Know in one minute about Relative velocity
|
Introduction
Relative velocity is a phenomenon that makes it easy to study the motion of an object relative to other objects.
It is like an optical illusion, in this, there are such incidents that even those objects which are not moving also appear to be moving.
Further in this article, information about it has been given in detail.
Relative velocity
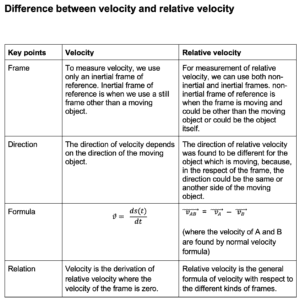
In physics, relative is a term that compares the many terms of physics like displacement, velocity, and acceleration between two objects.
It occurs when two different bodies have different velocities.
Generally, we consider the ground’s velocity zero.
- When we travel in a train, we see outside All the objects, trees, buildings, and even the ground going in the opposite direction to the train’s direction.
- We and all the passengers with us are traveling together in the train, that is, we are doing motion, yet we all seem to be stuck in the same place.
- When we drive a car, if another car comes alongside our car, it also seems stuck in its place.
all the phenomena mentioned above are happening because of relative motions between two bodies.
Definition of relative velocity
Velocity is a term that describes how fast an object can reach its destination. And the value of velocity could be anything.
But, at a particular time in its journey, its velocity can be different with respect to different objects.
It can be defined for any two objects, the condition is there should be a difference between the velocities.
So
“The time rate of change in displacement of an object with respect to the time rate of change in displacement of another object is called relative velocity.”
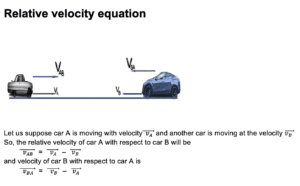
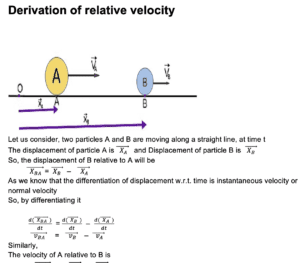
How to calculate relative velocity?
- First of all, it has to be noted which object is the observer and for which object the relative velocity is to be determined.
- After this, the relative velocity of each object will be determined with respect to the ground.
- After that, we will find the relative velocity between an object’s using the formula
Some examples for better understanding



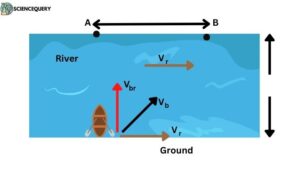
Example 3.
To cross a river on a boat, a man takes a minimum of 8 minutes to cross the river, with a drift of 80m, and if he takes the shortest path to cross the river, he takes 10 minutes to cross it, what will be:
a. width of the river
b. The velocity of the boat w.r.t water
c. Speed of the river flow

Q&A
- How is velocity related to position?
Ans. The time rate of change in position is called velocity. Therefore, velocity is directly related to position as the determination of the velocity of something depends on the position of that object.
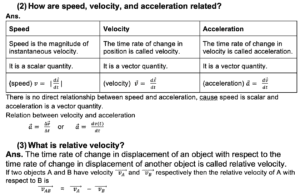
(3) Examples of relative velocity?
Ans. (1) When we sit inside the train and look at the train going on the opposite side of the window, then it is visible at a very high speed. The reason for this is that our train is moving in one direction. And we are sitting inside that train, so we are also moving in the same direction as the speed of the train.
When the train comes in the opposite direction, its speed and our speed get added due to relative velocity. Due to which we see the second train in the speed of our train + the speed of that other train.
(2) On crossing the river, the boat reaches a point away from the point opposite to the starting point at that end of the river, because the direction of the velocity of the boat changes with respect to the velocity of the river.
(3) The human sitting on the circular swing, the person standing far away and all the other objects appear to be rotating.
(4) When we put an umbrella on our head in the rain while walking, the umbrella has to be tilted slightly to avoid the rain completely, due to the relative velocity between the rain and our walk.
(4) What is the unit of relative velocity?
Ans. The S.I. unit is meter/second While the C.G.S. unit is centimeter/second.
References
Written By: Amber Soni
