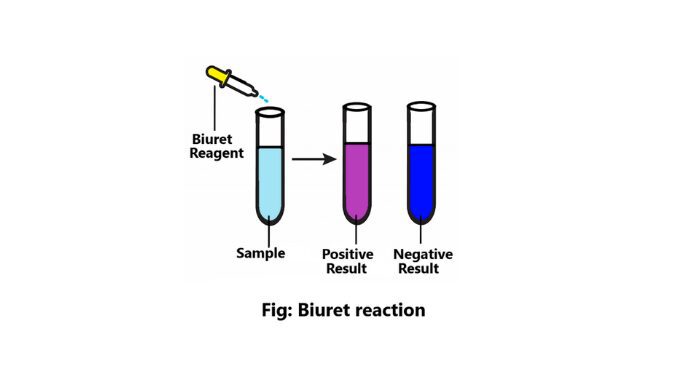
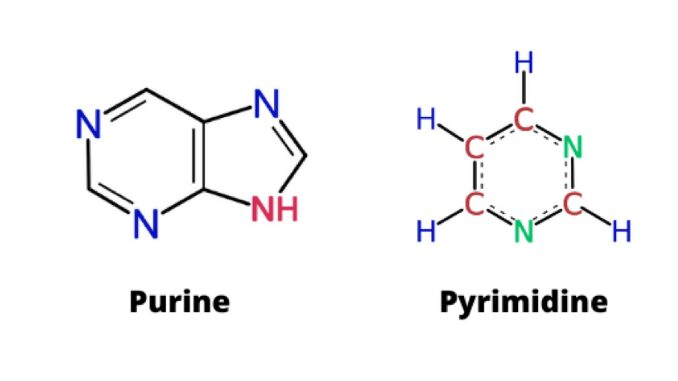
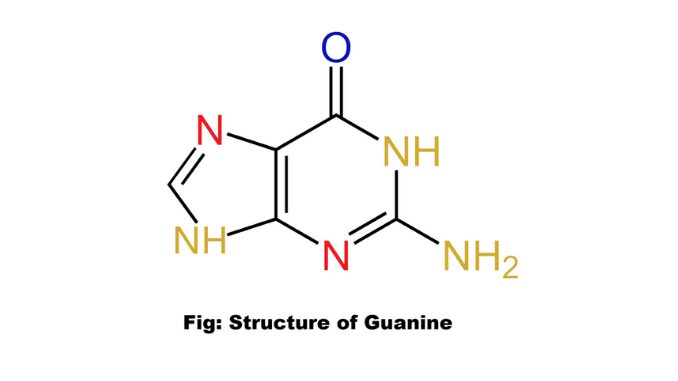
What is biuret reaction?
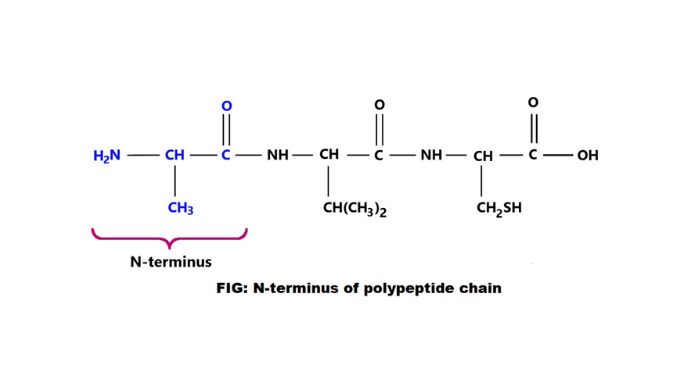
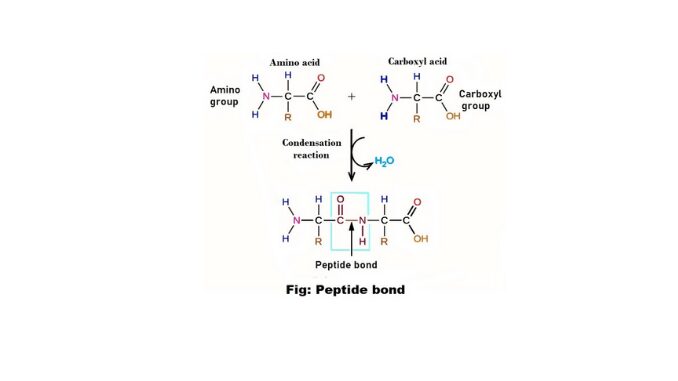
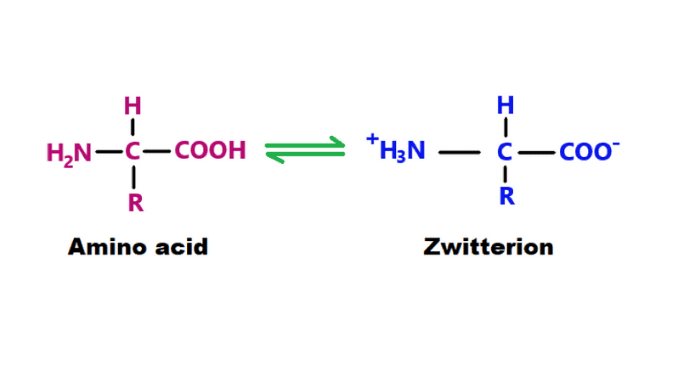
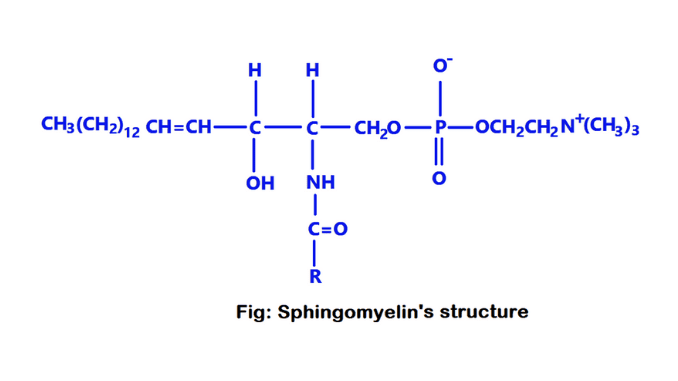
Introduction The biuret reaction is a chemical test for proteins and polypeptides. This test is used for all compounds containing two or more peptide bonds. There are various types of biochemical compounds in nature. Biuret is one such biochemical compound. It is a chemical substance that is used for the identification of proteins and peptides. […]
What is biuret reaction? Read More »