Introduction
Cytoplasmic inheritance or maternal inheritance is simply the transfer of genetic characters through the cytoplasm (that is other organelle DNA) instead of the nucleus.
In a cytoplasm, autonomous organelles like mitochondria and plastids are present as the genetic matter that is considered the key ingredients.
Mitochondria, usually referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, are present in both animal and plant cells. Plastids composed of chloroplast, leucoplast, and chromoplasts are present only in the plant cells.
Mitochondrial DNA
- Mitochondrial DNA is a complete loop-like structure of about 16000 base pairs. There are no introns in human mitochondrial DNA. The DNA is transcribed, as a result of a massive piece of RNA, that is cut into pieces.
- Mitochondrial tRNAs also allow imperfect matching between a codon and its tRNA.
Chloroplast DNA
- Chloroplast DNA is a type of genetic matter that can be found only in the chloroplasts of plants.
- They contain genes that help in photosynthesis and play an important role in the development of plants.
- The structure of chloroplast DNA deals with multiple copies per cell, thus increasing stability over time.
- This stability has enhanced the scientists to study the evolutionary mechanism of plants by analyzing the changes in the chloroplast DNA.
- They are hence used for studying population genetics, as different populations contain diverse mutations within their DNAs.
Mechanism of cytoplasmic inheritance
- Transmission of characters that are regulated by plasma genes is known as Cytoplasmic Inheritance. They can be also named “Extra-Chromosomal Inheritance”.
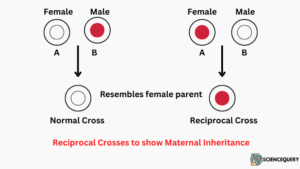
- This ‘chromosomal theory of inheritance’ was proposed by Correns in 1908. The gamete that contributes to the cytoplasm is called the female gamete.
- It consists of both the nuclear and the cytoplasmic material. The male gamete does not consist of any of the cytoplasm. So, this theory is generally known as the Maternal Inheritance.
Maternal Inheritance & Non-mendelian inheritance patterns
Maternal Inheritance
This is a type of inheritance that has an indirect impact on the nuclear genes. Here, the maternal effect or cytoplasmic effect is predetermined even before fertilization. This predetermination is because of the effect of the mother gene that decides the fate of the offspring.
Example
Shell Coiling in Lymnaea peregra
- Shell coiling towards the right is called Dextral Coiling.
- Shell coiling towards the left is called Sinistral Coiling.
- The dominant gene for dextral side coiling is D
- The recessive gene for sinistral side coiling is d
- Studies revealed that the nature of coiling is determined by the mother and not by the gene of an individual.
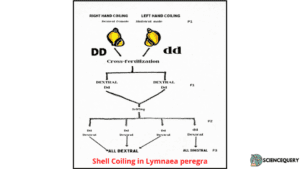
The reciprocal crosses showed variations and revealed the absence of Mendelian’s second law of segregation in F2 generations.
Non-Mendelian Inheritance
The type of inheritance that does not follow Mendelian laws is termed as Non-Mendelian Inheritance.
These traits are not representative of dominant or recessive traits, which means it may have more than one type of gene involvement.
Types Of Non-Mendelian Inheritance
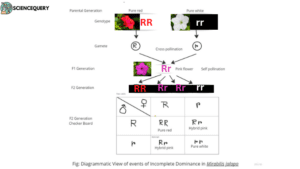
When neither of the two alleles of a gene is completely dominant over the other, then this phenomenon is called Incomplete Dominance.
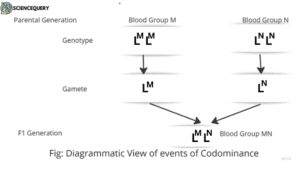
Codominance
When both the alleles of a heterozygote are equally expressed, then this phenomenon is termed as Codominance.
Sex-linked Inheritance
- Sex-linked inheritance is a form of non-mendelian inheritance. It happens when one of the genes is located on the sex chromosomes.
- This type of inheritance is observed in both humans and animals.
- An example of sex-linked inheritance in humans is color blindness. It affects males more than females due to the X chromosome.
- Genetic Disorders like Hemophilia, and Klinefelter’s Syndrome are some examples that show sex-linked inheritance.
- They are also acquired because of environmental factors like exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation.
Extranuclear Inheritance
Extranuclear inheritance is the transmission of genetic information from one generation to another that does not involve the nucleus. This type of inheritance occurs in a variety of organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and plants.
Mitochondrial Inheritance is an example of this type of inheritance. Here, only mothers transfer the traits to their offspring as mitochondria are inherited only from the mother’s egg cell during fusion.
Cytoplasmic DNA and genetic variations
Cytoplasmic DNA and genetic variations are interlinked and are studied because of the following factors:
- Cytoplasmic DNA provides an understanding of the evolutionary processes like cladogenesis ( also known as speciation ) and adaptation of an organism.
- Hence, they are also used to study the differences in gene expression patterns and their responses.
- Variations in the genetic information with respect to the cytoplasmic DNA have helped in research.
- The cytoplasmic DNA acts as key evidence that the transfer of genes occurs between different species and kingdoms.
Contribution to biodiversity
cDNA plays an important role in contributing to biodiversity because of the following reasons:
1. cDNA can be transferred between species by means of horizontal gene transfer, allowing variations and adaptive mechanisms within the populations.
2. The cytoplasm contains genes that are absent in nuclear DNA.
3. The presence of cytoplasmic DNA increases the rate of mutations among the individuals.
4. cDNA provides extra protection against the viruses and thus contributes a lot to maintaining the diversification among the species.
Diseases and cytoplasmic inheritance
- The transmission of genetic material from the cytoplasm and not from the nuclear material is simply known as cytoplasmic inheritance. It is also known as the mitochondrial inheritance.
- For example: Leigh syndrome is caused by the mutant gene present in the mitochondrial DNA. In short, it is caused by the deficiency of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase. It directly targets the central nervous system of the patient, causing head and motor dysfunction.
- Mitochondrial myopathy is another disorder that is autosomal recessive caused by the mutant gene received from the maternal genes. It targets the muscular functioning of the body causing weakness and fatigue.
Biotechnological implications
Cytoplasmic inheritance enables the transfer of genetic material without syngenesis. It has key implications in gene editing and manipulation. They also introduce new characters in the existing organisms that could prove to be a boon in agriculture and the medical field.
Hence, the introduction of cytoplasmic inheritance provided a better understanding of gene interaction and mutations required to treat an individual better.
Practical applications
- Agriculture – Cytoplasmic inheritance is used to improve the quality of the crop, resulting in high yields.
- Medicine – Diseases caused due to mutations in mitochondrial DNA are treated efficiently, which is a great achievement in the medical world.
- Genetics – This inheritance allows scientists to understand the inheritance of genes and their expressivity in other species.
- Evolution – The theory of cytoplasmic inheritance helps to understand the evolutionary relationships among different species.
Q&A
What type of inheritance is cytoplasmic inheritance?
Non-Mendelian inheritance.
What is the difference between nuclear and cytoplasmic inheritance?
Nuclear inheritance means the transmission of genes from parent to offspring through the nucleus, whereas cytoplasmic inheritance involves the transmission of genes from parent to offspring by the organelles present outside the nucleus.
How does cytoplasmic inheritance happen?
Cytoplasmic inheritance involves multiple sets of chromosomes that are inherited from both parents. In cytoplasmic inheritance, few of the traits can be passed on more strongly than others.
What is cytoplasmic vs mitochondrial inheritance?
Mitochondrial inheritance involves only maternal genes, while cytoplasmic inheritance can involve both maternal and paternal genes.
Summary
- Cytoplasmic inheritance or maternal inheritance is simply the transfer of genetic characters through the cytoplasm (that is other organelle DNA) instead of the nucleus.
- This ‘chromosomal theory of inheritance’ was proposed by Correns in 1908. The gamete that contributes to the cytoplasm is called the female gamete.
- Cytoplasmic inheritance involves multiple sets of chromosomes that are inherited from both parents. In cytoplasmic inheritance, few of the traits can be passed on more strongly than others.
- Mitochondrial DNA is a complete loop-like structure of about 16000 base pairs.
- Mitochondrial tRNAs also allow imperfect matching between a codon and its tRNA.
- Chloroplast DNA contains genes that help in photosynthesis, and play an important role in the development of plants.
- They are hence used for studying population genetics, as different populations contain diverse mutations within their DNAs.
- Cytoplasmic inheritance is used to improve the quality of the crop, resulting in high yields.
- cDNA can be transferred between species by means of horizontal gene transfer, allowing variations and adaptive mechanisms within the populations.
References
https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev.ge.05.120171.002045
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41437-022-00540-2
https://academic.oup.com/genetics/article-abstract/103/3/513/5995875
https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.53.2.275
https://muse.jhu.edu/pub/1/article/401331/summary