Introduction
The human body is composed of a total of 206 bones, where the femur, or thigh bone, forms the largest bone, while the smallest bone in a human body is called the stapes.
Stapes is a part of a group of three bones called ear ossicles, found in the middle ear. In this article, we are going to dive into the details of the smallest bone in the human body, called the stapes.
The Discovery of the smallest bone
- In 1546, at the University of Naples, Giovanni Filippo Ingrassia, an Italian physician, discovered stapes.
- He authored an ancient anatomical book titled “In Galeni librum de ossibus doctissima et expertissima commentaria,” which was a commentary on Galeno’s work “De Ossibus.”
- In his book Ingrassia described 24 chapters on human bones, introducing his findings, ideas, and critiques of Galeno’s and Vesalius’s (his teacher) incorrect concepts.
- Ingrassia’s most important discovery was his description of the third bone of the ossicular chain, which he named “stapes.” This was the first description of this bone and was crucial in understanding the hearing organ.(Dispenza, F., Cappello, F., Kulamarva, G., & De Stefano, A. (2013). The discovery of stapes. Acta otorhinolaryngologica Italica: organo ufficialedella Societa italiana di otorinolaringologia e chirurgia cervico-facciale, 33(5), 357–359.)
Structure of the smallest bone in a human body
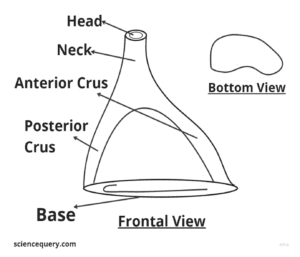
The stirrup-shaped bone in mammals consists of four components: head, neck, and two limbs or processes – the anterior and the posterior crus.
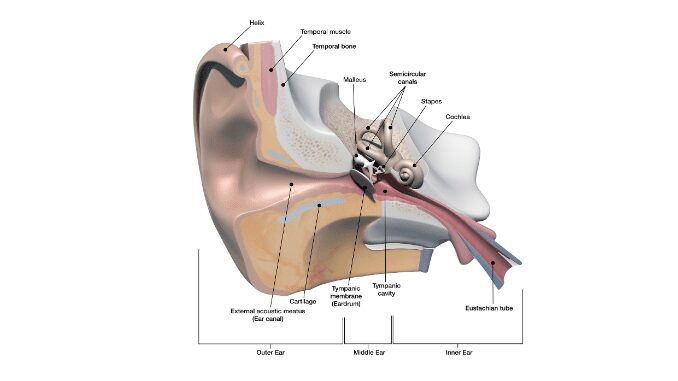
The Middle Ear and Position of Stapes
- The middle ear, situated in the temporal bone, is an airspace that opens to the exterior via the nasopharynx and the eustachian (auditory) tube.
- Tube is usually closed, but during swallowing, chewing, and yawning it opens, keeping the air pressure on the two sides of the eardrum equalized.
- Middle ear comprises three bones, namely the malleus, incus, and stapes.
- The manubrium of the malleus, which is the handle, attaches to the back of the tympanic membrane.
- Its head attaches to the wall of the middle ear, while its short process connects to the incus, which in turn links to the head of the stapes.
- The footplate of the stapes connects to the walls of the oval window through an annular ligament.
- It also contains two small skeletal muscles, the tensor tympani, and stapedius, which serve to reduce the vibrations of the tympanic membrane and pull the footplate of the stapes out of the oval window, respectively, upon contraction (1).
Conduction of Sound and Function of Stapes
- As a sound wave enters the external acoustic meatus, it contacts the tympanic membrane, causing it to move medially.
- The handle of the malleus is connected to the membrane, and so it also moves medially, thereby moving the head of the malleus laterally.
- Due to the articulation of the heads of the malleus and incus, the head of the incus moves laterally, which in turn moves the long process of the incus medially.
- As the stapes articulate with the long process of the incus, it also moves medially.
- The oval window is attached to the base of the stapes, and its medial movement completes the transmission of a large-amplitude, low-force airborne wave that causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate into a small-amplitude, high-force vibration of the oval window.
- This vibration generates a wave in the fluid-filled Scala vestibuli of the cochlea (2).
Q&A
-
Which is the smallest bone in the human body?
Stapes is the smallest bone in the human body found in the middle ear, it is part of ossicles (Incus, Malleus, Stapes).
-
Which is the shortest bone in the human body?
The shortest bone in the human body is stapes.
-
What is the smallest bone in the human body called?
The smallest bone in the human body is called Stapes. It is also known as the stirrup bone due to its shape resembling a stirrup used in horse riding.
-
How long is the smallest bone in the human body?
The stapes is typically around 3 to 4 millimetres in length in adults
Summary
- Stapes is one of the three small bones in the middle ear of mammals. It is located between the incus and the oval window of the cochlea. It is also known as the stirrup bone due to its shape resembling a stirrup used in horse riding.
- Stapes is the smallest and lightest bone in the human body, measuring around 3 to 4 millimeters in length. The stapes bone consists of a head, neck, and two limbs or processes – the anterior and the posterior crus.
- The primary function of stapes bone is to transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. Through the oval window of the cochlea.
- When sound waves enter the ear canal, they cause the eardrum to vibrate. Which in turn causes the three small bones in the middle ear, including the stapes, to move.
- As the stapes move, it creates pressure waves that are transmitted through the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, stimulating the hair cells lining the inner ear.
- These hair cells convert the pressure waves into electrical signals. Which are then transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve, where they are interpreted as sound.
