Introduction
Tertiary structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of all the atoms in a protein having different types of bonds. The disulfide bond is one of them, the secondary structure of the polypeptide chain is determined by the short-range structural relationship of amino acid residues. Whereas tertiary structure is conferred by long-range aspects of amino acid residues (3).
The tertiary structure is the most important structure of the polypeptide chain. This is what gives the protein its functional shape. The structure depends on the side chain of amino acids. Some side chains are hydrophilic types and some are hydrophobic. When these side chains of polypeptide structure come in contact with the internal aqueous part of the cell, the whole polypeptide chain begins to shrink (1).
The hydrophobic amino acids are located away from the water on the inside and the hydrophilic amino acids are located near the water on the outside. Once the polypeptide chain is folded, the side chains of different amino acids move closer to each other. As a result, some of them bind hydrogen bonds and some of them bind covalent bonds. Here we discussed function, some properties, and how this bond is formed (2).
Disulfide bond
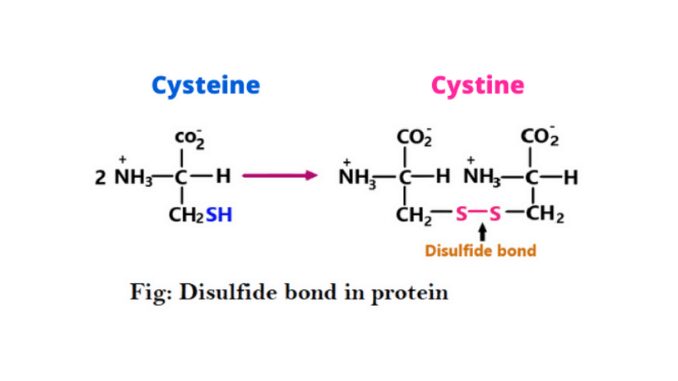
The –SH or sulfhydryl groups are present in the R group of cysteine amino acids. When two cysteine molecules are in close proximity, the sulfhydryl group present between them oxidizes and forms a bond called a disulfide bond a functional group. The structure of the disulfide bond is ‘R-S-S-R’. This bond is also known as a Disulfide Bridge S-S bond or cysteine bond (3) & (6).
It is a bond between two sulfur atoms formed by the linkage of two thiol or –SH groups. Many proteins, especially cysteine, have a –SH group in their side chain. It is easily dimerized to cystine in an aqueous solution and forms a disulfide bond (4).
The disulfide bond is also known as the disulfide bridge. Immunoglobulin molecules contain interchain and intrachain disulfide bridges. Interchain disulfide bridges or bonds are of two types, HH bonds, and HL bonds. HH bonds connect between two heavy chains and HL bonds connect a heavy chain. Interchain disulfide bridges or bonds have a role but are not essential. On the other hand, intrachain disulfide bridges or bonds play an essential role (8).
Bond type
A disulfide or S-S bond is a type of covalent bond that occurs between two sulfur atoms. The sulfur atoms are formed by the linkage of two thiol or –SH groups.
The covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where atoms are bound to each other by electron sharing. It is made up of two separate and neighboring sulfur atoms by sharing the electrons into two thiol groups by a single covalent bond.
When the –SH or sulfhydryl groups of two cysteine residues are both oxidized, then this covalent bond is formed. The enzyme ribonuclease consists of a single polypeptide chain of 124 residues and contains four disulfide bridges (1) & (6).
Determination of disulfide bond
If a protein molecule contains this bond, it can be broken before amino acid sequence analysis is started. This bond can be broken either by oxidation or reduction. The oxidation is generally carried out with performic acid when there occurs the cleavage of disulfide or S-S bonds present in proteins to produce chains containing cysteic acid residues which are stable and assist the separation of the oxidation mixture by ion-exchange methods (1).
Location
In eukaryotic cells, this bond mainly occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum. Besides the endoplasmic reticulum, disulfide or S-S bond is also found in the extracellular part. The bond occurs in the periplasmic space in prokaryotic cells (2).
Properties of disulfide bond
A disulfide bond is formed between two cysteine residues. It is the most important covalent bond in protein structure. This bond is mainly found in tertiary structures. They maintain the tertiary structure of the protein. There are some properties of these bonds.
1. It is the strongest type of bond in protein.
2. The disulfide bridge is oxidized by performic acid, which is therefore used to denature proteins or to separate polypeptide chains held together by S-S bonds.
3. They are covalent links that give some rigidity to the protein molecule.
4. It is relatively more stable than the other types of bonds.
5. A disulfide bridge is formed between two cysteine residues.
6. This bond is also found in the quaternary structure of the protein.
7. The bond can be broken either by oxidation or reduction.
8. This bond length is 2.2 Å and the bond energy is 60 kcal/mol.
9. All four polypeptide chains are connected to each other by disulfide bonds.
10. Disulfide formation does not utilize oxygen directly.
11. These bonds are also found in cytoplasmic proteins under oxidative conditions.
12. The disulfide or S-S bond can be broken by the addition of reducing agents like β-mercaptoethanol (3) & (7).
Formation of disulfide bond
It is sulfur-to-sulfur bonds formed in a protein. This bond is formed when the sulfhydryl of thiol groups of two cysteine residues are oxidized. Cysteine is oxidized and forms cysteine. It is a sulfur-containing amino acid characterized by low polarity.
Cysteine plays an important role in the stabilization of protein structure. When a reaction occurs between the sulfhydryl side chains of two cysteine residues, an S⁻ anion from one sulfhydryl group attack the side chain of a second cysteine. And then a bond is formed known as disulfide or S-S bond.
This bond is also formed between two polypeptide chains. The bonds can be reduced by some enzyme or reducing agent. 2-mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitol is this type of reducing agent. This bond is not affected by pH. That means any acidic conditions should not be enough to break this bond (4) & (2).
Functions of disulfide bond
There are various types of bonds in protein structure. A peptide bond is a primary bond between two peptide molecules. In addition to peptide bonds, there are a few other bonds present in protein structure. The disulfide bond is one of them. Peptide and disulfide are the two covalent bonds in a protein. Below are some functions of disulfide or cysteine bonds.
1. Disulfide bonds play a role in stabilizing the tertiary structure of proteins.
2. These bonds are essential for conferring the particular structure of the immunoglobulin.
3. It also stabilized the quaternary structure of the protein, because this bond is also found in the quaternary structure of the protein.
4. It gives some rigidity to the protein molecule.
5. This bond is also found in the quaternary structure of proteins, so it plays an essential role in stabilizing the quaternary structure of proteins.
6. It also composes the folding of a single protein chain.
7. This bond acts as the linkage of two segments of the protein chain.
8. The effective local concentration of protein residues is increased by this bond.
9. It also increases the effective local concentration of water molecules.
10. The nucleus of a hydrophobic core of folded protein is formed by a disulfide bridge (1) & (2).
Q&A
1. What is a disulfide bond?
The peptide is the primary covalent bond in protein structure. In addition to peptide bonds, there are some secondary bonds present in protein structure. The disulfide bond is one of them, this bond is a covalent bond. When a reaction occurs between the sulfhydryl side chains of two cysteine residues, the sulfhydryl group is oxidized and forms a bond, called a disulfide bond. Cysteine is easily oxidized into cystine in an aqueous solution and forms this bond (3).
2. Which amino acid can form a disulfide bond?
Cysteine amino acids form a disulfide bond, it is a double amino acid. This amino acid is formed by linking two cysteine molecules by a disulfide linkage (S-S bond).
3. A disulfide bridge is an example of which type of bond?
A disulfide is a covalent bond. This bond is formed when a cysteine in a sulfur atom forms a bond with the second cysteine of another sulfur atom. Each cysteine loses one hydrogen atom during disulfide bond formation.
4. How to break a disulfide bond?
The disulfide bond can be broken by the addition of reducing agents like β-mercaptoethanol (BME).
5. What type of bond is a disulfide bond?
A disulfide bond is a covalent bond. This covalent bond is formed between two cysteine residues.
References
2. Ajoy Paul. Zoology Honours, Volume- 1, Books & Allied (P) Ltd. Chapter: Proteins. Page no- 788.
