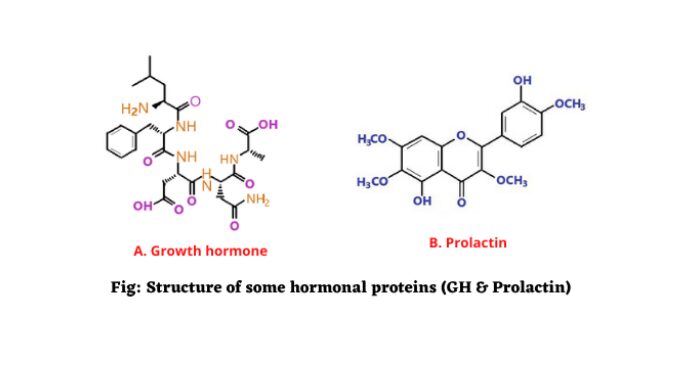
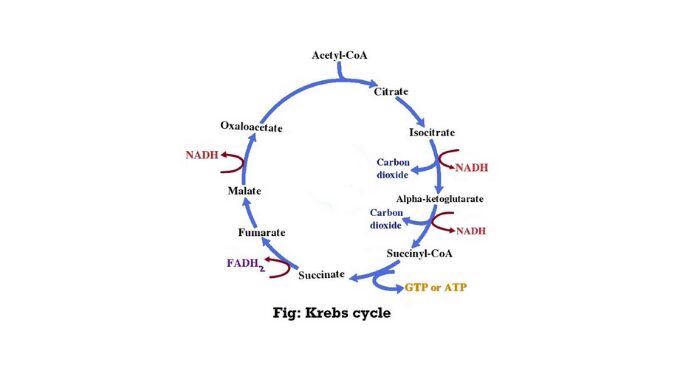
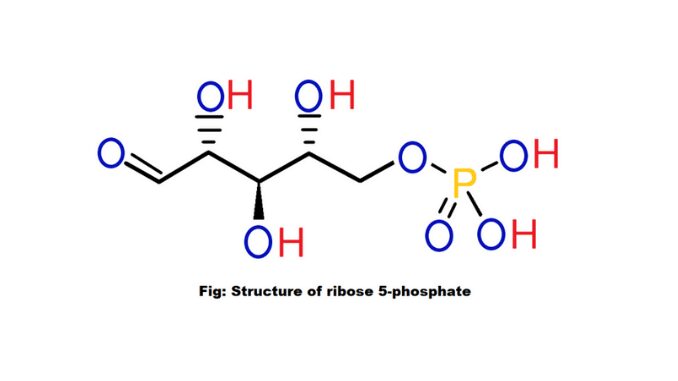
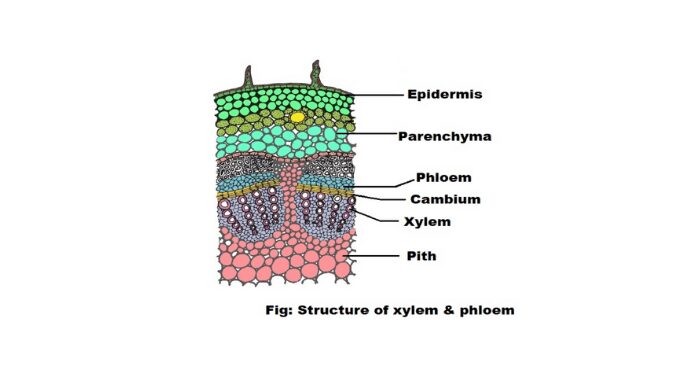
Hormonal proteins structure and functions
Introduction Protein is a complex nitrogenous complex with a high molecular mass that is a polymer of amino acids. This macromolecule is considered to be the main component of all life. It is not possible to imagine the existence of any animal without protein. All proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. There […]
Hormonal proteins structure and functions Read More »