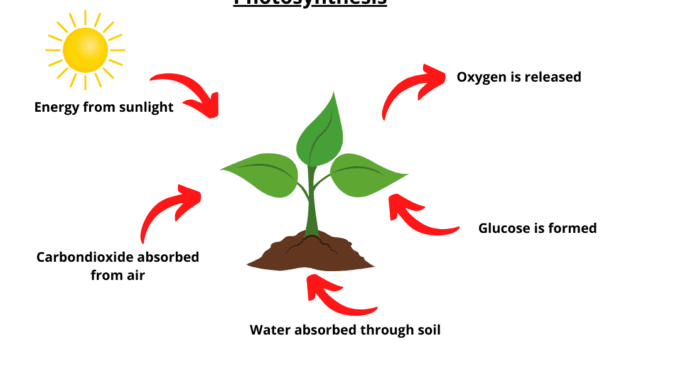
Concept of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physiological process of plants. In 1898, scientist Barnes first used the term photosynthesis. Photosynthesis comes from two Greek words ‘photo’ means light, and ‘synthesis’ means, synthesize, or produce. Therefore, photosynthesis is the synthesis or production of any element with the help of light. In photosynthesis, solar energy from the sun is bound to glucose in the form of chemical energy. It is also a type of autotrophic nutrition. This energy is used in the biological work of plants. Other organisms absorb this energy directly or indirectly through food and use it to survive. That means the presence of living things on Earth depends on photosynthesis (1) & (3).
What is the definition of photosynthesis?
The physiological process by which cells use chlorophyll and other pigments in the biochemical reaction of water and CO₂ taken from the environment to bind the solar energy to synthesize glucose and produce water and oxygen as by-products are called photosynthesis. In a word, the technique of making food for plants in the presence of sunlight is called photosynthesis. The chemical equation of photosynthesis is
6CO₂ + 12H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ + 6H₂O (1).
Site of photosynthesis
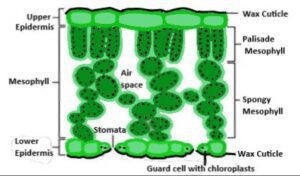
Fig: leaf structure
Photosynthesis occurs in all green chlorophyll-pigmented cells. Since plants contain mainly chlorophyll, photosynthesis occurs primarily in plants. The mesophyll tissue of the leaf is the ideal place for photosynthesis. This is because the leaves can absorb more sunlight as they are flattened and stretched. Mesophyll tissue cells have the highest number of chloroplasts and the highest amount of stomata, they are ideal for photosynthesis. Photosynthesis occurs on the young green stems of plants, on the green aerial roots of orchids, bodies of euglena, chrysamoeba, etc (2).
Components of photosynthesis and their roles
The main components of photosynthesis are water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, and sunlight. There are also some other components like NADP, ADP, RuBP, etc. But among all these elements water, CO₂, chlorophyll, and sunlight play an important role in photosynthesis. (2) & (3)
Sunlight
Source
Visible light is a part of the waves that constantly reach the Earth’s surface from space. This visible light of the sun is used in photosynthesis. It is actually made up of some tiny energy particles. These are called photon particles. These photos are used in photosynthesis. The sun is the main source of sunlight. Photosynthesis can also occur in artificial light.
Role
- Sunlight helps activate chlorophyll.
- Sunlight produces high-potency ATP by photophosphorylation in the cell and releases oxygen into the water.
- Assists in photolysis (2) & (3).
Chlorophyll
Source
Chloroplasts present in leaf mesophyll tissue are the main source of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is found in the grana area of chloroplasts.
Role
- Chlorophyll is excited by absorbing photons of sunlight and breaks down water into hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
- The electrons emitted from the active chlorophyll produce ATP in a light chemical process. (2) & (3).
Water
Source
Terrestrial plants absorb water from the soil through the roots. Aquatic plants absorb water from reservoirs by their submerged parts. Parasitic plants absorb water vapor from the air by gaseous roots. Environmental water is the source of water required for the photosynthesis of plants.
Role
- Water is used as a raw material in photosynthesis.
- Water provides electrons to chlorophyll during photosynthesis.
- In dark reactions, the hydrogen needed to oxidize CO₂ is produced by water analysis.
- Water is also the source of the oxygen that is produced in photosynthesis (2) & (3).
Carbon dioxide
Source
Terrestrial and parasitic plants absorb CO₂ from the atmosphere through the stomata. Aquatic plants absorb CO₂ dissolved in water by their submerged parts.
Role
- CO₂ is a raw material of photosynthesis.
- Carbon assimilation occurs with carbon dioxide.
Mechanism of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is done in two steps
- Light reaction
- Light-independent phase or carbon reaction.
1. Light reaction
This is the first stage of photosynthesis. The presence of sunlight is essential at this stage. This reaction occurs in the grana area of the chloroplast. Sunlight, water, chlorophyll, and other pigments, NADP, and ADP are essential components of this reaction (1) & (2). It involves the following process.
a. Activation of chlorophyll
The chlorophyll in the leaves is excited and activated by absorbing photons of sunlight. This causes the excited chlorophyll to release electrons.
b. Photolysis
This active chlorophyll breaks down water into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and hydroxyl ions (OH⁻). The effect of sunlight on the analysis of two ions in water in this way is called photolysis. In 1940, scientist Robin Hill first observed this process. Hence, as its name implies, this reaction is called hill reaction.
c. Reduction of NADP & NADPH creation
The hydrogen ions (H⁺) produced in the analysis of water combine with the hydrogen receptor NADP present in the leaf to form the NADPH. In this case, NADP acts as a hydrogen receptor. So it is called hill reagent. (1) & (2)
NADP + 2H⁺ + 2e⁻ → NADPH + H⁺
d. Oxygen emissions
The hydroxyl ion (OH⁻), another element formed in the analysis of water, leaves the electron to form the OH radical. The four OH radicals combine to form two atoms of water and one atom of oxygen. The water generated is used for the needs of plants and oxygen is released into the atmosphere through the stomata.
4OH⁻ – 4e⁻ → 4[OH]; 4[OH] → 2H₂O + O₂ ↑
e. Photophosphorylation
Photophosphorylation is the process where adenosine diphosphate (ADP) present in the leaves combines with inorganic phosphate (Pi) in the presence of sunlight to form high-potency adenosine triphosphate (ATP) (1) & (2).
ADP + Pi → ATP
2. Light-independent phase or carbon reaction
This is the second stage of photosynthesis. This process occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. This reaction does not require light, so this phase was formerly called the dark reaction. But even if the light is not used directly in this phase, the reactions depend on the substance produced in the light phase. So this phase is now called the light-independent phase. Scientist Blackman first noticed the reactions at this stage. That is why it’s called the Blackman reaction. The necessary components in this phase are CO₂, ATP, and NADPH(1) & (2). It involves the following process.
a. Carbon assimilation
It is the process where atmospheric CO₂ enters the leaf through stomata and reacts with the ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) in the presence of an enzyme called RuBisCO inside the mesophyll tissue to form phosphoglyceric acid (PGA).
6CO₂ + 6RuBP → 12PGA
b. Phosphoglyceraldehyde
Then phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAld) is formed when ATP and NADPH+ H⁺ react with PGA.
12PGA + 12 (NADPH + H⁺) + 12ATP → 12 PGAld + 12NADP⁺ + 12ADP + 12Pi
c. Reproduction of RuBP
Out of the 12 molecules, PGAld, 10 molecules of PGAld produce 6 molecules of RuBP through several chemical reactions. Thus the Calvin cycle continues in cycles.
d. Glucose synthesis
Glucose is produced in chloroplasts in a few steps from the remaining 2 molecules of 12 molecules PGAld.
2PGAld → C₆H₁₂O₆ (glucose)
Most of the glucose produced is transported to the plant body as sucrose food. The rest of the glucose is stored in the form of starch in various parts of the plant.
Photosynthesis controlling factors
External factors
1. Light
Photosynthesis depends on the intensity, nature, and duration of the light. When the intensity of light is high, the process is disrupted.
2. Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
As the amount of CO₂ in the air increases by 0.01%, the number of photosynthesis increases.
3. Water
When a certain amount of water is deficient, the cells that control the stomata and the chloroplast lose performance. As a result, the process is interrupted.
4. Temperature
Photosynthesis rates typically increase from 25°C to 37°C. At high temperatures, the enzyme action is lost.
5. Oxygen (O₂)
As the oxygen in the air increases, the rate of photosynthesis decreases.
6. Leaf age
As the leaf age of the plant increases, the rate of photosynthesis of that leaf decreases (1).
Internal factors
1. Chlorophyll
The process of photosynthesis depends on the activity of chlorophyll.
2. Enzyme
The rate of photosynthesis depends on the presence of different types of enzymes.
3. Protoplasm
The protoplasm indirectly controls the photosynthesis process.
4. Accumulation of photosynthetic substances
The rate of photosynthesis decreases when photosynthetic substances accumulate in mesophyll tissue cells.
5. Leaf structure
This process is largely dependent on the internal structure of the leaf (1).
Importance of photosynthesis
1. Source of energy
In the process of photosynthesis, solar energy is converted into chemical energy first bound to the ATP molecule, and is stored as potential energy in the food produced. Thus only photosynthesis is capable of converting solar energy and storing energy in food.
2. Source of food
Photosynthesis is the main source of food for all living things. The glucose produced in this process is converted into starch and is stored in various parts of the plant as future food.
3. Maintaining the balance of O₂ & CO₂
The photosynthesis process maintains the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The normal amount of O₂ in the atmosphere is 20 to 60% and the normal amount of CO₂ is 0.03%. Fauna takes in O₂ from the environment during respiration and releases CO₂. As a result, the amount of O₂ is decreased and the amount of CO₂ is increased in the atmosphere. Plants absorb CO₂ during photosynthesis and release O₂ to balance the two gases in the atmosphere.
4. Role in the progress of human civilization
The plant provides food, wood, coal, paper, textiles, herbal medicines, etc. Thus the contribution of photosynthesis to human welfare and the development of human civilization is immense (2).
Why photosynthesis is called anabolism?
The process by which the dry weight of an organism increases is called anabolic reaction. In the process of photosynthesis, simple compounds (H₂O and CO₂) produce complex compounds (glucose). As a result, the dry weight of the plant body protoplasm increases. Therefore, it is called anabolism.
Why photosynthesis is called an oxidation-reduction reaction?
In the light phase of photosynthesis, water is oxidized to produce O₂. And in the light-independent phase, glucose is produced when CO₂ is reduced. For this reason, photosynthesis is called an oxidation-reduction reaction.
