Introduction
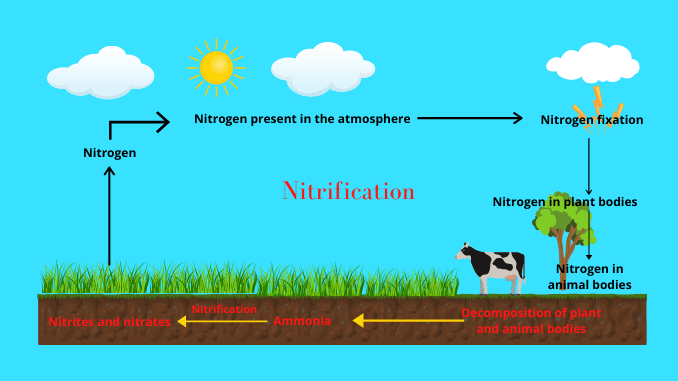
The atmosphere is the only source of nitrogen with a total amount of about 78%. The nitrification process is one of the steps of the nitrogen cycle. This nitrogen is the most essential element for all living organisms. This nitrogen circulates from the atmosphere to the biosphere and again from the biosphere to the atmosphere. As a result, nitrogen reserves are maintained throughout the world.
The natural cycle helps in recycling all the elements that are very low in quantity and are also essential to sustain life on the earth. That is, all these elements have been circulating in the organism and its environment for ages. As a result, all of these elements continue to exist on Earth. These elements are called nutrients. Because they are used in various physiological functions of the organism. The elements rotate on earth in cycles forming biogeochemical cycles. The nitrogen cycle is one such biogeochemical cycle. Nitrogen is a very important element in the whole plant and animal world. This rotation is accomplished through a few steps, nitrification is one of these steps (1) & (3).
What is Nitrification?
Nitrification is an important phase in the nitrogen cycle. It refers to the addition of nitrogen. Amino acids and urea are present in animal nitrogenous wastes, animal and plant dead bodies, etc. The amino acid and urea are decomposed by various bacteria in the process of ammonification. They are turned into ammonia and ammonium salts.
Ammonia or ammonium salt produced in the process of ammonification is converted to nitrate by the action of various bacteria. The process by which nitrate is produced from ammonia is nitrification.
Nitrification refers to the addition of nitrogenous compounds in the earth’s environment. Nitrogen compounds from dead plants, animals, and other organic matter are decomposed by various bacteria. This decomposed nitrogen at first produced ammonia, then nitrite, and finally nitrate compounds. When ammonia is analyzed and nitrite and nitrate are produced, nitrification occurs in the environment (1) & (5).
Definition
The process by which ammonia is oxidized and periodically produces nitrite and nitrate compounds is called nitrification. In this method, the toxic ammonia was converted into nitrate. The nitrate is stored in the soil as nitrate salt. And the plants can be absorbed by this nitrate salt from the soil by their roots (2) & (3).
Bacteria that participate in nitrification
Nitrogen gas is present in the air in the form of di-nitrogen (N₂), which is inert. This inert nitrogen is used by animals and plants through various processes and returns to the atmosphere. As a result, nitrogen balance is maintained in the environment. However inactive nitrogen cannot be easily used by animals and plants. This is because the various bacteria in the soil convert the nitrogen in the air into nitrogenous compounds and make it usable for plants and animals.
Some bacteria participate in only one or two stages of the nitrogen cycle and some bacteria participate in completing the nitrification process. All these bacteria convert ammonia or ammonium into nitrate compounds and are known as nitrifying bacteria. Examples are nitrosomonas, nitrosococcus, nitrobacter, nitrospina, nitrospira, and nitrococcus.
Nitrifying bacteria are aerobic bacteria. Those bacteria that oxidize ammonia to produce nitrites are nitrosomonas, nitrosococcus, and nitrospira. Bacteria that are oxidized nitrite and produce nitrates are nitrobacter, nitrospina, nitrococcus, and nitrospira. These nitrifying bacteria grow at intervals of 6 to 24 hours (4) & (7).
Some interesting facts about the nitrification process
1. Nitrification is the stepwise process, where ammonium (NH₄⁺) or ammonia (NH₃) is oxidized and converted into nitrite (NO₂⁻) and nitrate (NO₃⁻).
2. The nitrification process is an oxidation process.
3. This process is done at a temperature of about 15°C to 30°
4. Various bacteria participate in this process of the nitrogen cycle. The bacteria participating in this process are gram-negative and autotrophic in type.
5. The nitrification process always occurs under aerobic conditions.
6. The last product of the nitrification process is nitrate, which serves as an important source of nitrogen for the plant body.
7. The rate of the nitrification process depends on some environmental factors such as temperature, oxygen, pH, etc. (1) & (6).
Explain nitrification process
Nitrogen is essential for all living things and circulates throughout the environment through the nitrogen cycle. Nitrification is a significant part of this nitrogen cycle it refers to the addition of nitrogen to the soil.
Atmospheric nitrogen is bound to the soil in the form of nitrate. Nitrification is the process of binding nitrogen (N₂) to the soil in the form of nitrate. This process is completed through two stages (1).
1. Ammonia or ammonium oxidation
The nitrogen present in the soil is converted into ammonia in the process of ammonification of the nitrogen cycle. In the first stage of nitrification, the oxidation of ammonia occurs and nitrite is produced from ammonia or ammonium ions.
The role of different bacteria is very important in this process. The bacteria that participate in the oxidation of ammonia are nitrosomonas, nitrosococcus, and nitrospira. They break down the ammonia or ammonium into nitrite. This process is carried out by ammonia oxidizer microbes.
The two main enzymes used in this process are ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) and hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HAO). This process produces less energy than many other types of metabolism (2) & (7).
NH₃ (ammonia) or NH₄⁺ (ammonium ions) → NO₂⁻ (nitrite)
2. Nitrite oxidation
The second stage of nitrification is the oxidation of nitrite. That is, nitrite is dissolved and finally produces nitrate. This is a simple process and occurs slowly. The bacteria that participate in this process are nitrobacter, nitrospina, nitrococcus, and nitrospira. They are known as nitrite-oxidizing bacteria. In this process, nitrate is dissolved in water and absorbed by plants (5).
NO₂⁻ (nitrite) → NO₃⁻ (nitrate).
Controlling factors of nitrification rate
The nitrification process is the biological oxidation process of ammonia. It is an important step of the global nitrogen cycle. This stage of the nitrogen cycle is partially affected by the environment. The rate of this process is controlled by some factors like
Relationship between ammonification and nitrification
Each stage of the nitrogen cycle is related to each other. Nitrogen present in the air is bound to the soil by the nitrogen fixation method. Then the soil is absorbed by animals and plants.
Nitrogen present in the body of plants and animals is released back into the soil through various forms (Amino acid → urea → ammonia). This process is called ammonification. The ammonification process is related to the nitrification process.
This is because ammonia produced by the ammonification process is oxidized by the nitrification process to produce nitrite and nitrate (2) & (5).
Importance
Nitrification is a very important process of the nitrogen cycle. It is considered a major part of the nitrogen cycle. So the importance of this stage is immense.
- Nitrification is very important for plants. Nitrate is produced in this process and is absorbed by plants via water or soil. Therefore, nitrogen enters the body of plants through nitrate intake, which is important for protein synthesis and growth in their body.
- Bacteria of different types participate in the process of nitrification. All of these bacteria play a role in increasing soil fertility.
- Nitrification plays an essential role in agriculture. The process of nitrification produces nitrite and nitrate from ammonia or ammonium ions, which are used as fertilizers in agriculture.
- This process removes nitrogen from the wastewater.
- Nitrogen is important for animals. Nitrate is produced in the nitrification process by plants absorbed. Thus animals take the plants as food the nitrogenous compound enters the animal’s body and helps in the synthesis of proteins and growth of the animal body (1) & (2).
The nitrification process is an enzymatic and aerobic process. Here the oxidation of ammonia or ammonium ions occurs and at first produced nitrite and finally produced nitrate.
This process is a chemoautotrophic process because there are various bacteria participating in this process. All these bacteria help in the decomposition of dead bodies and waste substances of animals and plants.
As a result, the environment is clean. So nitrification also plays a vital role in the environment and fauna. From the above discussion, it is clear that the bacterial effect is most important in the nitrification process. Ammonia-oxidizers and nitrite-oxidizers bacteria participate in this process and release nitrogenous compounds (nitrite and nitrate) into the soil (5).
