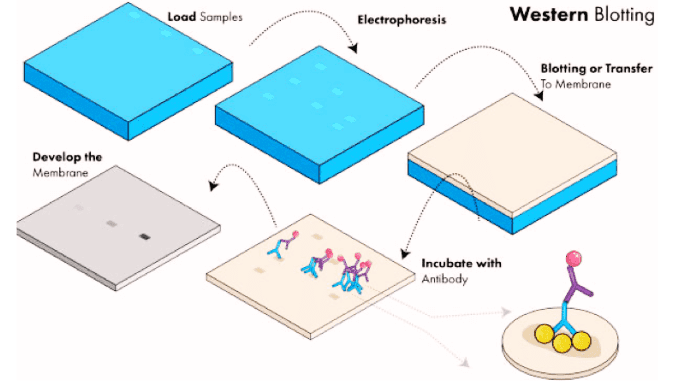
Know in one minute about Western blotting
|
Introduction
Western blotting is a technique used in molecular biology to amplify and detect proteins by using certain antibodies. This is a method to target low-abundance proteins and is based on pattern transfer membranes. The Scientist named WN Burnette the father of Western Blotting. Immunogenetics also involves the use of western blot to differentiate and is useful in quantifying the protein structures.
Applications
1. Diagnosis Of Diseases
Western Blots are used for the diagnosis of certain diseases by using ELISA and Immunosorbent Assay. It is also used to detect the presence of HIV type 1 infection in patients. Considered a super tool to detect direct protein confirmation.
2. Testimony to Lyme Infection
The western blotting technique is used to detect Lyme infection. It confirms the presence of Borrelia mayonii which is transferred to humans via black-legged ticks. Visible symptoms include skin rash, headache, and fatigue. WB IgM has proved an accuracy of around 96% in the case of early Lyme symptomatic patients.
3. Specific Protein identification
One of the most important uses of immunoblotting is to detect specific proteins amid hundreds of protein samples. It uses the SDS page methodology to separate batches of proteins in a given sample.
This process involves three major steps
- The protein samples are separated according to their size.
- Samples are then transferred to a solid support (e.g. nitrocellulose) to facilitate its detection by the use of antibodies.
- The target proteins are marked by the primary and secondary antibodies for clear vision.
4. Detection Of Contaminant Protein
It becomes easier to detect the defective protein and analyze recombinant protein expression. Western Blot technique is an efficient tool to measure the level of transferrins in blood.
Principal steps in Western blotting
1. Separation of proteins by electrophoresis
Protein bands are separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. A Commonly used form of gel electrophoresis is the ‘SDS (need full form) Page’. In this, the proteins are separated based on the size of the proteins. Electric current is applied which helps in the movement of proteins from one pole to another. The lightweight proteins move faster than the heavy-weight protein. Hence by this technique, the separation of protein is done.
2. Transfer of proteins onto a membrane
The protein bands after the electrophoresis method are transferred onto a nitrocellulose or a nylon membrane. This method or process of transferring the bands is known as blotting. The transferred protein in the membrane is now the replica of the original one. Electrophoretic blotting, both of proteins and nucleic acids, is much faster and more efficient than capillary blotting.
3. Blocking
This step is used to minimize the non-specific binding of the antibodies.
Blocking is an essential phase in the detection of specific proteins. Because it helps in preventing the binding of nonspecific antibodies to the membranes. After blocking the antibodies with specific solutions such as BUF029, the specific blot is washed with buffers. Generally, Tbst is used to elute and reduce the nonspecific binding of antibodies in the membranes.
4. Antibody Incubation
The blot is diluted and kept overnight for incubation at a temperature of 4°C. The blocking solution used depends upon the type of antibody binding to the membrane. A diluent namely BUF049A is used to reduce the cross immunity and binding to the nonspecific sites.
Visualization and analysis
Western Blotting is an important procedure to quantify proteins in a given sample. The specific protein bands are identified in a variety of ways.
- Antibodies are the most commonly used as probes (single strands) for detecting specific antigens.
- For example, Lectins work as probes for the identification of glycoproteins.
- It is a ‘sandwich reaction’.
- A species-specific secondary antibody or protein A of Staphylococcus aureus or streptavidin is used to bind to the antibodies bound to the protein bands.
- The second molecule may be labeled radioactive and can be employed as a general detector for various probes.
Reagents and equipment used in Western blotting
a) Gel Electrophoresis components
Functions of each component include:
- Buffers – Buffers are generally used to maintain the pH range of the proteins and provide necessary ions. Tris-acetate EDTA is a commonly used buffer.
- Wicks – Wick flow helps in the movement of buffers.
- Supporting Medium – It provides a matrix for the medium. Supporting mediums are necessary to separate, unlike molecules. Different types of mediums include:
Agarose gel – Agarose gel techniques are basically used in cases of DNA manipulation. The matrix provides resistance so that smaller molecules migrate more quickly than larger molecules.
Polyacrylamide gel – Formed by a combination of free radical polymerization of acrylamide and bis-acrylamide. It has a high affinity towards water and provides a clearer optical resolution.
Cellulose Acetate – A solid media generally used for separating lipoproteins at a higher resolution.
Whatman filter paper – They are used for general filtration of solids, liquids, and gas.
b) Transfer and membrane materials
-
Electrophoretic Transfer
Electric fields are used for the elution of proteins and membrane transfer. The gel is placed in between the membranes.
Transfer methods include
- Tank Transfer – The membranes are submerged along with the gels following the transfer buffers.
- Semi-dry transfer – A sandwiched mechanism takes place with a combination of flat-plate electrodes.
- Rapid Transfer – Specialized buffers are used to simplify the assemblage of proteins efficiently.
Antibodies and detection reagents
- Western Blot technique is purely dependent upon the sensitivity and specificity of the nature of the antibodies used. A primary antibody (that can bind to specific proteins or biomolecules) should be given preference over the secondary antibody to avoid cross-reactivity.
- Working with proteins requires the use of conjugated secondary antibodies. For instance, the use of fluorescence blot shows high sensitivity, when attached to a primary antibody. So secondary antibodies are a fit for western blot as it amplifies the desired protein of interest.
Detection and Labeling
Various procedures of immunoblotting detection include:
1. Colorimetric Blotting
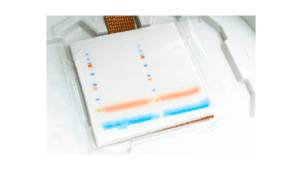
Colorimetric Blotting is an enzymatic detection method. In this, the conjugated antibodies bind with the reporter enzyme molecules and result in the conversion of chromogenic substrate into an insoluble colored product. Basically, this method shows the presence of color bands. It uses low sensitivity that ranges from 5-500 pg.
Colorimetric Blot
2. Fluorometric Blotting
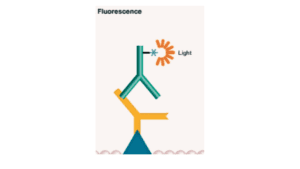
In this technique, the primary antibody is labeled with a fluorophore. It has a wide range of detection and is highly quantifiable. Here the signal is captured in the form of light. The photons of the molecules get excited and when they come to their original position or normal state they emit light of a wavelength of specific photons which are detected thus by this specific proteins are identified
3. Chemiluminescence
This deals with a smaller detection range with high sensitivity. It is an indirect detection method that emits light when reacts with the antibody that is conjugated to enzymes.
Applications
Western blotting is used to identify the following
1. Protein Detection
- The technique of western blotting is used for the detection of specific proteins from a mixture of complex proteins. – Detection of proteins is done by direct and indirect modes. X-ray films are a good example. The band intensity determines the amount of protein present.
- Protein-Protein Interaction – This interaction is direct contact with the protein to verify potential drug targets.
- Post-Translational Modifications – Post-translational changes occur when the proteins are modified by covalent bondings or interaction with amino acid chains. The ability to detect multiple proteins in a blot improves the quality of the data.
2. Discovery of Biomarkers
Biomarkers are generally called biological markers. A biomarker can be used as an indicator to clinically assess and intervene in a therapeutic condition. There are a variety of biomarkers used such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, heart rate, and measurement of glucose levels to keep a check on the health diagnosis.
Advantages of Western Blotting
- The bands are differentiated as per the molecular mass.
- The main principle is to work against a particular protein of interest.
- It helps in comparing the proteins of interest from multiple samples.
Limitations of Western Blotting
- Semi-quantitative test and time-consuming.
- The primary antibody is required to detect post-modification.
Other Protein Detection Techniques:
Techniques |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Mass Spectroscopy | High sensitivity along with developed automation. | Protein identification is less effective. |
| 2-D Page | Numerous peptides can be analyzed easily.
Identification of direct product analysis. |
Analysis of low and high Mr proteins is extremely difficult.
Productivity is low. |
| Western Blot | Molecular weight estimation is monitored.
High specificity towards the desired protein of interest. |
Sensitivity is low.
Time-consuming. |
| SELDI-MS | Sample volume is required at a minimum and ready to use. | It can be carried out for selected proteins only.
The resolution is low. |
| ELISA | High specificity and easily quantified. | Sensitivity is low. |
