Know in one minute about the Bunsen burner
|
Introduction
The Bunsen burner is an essential instrument found in laboratories, widely used for its ability to generate high temperatures. Named after German scientist Robert Wilhelm Bunsen, this heating device plays a crucial role in various scientific experiments and procedures. Its design consists of an iron tube with a gas supply at the base and a control ring attached to regulate air entry.
The primary function of a Bunsen burner is to provide a controlled flame for heating, sterilization, and burning purposes. It achieves this by combining a flammable gas, such as natural gas or propane, with air. The gas supply at the bottom of the tube allows the controlled release of gas, while the control ring adjusts the air intake, influencing the flame’s characteristics.
The Bunsen burner’s flame can be manipulated to suit specific requirements. By adjusting the air entry, the flame can be made to produce a hot blue flame or a cooler yellow flame. The blue flame, known as the “non-luminous flame,” is commonly used for heating, as it provides a higher temperature and minimal soot production. The yellow flame, or “luminous flame,” is less hot and often used for less sensitive operations or visual effects.
The Bunsen burner’s versatility makes it indispensable in chemistry laboratories, where precise and controlled heating is crucial for chemical reactions and analysis. Additionally, it finds application in microbiology and biotechnology for flame sterilization of equipment and lab materials.
In conclusion, the Bunsen burner serves as a fundamental laboratory instrument, offering controlled high-temperature heating for a range of scientific processes. Its efficiency, low pollution, and adaptability make it an invaluable tool in chemistry, microbiology, and other scientific fields, where precise heating and sterilization are essential (1) & (2).
Definition
A Bunsen burner is a small instrument or a gas burner used in laboratories as a source of heat. It is mainly a laboratory instrument. This instrument is used to provide a single, continuous flame by mixing gas with air (1).
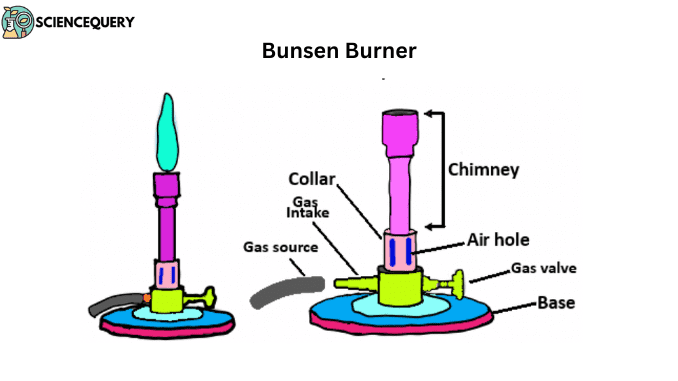
Parts and functions of Bunsen burner
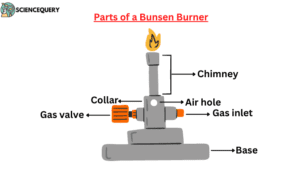
The Bunsen burner is a metal hollow sphere with air holes at the bottom. After mixing air with gas, it’s ignited. To prevent bursting, a grid is placed on it for heating with a test tube. Direct flame heating is avoided for flammable substances like ether, benzene, and alcohol, using a water bath. This widely used burner consists of six parts.
1. Base
This is the lower part of the burner. A side tube made of metal is attached here. With the help of this tube, the gas enters and rises up through the pores like a fine jet. Somewhere above this base, there is a stop cork. With the help of this stop cork, the entry of gas into the tube can be controlled. This helps keep the burner on the bench.
2. Chimney
It is a base-attached vertical metal tube about 5 inches long. At the bottom of this part, there is an air vent formed by holes in opposite positions. This part is also made of metal. It has one or more air inlet holes. There are screws on the bottom of the base and chimney. The chimney is connected to the base by twisting with these screws. In the air inlet, the gas coming from the side pipes of the base mixes with the air entering and rises up. When this gas is ignited, it ignites with a flame at the mouth of the tube.
3. Collar
This part joins the base and chimney. It is a small, cylindrical piece of metal with two holes. They are opposite to each other. It controls the amount of air entering the chimney. This part is a metal collar with one or more holes that surrounds the air passage. The air intake can be increased or decreased by turning the collar as needed (usually three parts air and one part gas are used). This gas and air mixture is pushed to the top of the tube by gas pressure where it is ignited. The collar is located at the base of the chimney. This part of the Bunsen burner can rotate clockwise or anticlockwise. It changes the burner’s flame color from yellow to blue.
4. Air holes
This part helps to allow oxygen to enter the chimney from the collar. This part of the Bunsen burner is next to the collar. The air holes allow air to enter the burner, creating a mixture of air and any liquid fuel with air.
5. Gas valve
This part is located next to the gas valve. The primary function of the gas valve is to control the flow of gas to the burner. It is mainly connected to the gas-receiving part. The gas supply in the burner can be controlled by rotating this part to the right or left.
6. Gas intake
This part of the Bunsen burner allows natural gas to enter the Bunsen burner. It connects the gas intake to the gas source with a rubber or plastic pipe (2).
Uses of Bunsen burner

- A Bunsen burner is required for the proper heating of chemicals used in chemistry.
- Bunsen burner is used for heating, sterilization, and burning and can safely burn gaseous fuels.
- These instruments are used in chemistry laboratories due to their high combustion efficiency and low pollution.
- It can also be widely used in microbiology or biotechnology for flame sterilization. In microbiology laboratories, it is used to sterilize needles, mouths of test tubes, etc.
- There is a convection current that can be produced by the heat of this burner flame. This convection current heats the top of the flame and removes airborne particles from the cold air below, keeping the work area sterile.
- One of the instruments used for the flammability of compounds and flash points of solvents is the Bunsen burner.
- The Bunsen burner helps to determine the melting point using classical calorimetry and the boiling point using the Thiele tube method.
- Bunsen burners are used in salt drying, moisture analysis, and detection of water crystallization, etc.
- It is used to clean and disinfect.
- It is also used to measure humidity (3).
Precautions
These instruments are flammable and burn at very high temperatures. If not handled carefully, an accident can occur. Some precautions should be considered in certain cases when operating a Bunsen burner.
- No dry wood or any flammable material shall be placed near the burner.
- When using this burner, we should always wear safety glasses and a lab coat.
- Do not keep long hair open. It should always be pulled back.
- Loose clothing or jewelry should be avoided when using this device in the laboratory.
- Shocks or tubes on feet should be replaced.
- Always look for cracks, holes, or other defects in the rubber tubing that could lead to a leak.
- Lighter with a flared nozzle is used instead of matches to light this burner.
- It should be allowed to cool completely after use.
- This burner should never be left alone even with the safety flame on.
- The gas should be turned off immediately after the test or experiment is over.
- It should be avoided to handle the equipment while it is ever hot.
- The only way to extinguish the Bunsen flame is to close the gas valve. Never attempt to extinguish a Bunsen flame by blowing on it.
- It should be allowed to cool completely after use (1).
Q&A
1. How to light Bunsen burner?
- Check the connections to the Bunsen burner and desk outlet valve.
- Close the needle valve and collar.
- Open desk outlet valve.
- Then open the needle valve ½ turn.
- Use the lighter to light the flame.
- Adjust the collar and needle valve until the blue flame is visible
2. Who invented the Bunsen burner?
Robert Bunsen.
3. How to use Bunsen burner safely?
- Use a Bunsen burner in a clean, uncluttered area.
- Always remember to wear closed-toe shoes in the lab.
- Consider wearing a lab coat to cover any loose clothing.
- Long hair should be tied back and jewelry should be removed.
- Before lighting the burner, know where to exit in an emergency, and locate the emergency gas switch and the fire alarm.
- The burner should be operated by its base.
- A lighted Bunsen burner should always be kept in sight.
4. What do Bunsen burners do?
Bunsen burner is a laboratory equipment. It is used to provide a single, continuous flame, used to heat substances, combust substances, and sterilize objects at high temperatures.
5. What does Bunsen burner do?
Bunsen burners are mainly used in a laboratory to provide a single, continuous flame.
Written By: Manisha Bharati
