Introduction
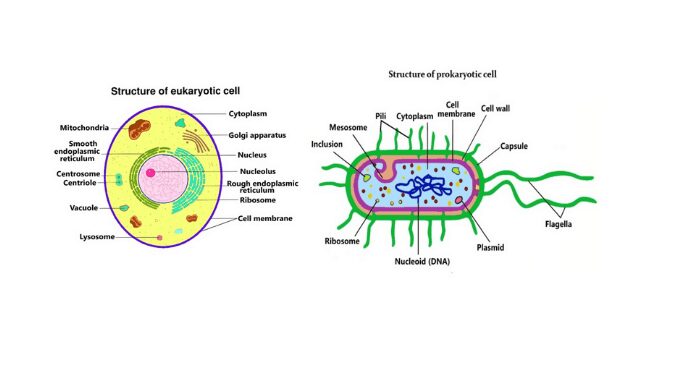
All organisms are made up of tiny billions of cells that cannot be seen with the naked eye. In 1665 scientist Robert Hooke first discovered the cell. The cells are arranged one on top of the other to form organisms. The size of a cell is about 0.1 micrometers to 100 micrometers. The unicellular smallest cell is Mycoplasma galliseticum. The diameter of the smallest cell is about 10 micrometers. On the basis of the nucleus, the cells are classified into two types eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are composed of cell walls, cell membranes, nuclei, cytoplasm, and some cell organelles located in the cytoplasm. On the other hand, prokaryotic cells are composed of capsules, cell walls, cell membranes, cytoplasm, genetic material, pili, and flagella. Each cell has a specific cell membrane. The cell membrane of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is the topic of the discussion below (3).
Prokaryotic cell
Origin of word
The prokaryotic word comes from two Greek words Pro and karyon. The word pro means, “Before” and the karyon means, “nut” or “kernel”.
Definition
A cell that does not have an organized nucleus, a membranous cell organelle, and does not have chromosomes, is called a prokaryotic cell. The genetic material of these undeveloped cells is a non-histone protein DNA type. Prokaryotic cells are unicellular types (4) & (2).
Example
Bacteria and blue-green algae are examples of prokaryotes. The cells that make up the body of bacteria and blue-green algae are prokaryotic-type cells (2).
Properties
1. The structure of a prokaryotic cell is very simple.
2. The prokaryotic cell does not have a well-organized nucleus.
3. The process of cell division of prokaryotic cells is simple. The cell division is completed by the method of amitosis.
4. The size of the prokaryotic cell is very small (0.05 to 10µm).
5. Although the nucleus of a prokaryotic cell contains DNA molecules, there is no specific nuclear membrane or nucleolus.
6. Prokaryotic cells do not have well-formed plastids for photosynthesis.
7. The chromosomes of prokaryotic cells are not well-organized. That means only DNA is present and DNA is a circular type.
8. The prokaryotic cells have no cytoplasmic organelles surrounded by a covering (except ribosome).
9. The ribosomes of prokaryotic cells are small and the type of 70s.
10. The main component of the cell wall of prokaryotic cells is muren or mucopeptide or peptidoglycan (1) & (5).
The cell membrane of prokaryotic cell
Structure
The cell membrane structure of a prokaryotic cell is simple it is made up of proteins and lipids called the plasma membranes. A prokaryotic cell membrane is actually a fluid phospholipid bi-layer submerged with proteins. The cell membranes of prokaryotic cells have two phospholipid layers. A prokaryotic cell membrane is a thin lipid bilayer. The thickness of the prokaryotic cell membrane is about 7 nm.
The plasma or cell membrane is semipermeable, quasi-fluid, and dynamic. This plasma membrane separates the prokaryotic cell from the surrounding environment. The prokaryotic cell membrane is made of 40% lipids 60% proteins and no cholesterol. The prokaryotic cell membrane consists of monounsaturated fatty acids. The phospholipid layer has two ends, the head part is of glycerol and the tail part consists of two molecule fatty acids. The head is called polar hydrophilic ends and the tail is called non-polar hydrophobic ends. The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells folds inwards to form mesosomes (4) & (3).
Function of prokaryotic cell membrane
1. Prokaryotic cell membrane helps to synthesize membrane lipids.
2. The process of diffusion and osmosis of cells is controlled by the prokaryotic cell membrane.
3. The prokaryotic cell membrane transports the proteins.
4. In addition to transporting proteins, the prokaryotic cell membrane may contain sensitive proteins that measure the density of molecules in the environment.
5. Many metabolic processes such as cell synthesis, septum formation, membrane synthesis, DNA replication, etc. take place in the membrane.
6. Prokaryotic cell membrane controls the exchange of various organic and inorganic substances inside or outside the cell.
7. The cell membrane of a prokaryotic cell is the location of transport systems for specific solutes (2) & (5).
Eukaryotic cell
Origin of word
The eukaryotic word comes from two Greek words Eu and karyon. The word Eu means, “well” or “good” and the karyon means, “nut” or “kernel”.
Definition
A cell that has a well-organized nucleus (nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and nuclear reticulum present), and is surrounded by the nuclear membrane, chromosomes are alkaline proteins, and multiple cellular organelles are surrounded by a membrane, are called eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes made up of histone, non-histone proteins, and DNA (2).
Example
All other living cells are eukaryotic cells, except for the monera. That is, all the developed species of animal cells, plant cells, and fungal cells are examples of eukaryotic cells (4).
Properties
1. The eukaryotic cells have living, fine, semipermeable, and microscopic membranes. This membrane is called the cell membrane. It also protects the protoplasm.
2. The structure of the eukaryotic cell is very complex.
3. The nucleus of a eukaryotic cell is well organized. That means nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and nuclear reticulum are present in the nucleus.
4. The chromosomes of eukaryotic cells are well-organized. That means chromosomes are made up of histone, non-histone proteins, and DNA. The number of chromosomes in eukaryotic cells is always multiple.
5. The ribosomes of eukaryotic cells are large in size. Ribosomes of both 70s and 80s types are present in eukaryotic cells.
6. The process of cell division of eukaryotic cells is complex. The cell division is mitosis and meiosis.
7. The eukaryotic cells have many cell organelles in the cell membrane.
8. The size of the eukaryotic cell is very large (10 to 100µm) (1) & (3).
The cell membrane of Eukaryotic cell
Structure
The cell membrane structure of the eukaryotic cell is complex and is made up of about 50% lipids, about 50% of proteins, and 5 to 10% of carbohydrates. The lipid is the first and primary component in the cell membrane and is formed by phospholipid, glycolipid, and cholesterol. It has two ends, the head, and the tail. The head part of the phospholipid layer consists of one molecule of phosphate, called hydrophilic ends. The tail part of the phospholipid layer consists of two molecule fatty acids, called hydrophobic ends.
Proteins are the second most abundant component of the cell membrane. There are three types of proteins integral or intrinsic proteins, peripheral proteins, and Lipid-anchored proteins. And 50% of proteins include lipoproteins, enzymatic proteins, carrier proteins, and structural proteins.
Carbohydrate is the third and essential component of the eukaryotic cell membrane. The carbohydrate chain is attached to the cell membrane protein and lipid layer. The cell membrane is about 75 Å thick. The cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell contains about 30% water (1) & (2).
The function of the eukaryotic cell membrane
1. The primary function of the eukaryotic cell membrane is to give the cell a specific shape.
2. The cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell plays a major role in the diffusion and osmosis of cells.
3. Membrane present in the eukaryotic cell controls the transport of various substances.
4. There are many types of enzymes in the cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell. These enzymes play a major role in cells.
5. The cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell helps in the entering of liquid and solid food into the cell in the process of pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
6. Eukaryotic cell membrane protects the various parts inside the cell from external damage.
7. Cell membrane of eukaryotic cells (plant cells) also participates in protein synthesis with the help of ribosomes (4) & (5).
Difference between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell membrane
Each cell has a different structure. The eukaryotic cell membrane structure is very complex. On the other side, the prokaryotic cell membrane structure is simple. There are some differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell membranes.
Content |
Eukaryotic cell membrane |
Prokaryotic cell membrane |
1. Definition |
The fine and elastic membrane on the outside of the protoplasm of every living cell, and the membrane that is made up of protein-lipids, is the cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell. | Cell membrane of prokaryotic cells is elastic, dynamic, quasi-fluid, and semipermeable, and a fine membrane located below the cell wall which is made up of lipoproteins. |
2. Structure type |
The eukaryotic cell membrane structure is more complicated than the prokaryotic cell membrane structure. | The prokaryotic cell membrane structure is simpler than the eukaryotic cell membrane structure. |
3. Thickness |
Thickness of the eukaryotic cell membrane is about 5nm | Prokaryotic cell membrane thickness is about 7nm. |
4. Presence of Carbohydrates |
Carbohydrates are present in the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells. | There are no carbohydrate chains located in the prokaryotic cell. |
5. Presence of cholesterol |
Cholesterol is present in the eukaryotic cell membrane. Cholesterol molecules are located in the gap of two phospholipid layers. | Prokaryotic cells do not contain cholesterol. |
6. Hydrophilic structure |
The hydrophilic structure of the phospholipid layer of eukaryotic cell membranes is of phosphate molecules (6). | The hydrophilic structure of the phospholipid layer of prokaryotic cell membranes is of glycerol molecules. |
7. Formation of mesosomes |
No formation of mesosomes in the eukaryotic cells. | The cell membrane of prokaryotic cells folds inwards to form mesosomes. |
8. Glycocalyx formation |
Eukaryotic cell membranes have a glycocalyx structure. Glycoproteins and glycolipids are collectively called glycocalyxes. | There are no carbohydrate chains located in the prokaryotic cell. That is why prokaryotic cell membranes have no glycocalyx structure. |
9. Formation of pinosome and phagosome |
The cell membrane of Eukaryotic cells folds inwards to form pinosomes and phagosomes. | No formation of Pinosomes and phagosomes (1) & (5). |
Similarities between the prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell membrane
Although there are differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell membranes, there are some similarities between the cell membranes of these two cells.
1. Phospholipid and protein molecules are present in the cell membrane of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
2. The phospholipid layers of both cell membranes have two ends, such as hydrophilic and hydrophobic ends.
3. There are two molecules of fatty acids on the hydrophobic ends of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell membranes.
4. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell membranes are elastic, fine, semipermeable, and quasi-fluid (4) & (2).
References
1. S. B Agarwal and V. K. Agarwal. Unified Botany, B.Sc. Third Year. Shiva Lal Agarwal & Company Publications, Indore. Chapter: plasma membrane: bilayer lipid structure and functions. Page no 222-224.
2. Ajoy Paul. Zoology Honours (volume 1). Books and Allied (P) Ltd., Kolkata (India). Chapter: plasma membrane. Page no 297 – 300.
3. Chandrasekhar Chakrabarti. Modern approach to a textbook of core Zoology, General & Honours. Nirmala Library, A Publishing House under the Prestigious International Standard Book Number (ISBN) System. Kolkata, (India). Part – II, Chapter- Cell and Cellular Organelles. Page no: 10-18.
