Introduction
Our environment is made up of many living and non-living factors like animals, plants, soil, climate, and temperature. These factors are also known as biotic factors and abiotic factors of ecosystems. These physical and organic components that are biotic and abiotic factors of the environment interact with each other and form a balanced ecosystem.
Environmentalists use the term ecosystem to describe the interrelationship of these physical and organic factors. Any ecosystem is considered a unit of the entire environment of the earth. In other words, ecosystems are the main functional unit of ecology. An ecosystem is a natural unit consisting of organic, inorganic, and biological organisms, where different organisms form a way of life by interacting with each other and their organic and inorganic components (1).
Components or factors of an ecosystem
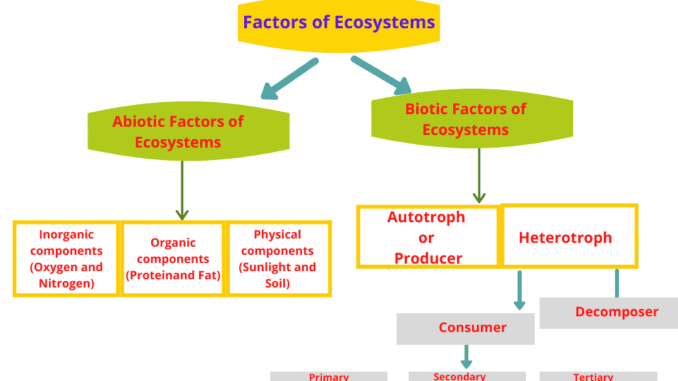
The ecological structure is basically a description of abiotic and biotic species, their life history, and their impact on the environment. The ecosystem is a collection of a variety of organic, inorganic, food-producing green plants, some animals that depend on plants for food, and some microorganisms that decompose dead bodies into the environment. The structure of the ecosystem depends on the living and non-living elements. Ecosystem components are mainly divided into two parts (1).
- Abiotic factors or component
- Biotic factors or component
Abiotic factors or component
The abiotic components are mainly composed of the nonliving part of the ecosystem. This is mainly divided into three parts.
1. Inorganic component
Nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, etc. are inorganic elements in the ecosystem. These inorganic elements play a very important role in the structure and life process of the organism. All of these elements balance the environment through biochemical processes (1) & (3).
2. Organic component
Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, etc. are the organic components of the ecosystem. All of these elements form the biochemical structure of the organism and relate to organic and inorganic elements (1) & (3).
3. Physical component
These are natural components or factors like sunlight, temperature, rainfall, humidity, soil, etc. are the physical components of the ecosystem. These elements have a significant impact on the environment. They play an important role in maintaining the way of life and survival of animals (1) & (3).
Biotic factors or component
All living component in the ecosystem forms the biotic factors or component. These components are divided into two parts.
1. Autotroph or producer
Chlorophyll in plants uses sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food through photosynthesis. There are also some bacteria that can make their own food through chemical synthesis. These are known as the producers of the ecosystem. They can make their own food via photosynthesis. Green plants, algae, and chemosynthetic germs come under autotrophs or producers. They are located at the lowest level of the trophic level and serve as the basis for the survival of higher animals (1)
2. Heterotroph
Another biotic factor or component of the ecosystems is the heterotrophs. These heterotrophs cannot able to produce their own food via photosynthesis and are dependent mainly on the autotrophs for their survival. In the ecosystem, heterotrophs are divided into two classes (1).
Consumer
These are the elements or organisms in the ecosystem that depend on others to make their own food. They depended on producers for food. Herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores are large consumers. They take in oxygen from the environment during respiration and provide carbon dioxide to the environment are located from the second level to the highest level of the trophic level. They are of three types (1) & (3).
-
Primary consumer
Consumers in the ecosystem who directly depend on green plants or producers for food are called primary consumers or herbivores. Cows, goats, grasshoppers, snails, oysters, etc. belong to this category.
-
Secondary consumer
Consumers who take primary consumers as food and get nutrients in their bodies are called secondary consumers or carnivores. Frogs, lizards, dogs, small fish, dogs, cats, foxes, snakes, etc. are the secondary consumers of the ecosystem.
-
Tertiary consumer
Eaters present in the ecosystem that survives by eating plants and other animals are called tertiary consumers. The tertiary consumer also eats the secondary consumer. Falcons, peacocks, tigers, lions, etc. are the tertiary consumers of the ecosystem.
Decomposer
All the elements whether it is microorganisms or microorganisms present in the ecosystem that decompose dead plants and consumers into simple chemicals are called decomposers. There are some decomposers who convert compounds into simple elements and return them to nature hence called a transformer. The role of decomposers in the ecosystem is very important. These are the highest consumers of the trophic level (1).
Role of decomposer in the ecosystem
These decomposers break down the complex chemical compounds in the protoplasm of plants and animals using some of them for their own needs. And releases the rest into the natural environment as inorganic salts. Producers or green plants use those salts for food production. Thus decomposers play an important role in ecosystems it helps in continuing the energy and components flow of the ecosystem (1) & (3).
How do the biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem interact?
The biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem are interdependent with each other. The combined effect of these two elements is called interrelationship in the language of science. This effect of biotic and abiotic components in this ecosystem has been termed by environmentalists as interaction. This interaction of ecosystems facilitates the transfer of energy at the trophic level.
For example, plants compromise the biotic components of the ecosystem. The plants are autotrophs in nature they do photosynthesis and synthesize their own food by taking the water and minerals from the soil. The leaves of the plant absorb the sunlight and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. therefore plants depend upon the abiotic factors of the ecosystem to make their food. Therefore, green plants (biotic components) are affected by water and carbon dioxide (biotic components) through photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, the green plant produces complex compounds from simple compounds. Thus a biotic element is related to other abiotic components in the ecosystem (1) & (2).
Difference between biotic and abiotic components
There are both similarities and differences between biotic and abiotic components. These are as follows
Similarities
Biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem are very closely related. So there must be some similarities between them. Every component of an ecosystem depends on each other. The biotic component of an ecosystem is a living component that affects humans and the environment. Abiotic components affect the environment in this way even though they are not alive. These biotic and abiotic components combine to form a large ecosystem. The biotic components of an ecosystem are directly dependent on abiotic components of the ecosystem for survival. When one of the two elements of the ecosystem is destroyed, the whole ecosystem is disrupted (1) & (3).
Difference between biotic and abiotic components
Properties |
Biotic component |
Abiotic component |
1. Definition |
Biotic components are the living components of the ecosystem | Abiotic components are the non-living components of the ecosystem. |
2. Independence |
These components are dependent on abiotic components. | These components are independent. |
3. Factors |
Parasites, consumers, prey, predators, etc. are the biotic factors of an ecosystem. | Sunlight, rainfall, oxygen, nitrogen, carbohydrates, protein, etc. are the abiotic factors. |
4. Adapt ability |
Adapt to ability changes in the environment. | It doesn’t change in the environment. |
5. Impact |
These components affect the community, biosphere, and biome. | These components affect the community, population, and biosphere. |
6. Physical component |
The biotic component is not a physical component. | This component is a physical component. |
7. Chemical component |
These components are not chemical components. | The abiotic components may be chemical components. |
8. Example |
Producer, consumer, decomposer, omnivorous, etc. | Sunlight, humidity, rainfall, water, soil, temperature, air, etc. (2). |
