Introduction
Food builds and nourishes the body and provides energy. This energy is important for the people and it helps in surviving. The energy released from food helps the body perform various physiological functions like the growth and development of the human body. So it is very important to take the proper amount of nutritious food to keep the body healthy. The process of nutrition of the human body is done in five ways namely ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. The human digestive system comprises a group of organs that do all the processes from ingestion to egestion. The important role that the human digestive system in the human body is described in detail below (1) & (2).
Definition of the digestive system
The human digestive system is the system that combines the organs that help the human body in ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, and egestion. Digestion is done through this system so it is called the digestive system. Food digestion is a physical process. Through this system, the food is first cut into small pieces and then gradually digested by various enzymes to make it suitable for assimilation in the body (4).
Importance of the digestive system
1. People usually eat complex foods that turn into simple food under the influence of various enzymes in the digestive duct. That is, the digestion of food occurs.
2. The digested food of human beings is absorbed in the digestive system (small intestine) and enters the bloodstream.
3. Digestive food of animals is excreted from the body in a special process after it is temporarily stored in a special part of the digestive duct.
4. The digestive juices secreted from the digestive glands. These digestive juices contain a variety of enzymes. Complex foods are converted into simple foods by these enzymes (2) & (5).
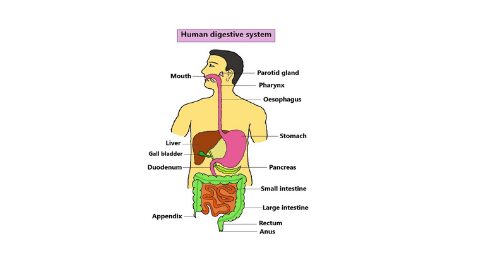
Human digestive system
The various parts that help in digestion play an important role in the human body. The different parts associated with nutrition and their role in nutrition were discussed. The digestive system consists of two parts. Such as the digestive duct and digestive glands (3).
1. Digestive duct or alimentary canal
The parts of the digestive duct that play the role of the digestive system are
a. Mouth
The first part of the alimentary canal is the mouth. It is protected by the upper and lower lips. The open part at the backside of the face is called the buccal cavity. There are numerous mucous glands in the buccal cavity. The mouth is moistened by mucus secreted from the mucous glands.
The tongue and salivary glands are in the mouth. The front of the tongue tastes sweet, the back part is bitter, the anterior part is salty and the posterior part is acidic. There are also four types of teeth in the upper and lower jaws of the mouth incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
Role in food digestion
- The buccal cavity helps in the digestion of food.
- Teeth also play a significant role in digestion. Incisors are used to cut food, canines to tear food, and premolars and molars teeth are used to chew and grind food.
- Many flavors are located in the tongue. So the tongue helps in tasting food. The tongue also helps in swallowing (2).
b. Pharynx
The next part of the buccal cavity is the pharynx. It is the part between the mouth and the esophagus. It is a slightly swollen cylindrical part. The glottis hole in the pharynx is connected to the trachea. Gullet is the hole that joins the esophagus from the pharynx and is covered by a lid called the epiglottis.
Role in food digestion
Food enters the esophagus from the mouth through the pharynx (5).
c. Esophagus
The esophagus is the muscular part of the alimentary canal that extends from the pharynx to the stomach. This duct is about 25 cm long.
Role in food digestion
Food is not digested or absorbed by the esophagus. Food is transmitted from the pharynx to the stomach through the oesophagus (3) & (4).
d. Stomach
The next part after the esophagus is the stomach which is a J-shaped muscular sac. It is the most swollen part of the alimentary canal. The stomach volume is about 1.5 liters. There are three parts of the stomach. The first part of the stomach that connects to the oesophagus is cardiac next part is the body and the last part is the pylorus, which is attached to the duodenum.
Role in food digestion
- Gastric juices are mixed into the food in the stomach.
- The function of the stomach is to temporarily store food.
- HCL destroys the germs involved in food. The stomach is engaged in this HCL secretion function.
- Partial digestion of proteins and fats occurs in the stomach. Carbohydrates are not digested in the stomach (1) & (3).
e. Small intestine
The small intestine is the next part of the pyloric ring of the stomach. It is a tube about 6 meters long from the stomach to the large intestine. There are three parts of the small intestine.
| Parts name | Description |
| 1. Duodenum | The first part is the duodenum. It is a U-shaped part adjacent to the stomach. Bile duct and pancreatic duct are exposed in this part.
|
| 2. Jejunum | The second part of the small intestine is jejunum. It is the next part of the duodenum. This part of the small intestine is about 2 -3 meters long. |
| 3. Ileum | It is the last part of the small intestine. It is attached to the large intestine. The ileum is a tube or duct about 3 to 4 meters long. It is connected to the large intestine by the ileocecal muscle. The ileum is innumerable folds. |
Role in food digestion
- As a result of the movement of the small intestine, the food mixes with the enzymes.
- The intestinal glands in the small intestine secrete digestive juices called intestinal juices which help in the digestion of food.
- Water, vitamins, mineral salts, etc. are all absorbed in the small intestine.
- As a result of digestion, simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, etc. are absorbed by the villi (numerous finger-shaped projections located in the small intestine) (3) & (5).
f. Large intestine
The large intestine is a thick, grooved, cylindrical part extending from the end of the ileum to the anus. It is about 1 to 2 meters long. The large intestine has 6 parts.
| Parts name | Description |
| 1. Cecum
|
It is the sac-type part located at the beginning of the large intestine. The appendix is on the back of the cecum. |
| 2. Ascending colon | This is the next special upward part of the large intestine of the cecum.
|
| 3. Transverse colon | It is a special horizontal duct of the large intestine that is separated from the ascending and descending colon by the colic fold.
|
| 4. Descending colon | It is the part of the large intestine on the left side of the abdominal hole that extends from the colic fold to the sigmoid colon.
|
| 5. Sigmoid colon | It is the s-shaped part of the large intestine.
|
| 6. Rectum | It is the last part of the sigmoid colon that extends to the anus.
|
Role in food digestion
- The main site of water absorption is the large intestine.
- Bacteria that live in the large intestine synthesize vitamins K and B₁₂.
- The large intestine makes and excretes feces.
- A small amount of glucose and amino acids are absorbed in the large intestine (2) & (4).
2. Digestive glands
The digestive glands in the human body also play an important role in digestion. Among the digestive glands that participate in digestion are-
a. Salivary glands
There are three pairs of salivary glands in the mouth. These are a pair of parotid glands, submandibular glands, and sublingual glands.
Role in food digestion
- The saliva juice secreted from the salivary glands helps in chewing and softening the food.
- The lysozyme enzyme present in the salivary glands destroys bacteria in the food.
- The ptyalin enzyme present in the saliva converts starch into maltose (3).
b. Liver
The liver is the largest gland in the body. It is located just below the diaphragm and above the abdominal cavity. The gallbladder is located below the right side of the liver.
Role in food digestion
- The liver secretes bile which accumulates in the gallbladder. Bile juice helps in the digestion of fatty foods.
- The liver stores fats and synthesizes sugars and proteins.
- Substances such as vitamin A, D, and glycogen are stored in the liver (5).
c. Pancreas
The pancreas is located just behind the stomach. It is a mixed gland, that is, it has internal and external parts. The juice secreted from the pancreas is alkaline. It contains the amylase, trypsin, and lipase enzymes.
Role in food digestion
Pancreatic juice is secreted from the pancreas, which enters the duodenum of the small intestine through the common bile duct. Pancreatic juice contains carbohydrate-breaking enzymes (amylase), which convert starch into maltose. It contains protein-breaking enzymes (trypsin and chymotrypsin), which convert peptone and undigested protein into peptides. And the pancreas also contains fat-breaking enzymes (lipase). It converts fat into fatty acids and glycerol (3) & (4).
d. Gastrointestinal glands
It is located in the inner wall of the stomach. Gastric juice is the secretion of gastrointestinal glands. This juice is acidic. It contains HCL, pepsin, and lipase.
Role in food digestion
- These glands help digest proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
- The HCL secreted from this gland destroys the bacteria that enter the body through food (3).
e. Intestinal glands
This gland is located in the lining of the small intestine. The juice secreted from the intestinal glands contains the enzymes maltose, sucrose, and erepsin.
Role in food digestion
The enzymes in the juice secreted by the glands help in the digestion of protein, fat, and mainly carbohydrates (5).
Human digestive processes
People get nutrition from digestion. This digestive system of human beings is accomplished through five methods. Some parts of the digestive tract play a key role in performing this digestive function. This is discussed below.
1. Ingestion
In this process, people take food through the mouth. The four parts of the alimentary canal, such as the mouth, lips, tongue, and teeth play an active role in this process.
2. Food digestion
In this process, solid and complex foods are converted into liquid and simple foods. This process is called the digestive process. Under the influence of various enzymes in this process, complex foods are gradually converted into simple foods. The mouth, stomach, and small intestine play a major role in this process.
3. Absorption
Simple foods digested in the process of absorption are absorbed in the villi located in the small intestine. The small intestine plays an important role in absorption.
4. Assimilation
Simple food that is absorbed in the process of absorption is incorporated into the protoplasm in the process of assimilation. The assimilation process occurs in different tissues and cells.
5. Egestion
In this process, indigestible food items are excreted out of the human body. The two parts of the alimentary canal that play a significant role in egestion are the rectum and the anus (4) & (5).
Enzymes involved in the digestive system
The three main types of enzymes secreted by the digestive tract and digestive glands help the digestion.
- Amylolytic enzymes
The amylolytic enzyme converts carbohydrate foods into absorbable foods. Examples of amylolytic enzymes are amylase, maltose, sucrose ptyalin, etc.
The enzymes that convert proteins into absorbable amino acids are proteolytic enzymes. Examples of these types of enzymes are Pepsin, trypsin, and chymotrypsin, etc.
- Lipolytic enzymes
These enzymes act on fatty foods and are converted to fatty acids and glycerol. Lipase is a type of lipolytic enzyme (5).
