Introduction
Cells are the smallest and basic unit of life for all plants and animals. Its effectiveness is wide and life is not possible without it. All the physiological functions of an organism are actually the sum of the functions of each cell in the body. A cell can be said to be living separately. There are mainly two types of cells eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. The nucleus and cell organelles of prokaryotic cells are not present. Eukaryotic cells are made up of various cell organelles, including the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The Golgi body is one of these cell organelles. The Golgi body plays an important role in the various activities of the cell. The golgi body is the manufacturing and shipping center of eukaryotic cells (Agarwal & Agarwal) & (4). Following is a detail discussion about Golgi bodies apparatus function.
Definition of Golgi bodies
The round or cylindrical densely embedded cellular organelles attached to the single membrane near the nucleus are engaged in the secretion of cells, called the Golgi body or apparatus. The Golgi bodies present in the plant cells are called dictyosomes. Dictyosomes help in the formation of plant cell walls and participate in cell secretion. Various cell organelles are not found in the cytoplasm around the Golgi bodies or Golgi apparatus. This is why the cytoplasmic part without this cell organelle is called the zone of exclusion. Golgi bodies are formed from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (1) & (6).
Location
The Golgi body is a unique cytoplasmic organelle of animal cells. It is commonly found in animal cells. Golgi bodies are also found in the cells of some plants. They are found in small numbers in plant cells. Golgi bodies are scattered in the cytoplasm of lower-class plant cells. In the cytosol of plant and animal cells, the Golgi body is located very close to the nucleus (8).
Discoverer
George, Platner, and Herman talk about this organelle in animal cells. The Italian scientist Camilo Golgi gave a special description of this organelle in 1896 by applying a pigment called osmium oxide to the owl nerve cells. According to its name, this cell organelle has been named Golgi bodies or Golgi apparatus (2) & (5).
Some interesting facts about Golgi bodies
- The Golgi body’s wall consists of proteins and lipids.
- It is considered a part of the system in the endomembrane of the cell.
- The Golgi body is located in the cytosol of eukaryotic cells.
- Golgi bodies cover some important proteins and enzymes (1).
- It is a system filled with a few liquid-filled foods.
- The Golgi body arranges, modifies, and distributes the components of a cell.
- Golgi bodies are often called lipochondria to produce lysosomes.
- It is a type of cell organelle that is involved in the selection and packaging of proteins intracellularly before they are transferred (7).
- The number of Golgi bodies in the cell is very high. The number of Golgi bodies in the secretory cells is also high.
- Golgi bodies play a central role in mutation, sorting, and protein transport.
- In the cells of mammals, the Golgi body is a dynamic structure, which divides into smaller vesicles and tubes during mitosis and is rearranged from these fragments during telophase and these stacks are associated with the formation of a ribbon during interface (3) & (8).
Golgi bodies in plant cell
The Golgi apparatus or Golgi bodies of plant cells are known as the Dictyosomes. They are made of single-membrane cisternae like flat discs. A Golgi body in a plant cell has 2 to 7 cisternae. Cisternae are scattered in the cytosol, but their functions are the same. The outer side of the cisternae in the plant cell is made up of many ducts. The secretion material accumulates inside the sac formed from the outside of the cisternae. The Golgi body of a plant cell provides the building blocks of the plant cell wall. Dictyosome completes the secretion of plant cells (1) & (2).
Why is the Golgi body called “traffic police” in a cell?
The Golgi body carries the membranous structure or vesicle from the central part of the cell to the plasma membrane around the perimeter of the cell. Golgi bodies also play a role in the collection and transport of cell secretions. That’s why the Golgi body is called “cell traffic police” (3).
Expansion
Prokaryotic cells do not have Golgi bodies. Some fungi, bryophytes pteridophytes, and red blood cells of animals do not have Golgi bodies. Golgi bodies are present in eukaryotic cells. Golgi bodies or Golgi apparatus are scattered in the cytoplasm of an ideal plant cell. But in animal cells, Golgi bodies are usually stratified near the nucleus or surrounded by the nucleus. In an animal cell, the Golgi body is sometimes arranged like a lattice (8).
Structure of Golgi bodies
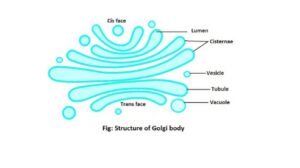
The Golgi body is a living cell organelle consisting of a number of small vacuoles and flattened sacs. This cell organelle is the eukaryotic cell manufacturing center. The Golgi body helps in producing some vitamins. There are three types of structures that can be observed in Golgi bodies (5).
1. Cisternae
Elements of ling and flattened ducts of unequal length are called cisternae. Cisternae look a lot like flat bags also called lamellae. They are arranged parallel to each other and are the most stable component of Golgi bodies. A Golgi body usually has 3 to 10 cisternae.
There are no ribosome grains found in their mantle. These are made with osmium tetroxide. The mantle is 60- 70Å wide. The duct between the mantles of the cisternae is 60- 90Å wide. The gap between each sac of cisternae is about 100- 200Å. These sacs are bent together.
The north side of the cisternae is towards the endoplasmic reticulum. This side is called the surface of creation. The concave side of the cisternae is opposite the endoplasmic reticulum. This side is called the turned surface. Vacuoles and vesicles are formed from the turned surface.
The cisternae are stacked together. The part near the plasma membrane of the Golgi bodies is called the trans-face and the part towards the center of the cell is called the cis-face. The cisternae at the end part of the trans-face are called the trans-cisterna. The cisternae at the end part of the cis-face are called cis-cisterna and the middle cisternae are called medial-cisternae (3) & (8).
2. Vacuole
The large round-shaped parts at the ends of the cisternae are called vacuoles. These are full of granular material and look a lot like a round dish. Vacuoles are formed by widening the cisternae wall located near the cisternae having a diameter of 60- 200Å (7).
3. Vesicle and tubule
The small sac-like objects at the bottom of the cisternae are called vesicles with a diameter of 30- 40Å. The long and narrow tube-like part near the vesicle is the tubule. Some irregular ducts and vesicles are called trans-Golgi-network (Agarwal & Agarwal) & (3).
Why is the Golgi body called a “carbohydrates factory” of cells?
The Golgi body helps in cell division by cell membrane renewal and cell wall formation. The Golgi body also binds to the oligosaccharide chain of glycoproteins and synthesizes and secretes complex polysaccharide substances. Golgi bodies help in cell secretion and the synthesis of complex large molecules that are carbohydrates. It sometimes secretes carbohydrates that help build cell walls. So Golgi bodies are called the “carbohydrates factory” of cells (3).
Chemical composition of Golgi bodies
Golgi bodies are made up of lipids (40%) and proteins (60%). Lipids contain mainly lecithin phospholipids. These cell organelles also contain carotenoids, fatty acids, vitamin C, etc. The Golgi body is full of various enzymes. The enzymes in Golgi bodies’ are, Mg++, ADPase, glucose 6-phosphate, CTPase, TTPase, and ATPase (8).
The function of Golgi bodies
The Golgi body is the most important cell organelle of the cell. The function and importance of the Golgi body are immense in the body of the organism. The function of the Golgi bodies is mentioned below.
1. The Golgi body serves as a storehouse of food.
2. Golgi bodies play an active role in the formation of plant cell walls.
3. Various types of synthesized objects are transferred by Golgi bodies.
4. It assists in the secretion and transport of enzymes and hormones.
5. Golgi bodies synthesize lipids and secrete proteins.
6. Mitochondria are stimulated by this organelle to produce ATP.
7. It participates in the synthesis and transport of various polysaccharides.
8. These cell organelles make lysosomes and expel water from the cells.
9. The Golgi apparatus helps in cell division through cell membrane renewal and cell wall formation.
10. Golgi bodies help in the formation of acrosomes in mature sperm.
11. Golgi apparatus or Golgi bodies participate in phospholipid absorption and neurosecretion.
12. The function of the Golgi apparatus is to make proteins, hemicellulose, and microfibrils (5) & (8).
The main function of the Golgi body or Golgi apparatus is to participate in the secretion of cells. The secretion substances that form in the endoplasmic reticulum gradually accumulate in the Golgi body. The substance then accumulates in the swollen part of the membrane towards the Golgi body. This results in the formation of a sac with substances. When the secretory sac meets the cell membrane, the substance exits the cell. Thus the Golgi bodies play the role of cell secretions. Therefore, the role of this cell organelle in all plants and animal cells is very important.
