Introduction
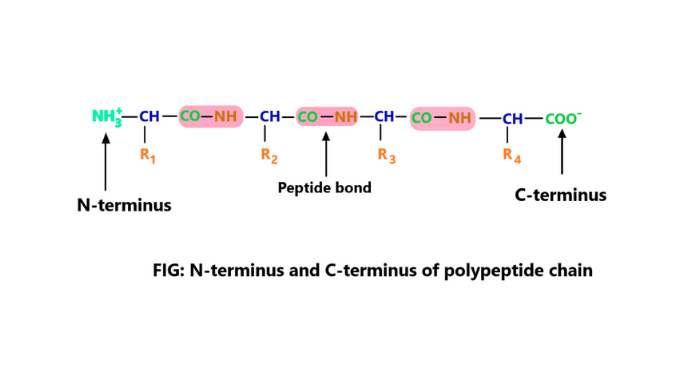
The Carboxyl group (-COOH) of one amino acid is attached to the amino group of another amino acid by a covalent bond called a peptide bond. When a peptide bond forms a water molecule is eliminated. Each amino acid unit in the peptide is known as the residue. All peptides have two ends, amino-terminal or N terminus and C terminus or carboxyl-terminal. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Both N and C terminus residues in protein play an important role in the peptide chain. These two groups are one basic and another acidic (3) & (6).
N-terminus
There are two residues present in peptide bonds. N terminus is one of them. The residue in a peptide that has an amino group (-NH₂), is called N-terminus.
In a peptide bond, the amino group is attached to the Carboxyl group (-COOH) of another amino acid. The end amino group of a polypeptide is only attached to the Carboxyl group (-COOH) end. Then the remaining amino group residues are the N-terminal (5).
Features
1. It is located at the end of a polypeptide or protein.
2. N-terminus is carried out by labeling the free alpha-amino groups.
3. When drawing a peptide structure the N-terminus is on the left side according to the convention.
4. It describes the start of polypeptide or protein and suggests the free amino group of amino acids.
5. In protein, its color is blue.
6. It is the primary part of a protein that comes out of a ribosome during protein synthesis.
7. The N-terminus has a free amino group.
8. Sometimes, the N-terminus contains a signal peptide that provides protein to the different cellular organelles (1) & (4).
C-terminus
C-terminus is one of the terminal groups of two ends of the peptide chain. The end of the polypeptide with a free Carboxyl group (-COOH) is known as C-terminus. This terminal group is also known as the carboxyl-terminal or c-terminal or carboxy-terminus.
The peptide bond is formed between the α-amino group of one amino acid and the α-Carboxyl group (-COOH) of another amino acid. Then the remaining Carboxyl group (-COOH) residues are C-terminus or carboxyl-terminal residues (5).
Features
1. All proteins start at the N-terminus and end at the C-terminus.
2. According to the convention, when drawing a peptide structure the C-terminus is on the right side of the peptide chain.
3. Carboxyl-terminal or c-terminus residue forms its fangs.
4. In protein, its color is red.
5. It has a free Carboxyl group (-COOH).
6. C-terminals describe the end of the polypeptide chain and mention the free Carboxyl group (-COOH).
7. It is a positively charged residue.
8. C-terminus is related to some processes like protein degradation, the efficiency of translation termination, etc. (1) & (2)
Analysis of N-terminus
The three methods that are generally used for sequencing peptides from the N-terminus.
- Sanger method or DNP method.
- Dansyl method.
- The Edman degradation (1).
Analysis of C-terminus
Two methods of C-terminus analysis are
- Enzymatic method
- Chemical methods
1. Treatment of the peptide with LiBH₄ followed by acidic hydrolysis and analysis method.
2. The treatment of the peptide with hydrazine and analysis of the products (1).
Structure of N-terminus and C-terminus in protein
N-terminus
A peptide is a polymer of amino acids linked by amide bonds between the amino group of each amino acid and the Carboxyl group (-COOH) of the neighboring amino acid.
Mainly they are short chains of amino acids. Each amino acid unit in the peptide is known as the residue and it is formed by the peptide bond.
One amino group of amino acid is attached to the Carboxyl group (-COOH) of another amino acid. This link is formed through a dehydration reaction. Then the end amino group of a Protein is only attached to the end Carboxyl group (-COOH).
And the residue amino group is the terminus in protein. So there is an amino group (-NH₂) present in this terminal. When drawing a polypeptide structure the N-terminus is on the left side according to the convention (3) & (2).
C-terminus
In a polypeptide chain, a peptide has two residues, the first is the N-terminus and the second is the C-terminus. When a Carboxyl group (-COOH) of amino acid is bound with another amino group of amino acid, then a peptide chain is formed.
The amino group and Carboxyl group (-COOH) are attached alpha-carbon atoms. Then the end Carboxyl group (-COOH) is attached to the first amino group. And the remaining Carboxyl group (-COOH) residues are C-terminus. When drawing a protein structure the C-terminus is on the right side according to the convention (4) & (5).
The function of the N-terminus and C-terminus in protein
N-terminus
1. It is the first part of the protein. So it plays an important role in the formation of proteins.
2. N-terminus directs the delivery of protein to the right cell organelles.
3. It often contains the signal peptide sequence.
4. This terminus is an important determinant of the protein.
5. Amino-terminal or N-terminus supplies many of the structural elements of a cell and binds cells together (3) & (5).
C-terminus
1. It can carry signals for protein sorting. This terminus keeps the protein in the endoplasmic reticulum.
2. The C-terminus attaches lipid anchors to the protein and allows the protein to enter the cell membrane without becoming a transmembrane domain.
3. It helps bind to other proteins with RNA polymerase to activate polymerase activity.
4. This terminus also plays a key role in the formation of peptide bonds, because it is the end of the polypeptide chain (1) & (6).
Difference between N-terminus and C-terminus
N-terminus |
C-terminus |
| 1. It is the first part of the polypeptide chain. | C-terminus is the end part of the protein or polypeptide chain. |
| 2. In protein, its color is blue. | The color of the C-terminus is red in protein. |
| 3. N-terminus is a positively charged residue. | It is a negatively charged residue. |
| 4. The N-terminus has a free amino group (-NH₂) | The C-terminus has a free Carboxyl group (-COOH). |
| 5. When drawing a protein structure the N-terminus is located on the left side according to the convention. | According to the convention, when drawing a peptide structure the C-terminus is on the right side of the peptide chain. |
| 6. It directly delivers the protein to the right cell organelles. | It can be carrying signals for protein sorting. The C-terminus also attaches lipid anchors to the protein and allows the protein to enter the cell membrane. |
| 7. During the protein translation from messenger RNA, the N-terminus is translated first. | During the protein translation from messenger RNA, the C-terminus is translated after the N-terminus. |
| 8. When a protein molecule is observed in a graphics program, the amino group that is visible with the lowest residue is the N-terminus. | If a protein molecule is observed in a graphics program, the terminus that is visible with the highest residue is the C-terminus (1) & (5). |
Similarities between the N-terminus and C-terminus
In addition to the above differences, some similarities exist between the N-terminus and C-terminus.
- They are both parts of the peptide chain.
- The N-terminus and C-terminus both are residues.
- Both are attached to alpha-carbon atoms (2).
Q&A
1. How to determine N and C-terminus?
- The N-terminus is determined by reacting the protein with dansyl chloride. Dansyl chloride reacts with an amino group in the protein. However, it does not react with the epsilon amino group of lysine.
- C-terminus is determined by the addition of carboxypeptidase enzymes. This enzyme divides amino acids from the C-terminal.
2. What are the N-terminus and C-terminus of a protein?
There are two ends of the polypeptide chain or protein. These are N-terminus and C-terminus. They are both residues of peptides. Residue means each amino acid unit of the peptide. The terminal group of amino acids with a free amino group is known as the N-terminus of a protein. The end of the peptide with the free carboxyl group is called the C-terminus of a protein (5).
3. How to identify C and N-terminus?
- The amino acids which have a free carboxyl group are C-terminus. They are at the end part of the polypeptide chain. This terminus is bound with α-carbon atoms.
- The terminal group which has an amino group is N-terminus. It is the first part of the polypeptide chain.
In this way, both are identified (2).
4. What is the C and N-terminus?
The first of the peptides with the free amino group is called the N-terminus or N-terminal end. And the end of the peptide with the free carboxyl group is known as the C-terminus (1).
5. How to determine N-terminus and C-terminus?
N-terminus
The N-terminus is determined by reacting the protein with dansyl chloride. Dansyl chloride reacts with an amino group in the protein.
C-terminus
C-terminus is determined by the addition of carboxypeptidase enzymes. This enzyme divides amino acids from the C-terminal.
References
1. Nimai Tewari. Advance Organic Chemistry. Books and Allied (P) Ltd. Chapter: Amino acids, peptides, proteins enzymes, and nucleic acids. Page No: 716 to 718.
