Know in one minute about instantaneous angular velocity
|
INTRODUCTION
Instantaneous Angular Velocity is a very important fundamental topic that makes the basics of circular and rotational motion in mechanics.
An object is considered a moving object when
- Object covers some distance in a specific time interval, and here we find its velocity or linear velocity.
- It rotates or revolves, and here comes angular velocity which is the rate of change in angular displacement of a rotating object.
The symbol of angular velocity is ω(Omega) or sometimes Ω(ohm).
What is the relation between Angular velocity and Instantaneous angular velocity?
Well, Instantaneous Angular Velocity is a type of angular velocity.
Definition
“Rate of change of angular displacement of a particle performing circular motion is called angular velocity.”
ω = θ/d
ω is Angular velocity, is angular displacement and t is time in seconds.
Angular velocity and Instantaneous angular velocity are similar and related to each other. Angular velocity takes a long time interval into consideration whereas instantaneous angular velocity takes a very short interval of time into consideration.
To understand this, let us take an example
Consider, a ball is rotating around a point, if it is rotating some angular displacement for 2 (t₁= 1s to t₂= 3s) seconds, here the time interval will be
∆t= t₂ – t₁
and ∆t= 3 – 1
∆t= 2 seconds

Then if we divide this angular displacement by time interval, we will get angular velocity or average angular velocity.
On the other hand, if the ball is rotating for a small time 0.003s (t₁= 1s to t₂ = 1.003s), then angular displacement will also be small, here the time interval is
∆t= t₂ – t₁
and ∆t= 1.003 – 1
∆t= 0.003 seconds
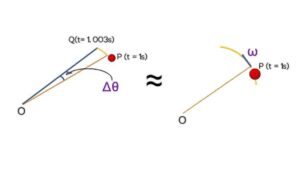
or time interval is very small as it is going to be zero (∆t ≈ 0) just like it is approaching zero, that means it is referring to a particular time that is 1 second in this case,
So in this situation, angular velocity becomes Instantaneous angular velocity, and to determine it, we use differentiation.
In other words, if the rotation happens for a long time then the change in angular position concerning time is the angular velocity, while if the rotation happens for a very short period, for just a very small moment, it is called Instantaneous angular velocity.
So the definition of Instantaneous Angular velocity is
“The instantaneous angular velocity is the limit of average angular velocity when its time interval is approaching zero.”
ω = (lim)(Δt →0) = Δθ/(Δt ) or ω = dθ/dt
- Its unit is radian s⁻¹
- Its dimensional formula is [M⁰L⁰T⁻¹].
- Although angular displacement is a scalar quantity, if a body is rotating in a plane, then we treat it as a vector. Generally, anticlockwise is taken as positive, and clockwise is taken as negative.
The direction of Instantaneous Angular Velocity
The direction of the angular velocity of any object cannot be measured by the object itself. Because rotating object changes their direction at every moment. Of course, because of it, we have to find another option to find the direction of the rotating object.
So to find the direction of the object we use the Right-hand Thumb Rule.
Right-Hand Thumb Rule
During the rotation Axis of rotation remains at its position, so we use it to find the direction of the angular velocity of the object. To find the direction of instantaneous angular velocity, follow these steps:-
- Rotate your fingers in the direction where the object is moving
- Take your thumb at the position of the Axis of rotation
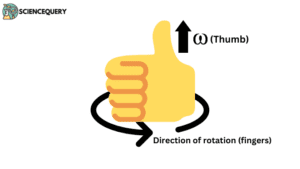
And then you will get the direction of Angular velocity, yes the thumb is determining the direction of angular velocity by verifying these two outcomes:-
- The upward Thumb represents the Anti-clockwise direction.
- The downward Thumb represents the Clockwise direction.
Instantaneous angular velocity application and uses
Let us consider some real-life examples.
1. Rotation of wheels of a car
When the car moves on a road its wheels rotate along the axis of rotation that is positioned at the center of the wheel and perpendicular to it.
If we consider the linear velocity of the car as v and the radius of the wheel as r. Here angular velocity of the wheel gives linear velocity according to this relation
ω = v/r
Now if we want to calculate the car’s linear velocity at a particular time, we find the instantaneous angular velocity of the wheel at that particular time using the formula ω = dθ/dt and determine the car’s velocity by v = ωr.
2. Rotation of Carnival
In the case of carnival, Instantaneous angular velocity is used to measure the centripetal force at an instant of time, whose value increases beyond a maximum value, which increases the risk of breaking the basket and this may cause an accident. This formula is used to measure it,
F = mrω²
Here m = mass of basket
r = radius of carnival
F = centripetal force
3. Turning of a bike on a curved road
A bike is turning on a curved road then the bike will have angular velocity while turning.
cause a curved road is some sort of part of a circular path, obviously, we know that in a circular path, the object has angular velocity.
Instantaneous angular velocity is used to determine the maximum speed a bike can travel on a curved road. So that the value of the centripetal force on the bike does not exceed the maximum value of the fall and avoid accidents.
Determining the Instantaneous Angular Velocity
In previous segments, we have already known about angular velocity and its definition which was “The Rate of change of angular displacement of a particle performing circular motion is called angular velocity.”
But how was this definition made and how are we able to write that formula?
Here we will learn how were these formulas determined.
Let me explain to you,
Suppose a particle P is moving in a circle of radius r (fig). Let O be the center of the circle. Let O be the origin and OX the X- axis. The particle P at a given instant may be described by the angle θ between OP and OX. We call θ the angular position of the particle.
As the particles are moves on the circle, their angular position θ changes. Suppose the particle goes to the nearby point P’ in time ∆t so that θ increases to θ + ∆θ.
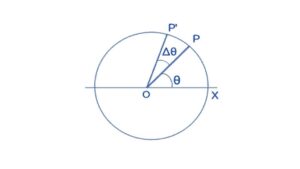
By the definition, we know that rate of change of angular position is called angular velocity or average angular velocity, thus the angular velocity is
ω = Δθ/Δt = dθ/dt
Difference between Instantaneous Angular velocity and Average Angular velocity
Key Points |
Average Angular Velocity |
Instantaneous Angular Velocity |
| Definition | It is the ratio of Total angular displacement and total time taken for this displacement. | The angular velocity is the limit of average angular velocity when its time interval is approaching zero. |
| Time interval | Time interval for Average angular velocity is large | The time interval is very small and approaching zero. |
| Vector and Scalar | It is a Scalar quantity. | Is a Vector quantity. |
| Formula |
ω av= Δθ/Δt |
ω = (lim)(Δt →0) = Δθ/(Δt ) = dθ/dt |
Q&A
1. How to find instantaneous angular velocity?
Ans. By differentiating the function with respect to time using the formula
2. What is instantaneous angular velocity?
Ans. The instantaneous angular velocity is the limit of average angular velocity when its time interval is approaching zero.
3. A hoop of radius r and mass m is rotating with an angular velocity ω₀ is at a rough horizontal surface. the initial velocity of the center of the hoop is zero. What will be the velocity of the center of the hoop when it ceased to slip?
Ans. Initially, the hoop is rotating on a rough surface, which means it is rotating with slipping, so friction will act on that point that is touching the surface
Here angular velocity is and velocity of the center of the hoop is zero( )
After that, it stops slipping hence, called pure rolling where
(v is the velocity of the center and is angular velocity at pure rolling)
By using momentum conservation
Li = Lf
Angular momentum of touched point initially + linear momentum of center initially = Angular momentum of touched point finally + linear momentum of center finally

4. If the angular displacement of a rod as a function of time Is θ = 2t²+3t.What is the instantaneous angular velocity in (rad/s) of the rod at t = 7s?

5. Why is instantaneous angular velocity important?
Ans. It is a very important topic to learn in physics, cause it helps us to determine how fast something is spinning at that instant in time.
Used to calculate the chances of an accident. By using its limited value, We can avoid accidents involving damaging or breaking of any rotating object, as we have studied in the earlier examples in the case of carnival and turning of a bike.
Written by: Amber Soni
References
- Concept of physics 1, By H.C.Verma, Bharti Bhawan publishers and distributors, page no.101-102.
- NEET Objective PHYSICS Volume 1, By DC Pandey, Arihant Prakashan, Meerut, page no.308-309.

Very nice content I found it very helpful for my board exam as well as neet prepration thanku so much.