Paper chromatography definition
Chromatography mainly consists of two phases one is the mobile phase which is the mixture of substances that are to be separated and dissolved in liquid or gas. Another is the stationary phase is the porous solid matrix through which the mobile phase percolates. the interaction which results in the separation of the compounds includes physiochemical principles like adsorption, partition, ion exchange, affinity, and molecular sieving. paper chromatography definition is the separation of compounds based on partition chromatography where the molecules get partitioned between the stationary phase and the mobile phase.
Use of Paper Chromatography
Originally this chromatography technique was first developed in the Cambridge school of workers. It was used for the separation of mixtures of organic substances like dyes and amino acids. Nowadays it is also used for the separation of cations of inorganic substances.
Process of doing paper chromatography?
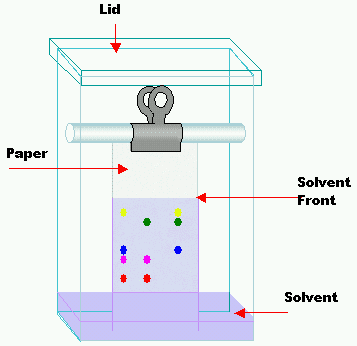
- Take a filter paper to apply a drop of the test solution and allow it to dry.
- Prepare a chamber with a developing solvent and close it to get the chamber saturated.
- Now place the paper in the chamber dipping the edge into the solvent.
- The liquid reaches the spot of the filter paper through capillary movement, as a result, various substances of the spot move at different speeds along with the solvent.
- After the movement of the solvent to a suitable height of 15-20 cm remove the filter paper and let it dry.
- various spots are then visualized after spraying suitable reagents like ninhydrin.
- The movement of the solvents is then calculated by using migration parameters called Rf.
Calculation of migration parameter Rf
The migration of the substance is expressed by the Rf value. It is defined as the migration of the solute front relative to the solvent front.
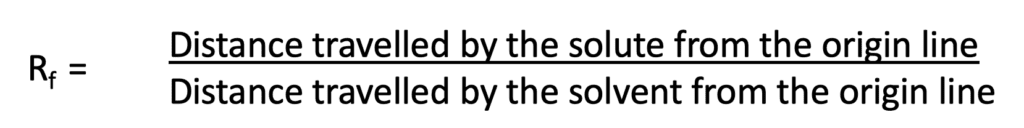
The Rf value of a substance depends upon a number of factors like
- The type of solvent used
- The medium like the quality of paper used for the separation.
- the nature of the mixture
- The temperature
- The size of the chamber
Types of paper chromatography
Descending chromatography
In this, the solvent is allowed to travel down the paper. This is used for the separation of biochemical substances.
Ascending chromatography
The development of the paper is done by allowing the solvent to travel up the paper. This is also used for the separation of biochemical substances.
Ascending-Descending chromatography
This technique is a hybrid of the above two techniques. the upper part of the filter paper is folded over a glass rod allowing the ascending development to change over into the descending after crossing the glass rod.
Radial or circular paper chromatography
In this method, a circular filter paper is used. the test material is placed in the center. after drying the spot the paper is placed horizontally with the wick dipped into the solvent. the solvent then rises and moves to a distance and the components get separated in the form of the concentric circular zone.
Two-dimensional chromatography
Square or rectangle paper is used and the solvent is applied at the corner. the second run is performed at a right angle to the direction of the first run. this type of chromatography can be performed with identical solvent systems in both directions.
