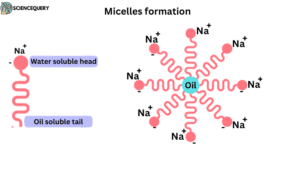
- For micelles formation hydrophobic tail of the soap is towards the oily or dirt particles while the hydrophilic head occurs outside of dirt and it interacts with water.
- This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelles help eliminate the dirt particles in water.
- Mechanical and physical action like scrubbing causes oil or dust particles to be disposed of into tiny droplets.
- When we rub the cloth the micelle is removed from the cloth along with the dirt and dirt dissolves in water whereas the cloth comes out clean and water becomes dirty.
- The carboxylate (COO–) group of soap molecule project outwards.
- The surface of micelles carries a negative charge. Two micelles do not coalesce with each other due to similar charges.
Soap acts as an emulsifier
- A mixture of two immiscible liquids is called an emulsion which is in unstable form.
- Emulsifiers stabilise the emulsion in stable form and this process is called emulsification.
- Emulsifiers initiate mixed oil and water because they don’t normally mix with each other.
- The soap works as an emulsifier it stabilises emulsion between oil and water. The polar or ionic part connects with water and the polar part is attached with an oil droplet.
- All soap particles are arranged around the oil droplet. As a result, the interface is decreased between oil droplets and water. It is stabilized by micelle formation.
Detergent: Utilizes surfactants to lower the surface tension
- Detergents have the capacity to reduce the surface tension of the water.
- It’s increased the cleaning property of detergents.
- Surfactants are the surface active agents that reduce surface tension at the boundary between two regions.
- In surfactants, one end is attached to a water molecule and the other end is attached to an oil or dirt particle.
- It allows the surface to be wet and penetrates to remove dirt particles.
- It reduces the cohesive power of oil particles along with surface tension. Hence dirt particle break down in smaller units then it is easily removed from the surface.
Biodegradability and impact on the environment
- Soap is the least toxic of all detergents and easily biodegradable. So, it does not cause stream pollution.
- Detergents are excellent foaming agents. They have bactericidal and germicidal properties.
- The foam produced by some detergents is so extensive and stable that it forms a foam bed over rivers, ponds and lakes receiving the sewage water.
- This is mainly due to the branched chain hydrocarbon surfactants which are not easily biodegradable.
Breakdown of Soap
Soaps are easily broken into Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), and Oxygen (O) by microorganisms present in the water and soil.
Breakdown of Detergent
The detergent breaks down similar to soap but takes much longer times compared to soap this is why foam is seen on rivers and streams. It is not easily decomposed because of the cross-linked chains.
Soap Vs Detergent
Subject |
Soap |
Detergent |
Definition |
They are the sodium salts of long-chain fatty acids. | These are sodium or potassium salts of sulphonic acids of hydrocarbons. |
Composition |
Soaps made with natural compounds like fatty acids or animal fat etc. | Detergents are made with synthetic materials like chemicals. |
Hard water compatibility |
Soaps cannot be used with hard water. They are insoluble in water. | They can be efficiently used even in hard water. |
Biodegradability |
Soaps are easily biodegradable because they consist of linear chains of hydrocarbons. | Detergents are non-biodegradable due to the presence of cross-linked chains. |
Solubility in water |
Soaps take time to dissolve in water. | They dissolve faster in water. |
Scum formation |
In hard water, it forms an insoluble solid substance ((i.e. Ca2+ and Mg+2 precipitate) called scum. | They do not form scum. |
Impact on environment |
Soap is environmentally friendly. It is easily broken down by microorganisms. | In comparison to soap, detergent takes much longer times for break down. |
Applications
Laundry cleaning products
Soap or detergents are useful for making laundry cleaning products like Detergent Powder, Detergent Cake, Fabric Softener, Laundry Liquid, Stain and Odor Eliminator etc.
Household cleaning products
They are used for making household cleaning products like Floor Cleaners, Glass Cleaners, Toilet Bowl Cleaners, and Wood Cleaners.
Dishwashing Products
They are used for making Dishwasher Liquid, Dishwasher Powder, Dishwasher Gel, Dishwasher Tablets, and Fuel Additives.
Washing laboratory equipment
They are used for washing laboratory equipment like glassware. An example is labolene.
Cosmetic or beauty products
It is used for making cosmetic products like face wash, spray, shampoo etc.
Sensitivity and allergies
- Skin allergy and sensitivity are generally common with detergents and soaps.
- This allergy is caused by chemicals used in the production of soap and detergents.
- Detergents are made with synthetic material that can irritate the skin if you have sensitive skin.
- Aqueous solution of soap is alkaline due to hydrolysis. So soap solutions cause irritation to the sensitive skin.
- In the detergent industry, during detergent manufacture workers are exposed to enzyme additives.
- The enzyme attacks the proteins in the lung tissue which is responsible for the allergic conditions.
Q&A
1. What is the difference between soap and synthetic detergent?
Soaps are the salts of oil or fatty acids while synthetic detergents are salts of sulphonic acid or alkyl hydrogen sulphate.
2. Is soap or detergent better?
Detergent is better in comparison to soap. Detergent works in hard water but soap does not.
3. Is detergent also a soap?
Detergent is a type of soap because its cleansing mechanism is the same as soap but it is different from soap in composition or molecular structure.
4. Can you use laundry detergent as soap?
Laundry cannot be used as soap because soap is made with natural fatty acids but it is made with harsh synthetic material is not safe for our skin in a long time.
5. Is soap or detergent better for the skin?
Soap is better for the skin because it makes natural products like animal fat, vegetable oil, and fruit extracts. They did not cause harm to the skin as compared to detergent.
Summary
- Soaps and detergents both are cleaning agents that are used for removing dirt or oily particles from the surface.
- Soaps are sodium and potassium salts of oil or fatty acids like palmitic acid, stearic acid or oleic acids.
- Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonic acids or ammonium salts with chlorides or bromide ions.
- Soaps are produced by saponification and direct neutralization of fatty acids by alkali.
- Soaps are made with natural products but detergents are made with chemicals or synthetic materials.
- Soap and detergent cleaning mechanisms are the same but have different molecular structures.
Reference
Soaps, detergents and disinfectants technology handbook (3rd revised edition).