Introduction
Ribose 5-phosphate is a product produced in the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway. The sequence of steps of enzymatic reactions where a precursor is converted into a product through a series of metabolic intermediates is known as the metabolic pathway. The pentose phosphate pathway is also a metabolic pathway. It is the intermediate product of this pathway.
The pentose phosphate pathway is an alternative pathway of carbohydrate metabolism. It is another method by which glucose molecules can be broken down. In this pathway, the glucose molecule forms glucose 6-phosphate similar to the first stage of glycolysis. The glucose 6-phosphate is oxidized by NADP⁺ to form 6-phosphogluconic acid. This acid forms some pentose sugars. Ribose 5-phosphate is one of them (1) & (3).
Ribose 5-phosphate
1. This is a pentose sugar that is a monosaccharide with five carbon atoms. It is made up of 5 carbon atoms, so it is known as pentose sugar.
2. The molar mass of ribose 5-phosphate is 230.11 gm/mol.
3. It is an aldose sugar because ribulose 5-phosphate contains an aldehyde group (-CHO).
4. The chemical formula of this pentose sugar is C₅H₁₁O₈
5. This pentose sugar is a precursor for purine, pyrimidine, and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis.
6. Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is formed when it reacts with ATP.
7. It may also be the acceptor, in which case octulose 8-phosphate may be formed.
8. This enzyme forms glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway which is a triose phosphate.
9. It is needed for the synthesis of nucleotides and nucleic acids (3).
Function of Ribose 5-phosphate
1. Acts as an enzyme in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabolic pathways.
2. It is used to form the main component of nucleotide coenzymes.
3. The first carbon of the ribose 5-phosphate formed a double bond.
4. It forms an aldose that helps to bind carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle.
5. This pentose sugar activation by ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase forms phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate during nucleotide biosynthesis.
6. Histidine is an amino acid. It is not synthesized in the human body. Ribose 5-phosphate helps in the biosynthesis of histidine.
7. It can be converted to adenosine diphosphate ribose.
8. Adenosine triphosphate and guanosine triphosphate are synthesized from ribose 5-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway.
9. In addition to histidine, ribose 5-phosphate and its derivatives act as precursors to many biomolecules, including DNA, RNA, ATP, coenzyme A, Flavin adenine dinucleotide (3) & (2).
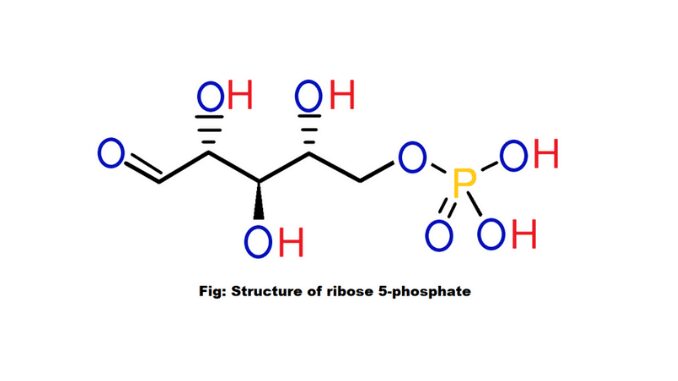
Structure of Ribose 5-phosphate
It is a pentose sugar and is consists of five-carbon sugars. There is a phosphate group present in this type of sugar. One phosphate group and five carbon atoms combined together to form the above.
The chemical formula of this type of carbohydrate is C₅H₁₁O₈P. In addition to the five-carbon molecules and a phosphate group, there are 11 atoms of hydrogen and 8 atoms of oxygen.
This product forms a furanose or open chain. Furanose is a chemical structure of carbohydrates. A furanose consists of four carbon and one oxygen atom with a five-membered ring system. The furanose form is known as ribose 5-phosphoric acid (1).
Importance in pentose phosphate pathway
It is generated in the pentose phosphate metabolic pathway. This pentose sugar is an important source for the production of NADPH for reductive biosynthesis. It has two phases, the oxidative and non-oxidative phases.
NADPH is produced in the oxidative phase and the interconservation of the process of the sugar is completed in the non-oxidative phase. It is also produced in the glycolysis process. In many tissues, this enzyme is produced in the non-oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Two products are produced in this pathway, ribose 5-phosphate, and NADPH. The former is needed for synthesizing DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic acid). So ribose 5-phosphate is very important for the pentose phosphate pathway. The following describes how ribose 5-phosphate is produced in the pentose phosphate pathway (3).
Process of pentose phosphate pathway
There are two phases in this metabolic pathway. One phase is linked with another.
1. Oxidative phase
- In the first stage, glucose is phosphorylated by a phosphate group obtained from the breakdown of ATP to ADP to form glucose 6-phosphate. This stage is completed by the hexokinase enzyme.
Glucose + ATP → Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP
- The oxidation of Glucose 6-phosphate forms 6 phosphogluconic acids. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase is the enzyme that participates in this process. Here NADP⁺ acts as an electron acceptor. NADP is linked with glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme.
Glucose 6-phosphate + NADP⁺ → 6 phosphogluconic acid + NADPH + H⁺
- 6-phosphogluconic acid is decarboxylated and oxidized to form D ribulose 5-phosphate. NADP is reduced to form NADPH + H⁺. This reaction occurs by 6- phosphogluconic dehydrogenase enzyme. Here the oxidative phase is completed.
6-phosphogluconic acid + NADP → Ribulose 5-phosphate + CO₂ + NADPH + H⁺
2. non-oxidative phase
Biosynthesized pentose sugar occurs in this stage.
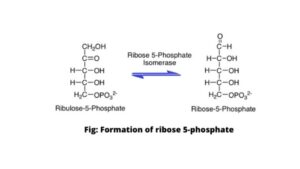
- Ribulose 5-phosphate is isomerized into ribose 5-phosphate. The phosphoriboisomerase enzyme participates in this process. The remaining ribulose 5-phosphate is converted into xylulose 5-phosphate. The reaction is catalyzed by epimerase enzymes.
In the first stage of the non-oxidative phase ribose 5-phosphate is produced from ribulose 5-phosphate. In addition to ribose 5-phosphate, xylulose 5-phosphate is generated in this process.
Ribulose 5-phosphate → Ribose 5-phosphate (Phosphoribosyl isomerase enzyme)
- Then ribose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate interact with each other to form sedoheptulose 7-phosphate and 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde. The process is completed through transketolase enzymes.
In this way, this is produced in the pentose phosphate pathway. And various compounds are formed from this pentose sugar (1) & (2).
Q&A
1. What is the purpose of producing ribose-5-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway?
The primary purpose of producing this in the pentose phosphate pathway is ribose 5-phosphate is a pentose sugar that is used to make Deoxyribonucleic acid and Ribonucleic acid.
2. Which of the following requires large amounts of both ribose-5-phosphate and NADPH?
During cell growth, large amounts of both ribose-5-phosphate and NADPH are needed for the biosynthesis of nucleotides (RNA and DNA) and the synthesis of fatty acids.
3. What is ribose 5 phosphate used for?
- It is used for synthesizing DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
- This pentose sugar forms an aldose that helps to bind carbon dioxide in the Calvin cycle.
- It acts as precursor to many biomolecules, including DNA, RNA, ATP, coenzyme A, Flavin adenine dinucleotide, and histidine.
4. Where does ribose 5 phosphate come from?
It comes from glucose 6-phosphate in the pentose phosphate pathway. The glucose molecule forms glucose 6-phosphate similar to the first stage of glycolysis. Glucose 6-phosphate is oxidized by NADP⁺ to form 6-phosphogluconic acid in the pentose phosphate pathway. This acid forms ribose 5-phosphate, a pentose sugar.
5. Which enzyme in the pentose phosphate shunt, creates ribose-5-phosphate and xylulose-5-phosphate?
Transketolase, a thiamine pyrophosphate enzyme creates ribose and xylulose-5-phosphate in the pentose phosphate shunt.
Written By: Manisha Bharati
References
1. B. Powar and G. R. Chatwal. Biochemistry, B. SC (general & honors course) and M. Sc. Himalaya publishing house, Chapter: Metabolism of carbohydrates. Page no- 404 to 407.
2. Ajoy Paul. Zoology Honours, Volume- 2, Books & Allied (P) Ltd. Chapter: Carbohydrates metabolism. Page no- 302 to 304.
