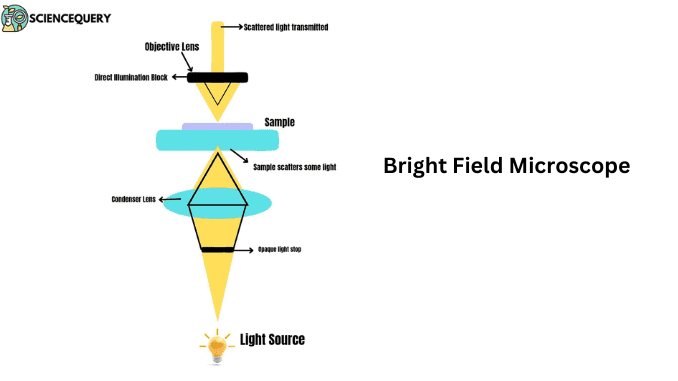
Introduction
A bright field microscope can be said to be an optical microscope that uses light to illuminate an object. Another name for a bright field microscope is a Compound microscope. They are highly used in the areas of research, education, and industrial purposes. The compound microscopes are used for quantitative and qualitative analysis of the living specimens.
The bright-field microscopic technique is widely used in the biotechnological world. This microscope allows scientists to magnify images at variable ranges while maintaining good quality. Visual magnified image of 10X image and 15X eyepiece is 150X.
Components of Bright Field Microscope
The components of a bright field microscope comprise:
Objective
The main purpose of the objective is to pass the light through the specimen and create a real, inverted image of the given specimen. It should possess the capacity to reconstruct certain points to form an image in the anti-points region.
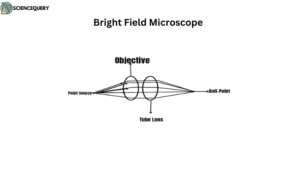
Eyepiece
The main function of the eyepiece is to magnify the image. It consists of two lenses that allow the target to focus.
Condenser
Its main function is to collect the light coming from the light source and to concentrate on the specimen through a beam of parallel lights. The light again comes back to the focus of the objective. The condenser plays a special role in dark-field microscopy.
Tube Lens
This lens collects parallel rays of light projected by the objective to focus on the plane at a fixed diaphragm of the eyepiece.
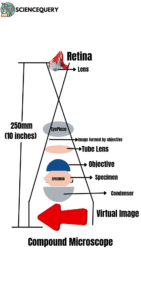
Lens System Of Bright Field Microscope
The lens system of a compound microscope has two sets of lenses. One is the objective lenses, that are situated at the base and are used to magnify objects up to 100x. Another is the eyepiece, situated at the top and hence further magnification of images. These pairs of lenses help in creating a better resolution and magnification of images.
Condenser
The main purpose of the condenser is to focus light as well as control the amount of light falling onto the specimen. It consists of three basic components :
- Lenses
- Diaphragms
- Filters
Stage
The stage of a bright field microscope is the platform that holds the specimen in position. It is composed of two parts- an upper and lower part, joined by a hinge.
Working principle of a substage condenser
The working principle is strictly based on the principles of refraction and reflection. The condenser has two lenses, an objective and an eyepiece lens.
When light passes through these lenses it is directed towards the specimen. This helps create a bright image that can be viewed by the eyepiece lens.
The condenser also contains adjustable components like diaphragms that tune the amount of light. Some microscopes have filters or polarizers that help in enhancing brightness levels while observing the specimens under low-light environments.
Sample preparation
Sample preparation is the initial process in bright field microscopy so that the sample can be viewed with ease. The sample needs to be mounted by using chemicals such as formaldehyde or wax. Now the specimen is stained so that the sample can be clearly studied under the microscope. One of the most common stains used is Gram’s stain used to enhance the contrast effect (1)
The stain is now washed and dried to remove excess water enabling the light to pass easily. Ethanol is generally used for this dehydration process. At last, coverslips are mounted to protect the sample and better viewing under the bright field microscope.
Advantages
The bright field microscope has several advantages :
- Bright-field microscopy enables us to observe high-contrast images and to point out the fine details in specimens (2)
- The technique is very simple and easy to use compared to other techniques like phase contrast or fluorescence microscopy.
- This technique is cost-effective.
- It helps in creating a highly magnified image enabling us to study better (3)
Limitation
- We can not observe the specimen three-dimensionally as it requires advanced techniques like Phase contrast microscopy (4)
- Resolution is low as compared to other microscopies. Thus, it becomes difficult to study microscopic objects.
- This microscopic technique requires staining of the specimen for better observation.
Applications
-
Cell Division
- The division of cells that include mitosis and meiosis can be easily studied with the help of bright field microscopy. Mitosis involves the replication of chromosomes and finally equal distribution of daughter cells. This type of division can also be said as equational division.
Whereas meiosis is a process of reduction of chromosome number into halves. It is therefore considered a reductional division.
To analyze the biochemical pathways
- Bright-field microscopy is used by biologists to analyze various biochemical pathways (5)
-
Microbiological observations
- It is also used to study colonies of organisms on agar plates that are highly used by microbiologists to study the microbial colonies in a better way.
Comparison with other microscope
| Characteristics | Dark Field microscope | Light Field Microscope | Phase-contrast Microscope | Scanning electron microscope | |
| Illumination Sources | Visible Light | Visible Light | Visible Light | Electrons | |
| Nature of Lenses | Glass lens | Glass lens | Glass lens | Electrostatic and electromagnetic | |
| Image | 2-D | 2-D | 2-D | 3-D | |
| Specimen Contrasting | Through patch stop | Light Diffraction | Through Phase Plate | Electron Scattering | |
| Focus and Magnification | Changing Objectives | Changing Objectives | Changing Objectives | Electrical, using Deflection Coil |
Summary
- A bright field microscope can be said to be an optical microscope that uses light to illuminate an object.
- This microscope is also known as a Compound microscope.
- They are highly used in the areas of research, education, and industrial purposes.
- The compound microscopes are used for quantitative and qualitative analysis of the living specimens.
- This microscope allows scientists to magnify images at variable ranges while maintaining good quality.
- The technique is very simple, easy to use, and cost-effective.
- Bright-field microscopy enables us to observe high-contrast images and to point out the fine details in specimens
- Its components include an objective, lens system, condenser, and eyepiece.
- We can not observe the specimen three-dimensionally as it requires advanced techniques like Phase contrast microscopy.
- Resolution is low as compared to other microscopies. Thus, it becomes difficult to study microscopic objects in bright field microscopy.
- This technique is used by biologists to analyze various biochemical pathways.
- It is also used to study colonies of organisms on agar plates that are highly used by microbiologists to study the microbial colonies in a better way.
