Know in one minute about Enzyme immunoassay
|
Introduction
Definition
- Enzyme immunoassays (EIA) are a diagnostic tool that detects the biological molecules utilized by enzyme-labeled antigens or antibodies.
- Where assay refers to analysis or test and “immune” is related to our immune system and its mechanism or action.
- It is used in medicine and in biomedical research for the detection of specific antigens or antibodies.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a technique of EIA.
- Alkaline phosphatase, Horseradish Peroxidase, and glucose oxidase are normally used for labeling antigens. These entire enzymes have chromogenic substrates.
- Enzymes worked as a marker for the foreign antigen presence in the patient sample. It’s conjugated with antibodies and used to produce colored or fluorescent products.
- EIA uses the concept of antigen-antibody binding. We can determine the small quantities of antigens like protein, peptides and hormones, drugs, etc.
How does enzyme immunoassay work
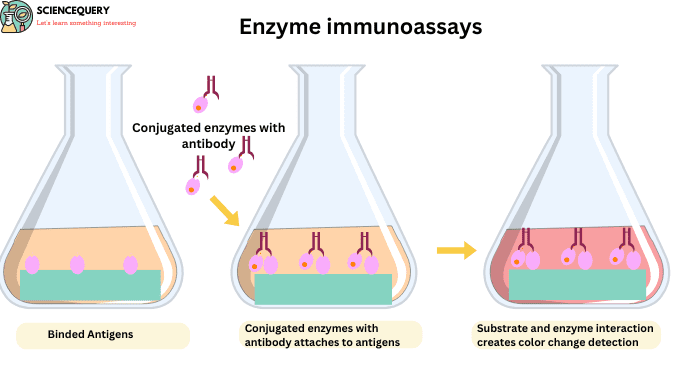
- In enzyme immunoassay, enzyme-linked antibody is used for the detection of antigens or antibodies in the given sample.
- Linked or conjugate enzymes are selected on the basis of their ability to catalyze the conversion of a substrate into a colored product. Enzymes give a sign of the presence of antigens.
- The antigen that is determined is bound with the primary antibody because antibodies have specific sites for their antigen.
- Then an enzyme-linked antibody is added to the well which is bound to the primary antibody.
- After adding enzyme-specific substrates these enzymes act upon their substrate and colored products are formed.
- The color product indicates the presence of antigen and if the color product is not obtained that means antigen is not present in the sample for specific antibody.
Enzyme immunoassay tests
- In EIA we can detect substances (antigen or antibodies) that are present in very low concentrations. EIA performs both qualitative and quantitative tests.
- All quantitative tests were compared with the slandered range. To perform EIA we take urine or blood samples.
- Through EIA we can detect the viruses and bacteria which are causing diseases in our body.
- Examples are
- HIV virus
- Hepatitis virus
- Herpes Virus
- Treponema pallidum bacteria (It’s caused syphilis disease)
- Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria (It’s caused Lyme disease)
- EIA is used in the detection of hormone levels in the body. These are the following examples of hormones.
- Example is
- Luteinizing hormone
- Follicular stimulating hormone
- Prolactin
- Testosterone
- EIA is useful for the determination of levels of Tumor markers like Prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
Result Interpretation
- The test result is observed indirectly by detecting the label attached covalently to either the antigen or antibody partner.
- In this test, enzymes are used as tags or labels.
- These enzymes convert a colorless substrate into an easily detectable colored end product.
- Such substrates are known as chromogens. Chromogens are colorless substrates acted on by the enzyme to produce a colored product.
- If colored products are obtained, the result will be positive and if colored products are not obtained, the result will be negative.
Types: – Enzyme immunoassay is classified into two types
- Homogeneous enzyme immune assay (HEIA)
- Heterogeneous enzyme immune assay (HTEIA)
Homogeneous enzyme immune assay (HEIA)
- HEIA performs only in the liquid phase. They are rapid and simple to perform and less sensitive than heterogeneous assays.
- An example of HEIA is EMIT (Enzyme multiplied immunoassay technique)
- HEIA do not require a washing or separation step and they are used to determine low molecular weight analytes in serum or urine.
- Analytes like Hormones, Therapeutic drugs, Drugs of abuse, etc.
- Hormones and drugs contain antigens and they are also known as haptens. In this assay, haptens are labeled with enzymes like lysozyme, malate dehydrogenase, etc. They react with antibodies.
- Enzymes labeled hapten and free hapten compete with each other for binding with antibody molecules.
- After adding substrate color will be produced. The intensity of color is measured by a colorimeter or spectrophotometer.
Heterogeneous enzyme immune assay
- This type of assay requires physical separation. It is simple, has high sensitivity and specificity, and low cost.
- An example of HTEIA is ELISA.
- HTEIA is further divided into two types
1. Competitive assays
2. Non-competitive assays.
1. Competitive assays
This type of assay is based on competition between labeled antigens and unlabeled antigens for binding sites on antibody molecules.
2. Non-competitive enzyme immunoassay
- The antigen is bound to the solid phase. Patient serum with an unknown primary antibody is added. After washing, an enzyme-labeled antibody is added.
- The second antibody reacts with any patient antibody that is bound to the solid phase.
- If no patient antibody is bound to the solid phase, the second labeled antibody will not be bound.
- After a second washing, the enzyme substrate is added. Enzyme bound with substrate and produced color product.
- The amount of color is measured; this amount is directly proportional to the amount of antibody in the sample.
- It is used to determine antibody production for infectious agents that are difficult to isolate. Infectious agents like HIV B and C etc.
Important notes: 1. ELISA: – ELISA is a type of enzyme immunoassay where enzymes are used as a label.
2. The principle of ELISA is based on the immunochemical principles of antigen-antibody reaction.
3. ELISA is more sensitive to Radioimmunoassay (RIA).
Enzyme immunoassays (ELISA) types
- Direct ELISA
- Indirect ELISA
- Sandwich ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
1. Direct ELISA
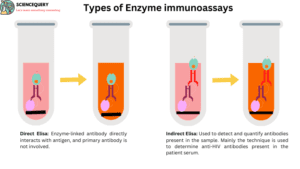
- In this type of ELISA enzyme-linked antibody directly interacts with antigen, and primary antibody is not involved.
- Through direct ELISA we can identify both antigen and antibody.
- Microtitre plate coated with antigen or antibody then add enzyme conjugate antibody.
- Antigen binds with enzyme conjugate antibody then the substrate is added, and an enzyme converts the substrate to a color product.
- Product color gives the positive result of the test.
2. Indirect ELISA
- Indirect ELISA is used to detect and quantify antibodies present in the sample. Mainly the technique is used to determine anti-HIV antibodies present in the patient serum.
- Whenever a person is infected with the virus, bacteria, or any other kinds of infectious agents.
- His body produces antibodies against it. This antibody can be detected in the serum of the patient by Indirect ELISA.
- It is performed in two stages. Microtitre plate coated with antigen then adds a primary antibody which is specific for the antigen.
- After binding of Ag-Ab, an enzyme-labeled antibody is bound with primary Ab, then adds enzyme-specific substrates which produce color products.
3. Sandwich ELISA
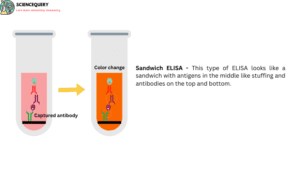
- This type of ELISA looks like a sandwich with antigens in the middle like stuffing and antibodies on the top and bottom.
- Sandwich ELISA is performed in two stages. Unlabeled antibody coated in microtitre plate which is specific for antigen.
- Add a sample that contains antigen then add an enzyme-labeled antibody bound to the primary antibody.
- After adding substrate color change of the solution is the indication of a positive result.
4. Competitive ELISA
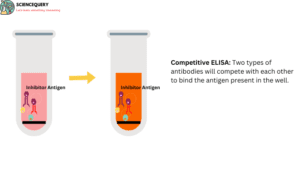
- It is used to determine the concentration of antigens or antibodies in a particular sample.
- In their microtitre plate is coated with antigen. This coating is mediated with the help of a coating buffer.
- Then add a sample that contains an antibody that is determined and add a fixed amount of enzyme-labeled secondary antibody.
- These two types of antibodies will compete with each other to bind the antigen present in the well. Hence it’s called competitive ELISA.
Method of Enzyme immunoassays (ELISA)
- Take an antibody-coated plate, it is fixed on an inert solid like polystyrene. This antibody is against the sample antigen which is determined through this immunoassay.
- The sample containing the protein to be estimated is added to the antibody-coated plate.
- Proteins have specific antigens for antibodies hence they react to formed antigen-antibody complexes.
- Then add an enzyme-linked secondary antibody to the plate. These enzymes are easily attached and produce colored products.
- Enzyme-linked secondary antibodies attached to the primary antibody do not bind to antigens.
- Unbound antibody-linked enzyme washed out through washing.
- The enzyme activity is measured by its action on a substrate (protein or other biomolecule that is determined) to form a product.
- Production of products related to the concentration of the protein being estimated.
Q&A
1. How many enzymes are in the human body?
Enzymes catalyze all biological processes. The body produces these enzymes itself approximately 1300 enzymes produced by the body.
2. How does immunoassay work?
Immunoassay works based on the antigen-antibody reaction. In Immunoassay antibody is used for the determination of any infectious agent, or biomolecule in patient samples. Each substance has an antigen that shows high affinity to antibodies. Antigen binds with antibodies.
3. What is the purpose of the enzyme in the ELISA?
In ELISA enzymes are used as labels to determine the foreign substances or biological substances. After entering the substrate enzyme binds with the substrate and forms coloured products.
4. How do immunoassays work?
Enzyme immunoassays utilize enzyme-labeled antigens and antibodies to detect biological molecules.
5. Which enzyme is used in ELISA?
Peroxidase, amylase, and alkaline phosphatase enzymes are commonly used in ELISA.
6. What is measured in enzyme immunoassays?
Enzyme immunoassays are used as a diagnostic tool. They measured small quantities of antigens such as proteins, peptides, hormones, antigen or antibodies in a sample for detection of diseases.
7. What are enzyme immunoassays?
The technique or test to detect the presence or quantity of substances such as hormones, drugs, and specific proteins based on specific antigen-antibody binding reactions. These substances can act as antigens or antibodies.
References
- Enzyme immunoassay techniques, Stephan T. Kiessig
- Kuby immunology
- Essentials of Biochemistry, Pankaja Naik
- Biochemistry 4th edition, U. Satyanarayana & U. chakrapani
