
What is Hydrogen Oxide?
Introduction Water, also called Hydrogen Oxide is formed by 88.89% oxygen and 11.11% hydrogen by weight. Water is a compound that possesses a definite composition […]

Introduction Water, also called Hydrogen Oxide is formed by 88.89% oxygen and 11.11% hydrogen by weight. Water is a compound that possesses a definite composition […]
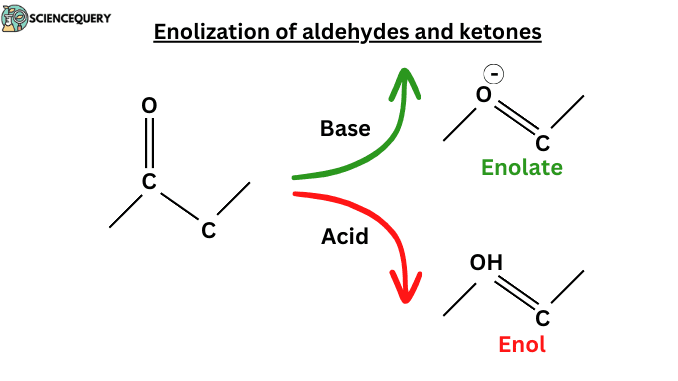
Introduction The enol is formed by the transfer of a proton from the central CH2 group of the Keto form to one of the OH […]

Introduction Definition of Disaccharides is a compound that consists of two units of monosaccharides like glucose, fructose, galactose, and mannose. Disaccharides are generally formed in […]

Introduction In 1923 Bronsted and Lowry proposed this theory to define acid and base. It’s applied on both aqueous and non-aqueous solution. They focused on […]

Introduction Silver is not only used for making jewelry but also is required for many industrial purposes like batteries, dentistry, nuclear reactors to photography (1). […]
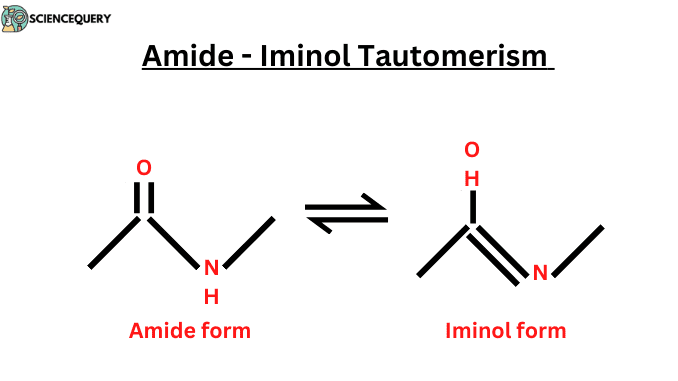
Know in one minute about tautomerization Tautomerism is the process in which a single compound exists in two interconvertible structures that differ in the relative […]
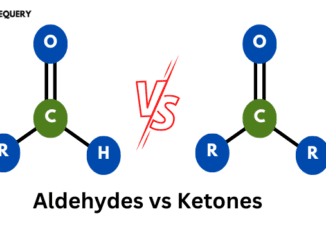
Introduction Functional groups of carbon are groups of elements that on adding to a carbon chain or elemental chains like that of a nitrogen or […]
Introduction The chemical element carbon is one of the most commonly used elements in day-to-day life. One can find carbon in almost all the objects […]

Introduction Carbon is considered to be the element that is present in almost all objects that we use in our day-to-day life and also is […]
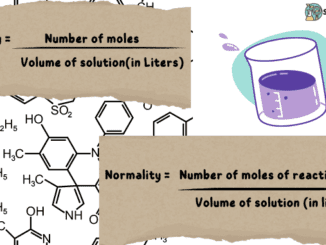
Introduction In science, almost all quantities being measured have a specific unit or way to complete the measurement process. Some quantities are measured using a […]
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes