
Autotrophic Nutrition
The process by which plants collect essential components from the environment and synthesize food for themselves is known as autotrophic nutrition. It is the method where the energy is extracted by autotrophs in the presence or absence of light. Autotrophs like plants, algae, and bacteria use the process of Photosynthesis to get energy. Autotrophs like giant tube worms use chemicals in place of sunlight to get energy and the process is known as Chemosynthesis.
Nutrition is the basic essential part of any living organism. This helps the body to grow and develop via further functions like digestion, absorption, assimilation, and excretion (in animals) or synthesis and assimilation (in plants). Plants make their own food and animals depend on others for food. Nutrition is not just about supplying energy to the body. The scope of nutrition is huge. Nutrition is divided into two parts. These are plant nutrition and animal nutrition. Autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition are part of plant nutrition (1).
Some examples of Autrotophic nutrition
Trees, algae, moss, fern, etc. synthesize their foods or derive energy for development through autotrophic nutrition methods. Protozoa like euglena, chrysamoeba can also derive their energy and food through autotrophic nutrition as they contain chlorophyll in their bodies.
Process of autotrophic nutrition
Autotrophic nutrition occurs in two processes.
- Synthesis (food production by photosynthesis)
- Assimilation (food comprising protoplasm).
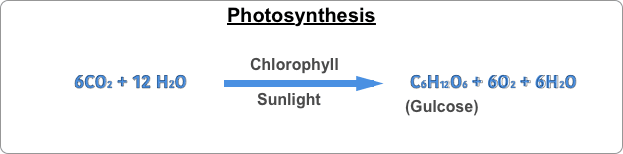
What is Photosynthesis ( using sunlight to extract energy)?
The Photosynthesis process involves converting atmospheric carbon and water to carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll and as an outcome of this process oxygen, glucose, and water are released by the plants. Excess carbohydrates produced during this process are stored as starch and it serves as an energy reserve when needed by Plants or bacteria.
Plants collect carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) from the environment and bring it to the leaf mesophyll tissue. In the presence of sunlight and the activation of chlorophyll, the chemical reaction of water and carbon dioxide produces glucose. Solar energy is bound to the generated glucose as potential energy. Water and oxygen are produced during glucose production. Oxygen is released into the environment and water participates in metabolism. The process of making food for plants in the presence of sunlight is called photosynthesis. The presence of fauna on Earth depends on photosynthesis.
Steps involved in photosynthesis
i) Chlorophyll absorbs the sunlight
ii) Light energy converts water into Oxygen and Hydrogen molecules and releases chemical energy
iii) Chemical energy converts carbon into carbohydrates
Process of photosynthesis
- The process of photosynthesis mainly occurs in the green leaves of the plant.
- But in addition to the leaves, different parts of the plant participate in the process of photosynthesis. These are stomata, roots, and stems.
- The mesophyll tissue of the leaf is the main site of photosynthesis. The leaves can absorb more sunlight because they are flattened and stretched.
- Mesophyll tissue cells have the highest number of chloroplasts and the highest amount of stomata. So more CO₂, which is needed for photosynthesis, can be collected and entered by the leaves by the stomata.
- The water necessary for food production is obtained from the soil. Water is absorbed by roots and reaches the leaves through the stems.
- The chlorophyll in the leaves absorbs large amounts of sunlight and prepares food (glucose) through the chemical reaction of CO₂ and H₂O. Later the food made from these leaves reaches different parts of the plants.
- Extra food is stored in the leaves as starch. Potential energy is stored in food produced by photosynthesis. Food produced in the process of photosynthesis helps in the growth and development of plants and provides nutrients (1) & (2).
Essential elements for photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), sunlight, and chlorophyll are the essential raw materials for photosynthesis (1) & (2).
Importance of photosynthesis
- The presence of fauna on earth depends on photosynthesis.
- Green plants produce carbohydrates in their bodies in the process of photosynthesis. The plant takes these carbohydrates as food. Animals and all other organisms eat this food directly or indirectly and survive.
- The photosynthesis process maintains the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- In this process, solar energy is bound and converted into potential energy (1) & (2).
Assimilation
The process by which plants absorb food into their cellular protoplasm is called assimilation. At this stage, the plant incorporates the synthesized food into the protoplasm. This causes the plant to gain weight (1).
Autotrophic nutrition in mitochondria

The mitochondria are the gray matter scattered in the center of the cell’s cytoplasm. This organelle produces the energy needed to perform all the biological functions of the cell. Mitochondria are rod or oval-shaped with two single coatings. These are outer and inner membranes. It is found in eukaryotic organisms. The mitochondria are called the powerhouse of the cell because it helps the cellular respiration of the organism.
The Krebs cycle of aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria and produces powerful compounds ATP. Mitochondria can make their own proteins. Because it has ribosomes, DNA, and enzymes. The ribosomes have the ability to produce proteins by their own genetic formula. Mitochondria are capable of synthesizing some structural proteins required for their function. So mitochondria are called semi-autonomous (3).
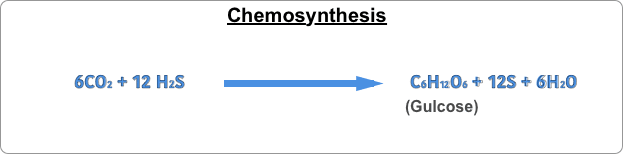
What is Chemosynthesis ( using chemicals to extract energy)?
The chemosynthesis process involves converting carbon-containing molecules like carbon dioxide or Methane to carbohydrates using chemicals like Hydrogen Sulfide or Hydrogen. Many organisms in the deep ocean where sunlight can’t reach use this process to get nutrition and survive. In nature, it’s very rare to find chemosynthesis in the presence of hydrogen, and largely chemosynthesis is done in the presence of Hydrogen sulfide.
Giant tube worms use bacteria in their trophosome to fix carbon dioxide and produce Glucose (carbohydrates) and sulfur as a result. Given this reaction can only occur in the presence of hydrogen sulfide all the giant tube worms are found around volcanic hydrothermal vents in the oceans.

Heterotrophic nutrition
The process by which organisms absorb nutrients from the body of another host or from dead organisms without synthesizing food in their own bodies is called heterotrophic nutrition. Organisms that are nourished in this way are called heterotrophs. All heterotrophs depend on autotrophs for their food (1). Examples are all animals that have heterotrophic nutrition. Most bacteria and fungi also have heterotrophic nutrition.
Types of heterotrophic nutrition
Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types.
- Saprotrophic or saprophytic nutrition
- Parasitic nutrition
- Holozoic nutrition
Saprophytic nutrition
The nutrient system in which plants absorb nutrients from decomposed plant or animal carcasses or other organic matter is called saprophytic nutrition. Plants that get nutrients in this way are called saprophytes.
Examples are Yeast, penicillium, Agaricus, etc. All these plants are nourished in saprophytic nutrition (1).
Parasitic nutrition
The process by which a plant absorbs nutrients from the body of another living host is called parasitic nutrition. Plants that get nutrients in this way are called parasites. Parasites are two types.
1. Full parasites
Organisms that are completely dependent on the host for nutrition are called full parasites. Like rafflesia, balanophora, etc. are full parasitic plants.
2. Partial parasites
Organisms that are partially dependent on the host for nutrition are called partial parasites. Such as viscum, striga asiatica, santalum, etc. are partial parasites (1) & (2).
Holozoic nutrition
A special type of heterotrophic nutrition is holozoic nutrition. This type of nutrition occurs in animals. The heterotrophic nutrient system in which animals consume any solid or liquid food and complete nutrition through certain stages is called holozoic nutrition.
Examples are humans, caws, dogs, amoeba, and protozoa, etc. are nourished by holozoic nutrition (1).
4 different types of heterotrophic plants
Saprophytes, parasites, symbionts, and insectivorous plants
Saprophytes
Yeast, penicillium, Agaricus, etc. are the saprophytes plants. Because it does not have chlorophyll and gets nutrients from decomposed plants or animal carcasses or other organic matter (1) & (2).
Parasites
Rafflesia, viscum, striga asiatica, santalum, etc. are the parasites plants. They get food from the body of another living host. Parasite plants are of two types. These are full parasite plants and partial parasite plants (2).
Symbionts
The nutrients for which one organism lives in the company of another organism and benefits each other are called symbionts. Symbionts are of two types- mutualism and commensalism. In mutualism, two organisms coexist and complete nutrition with the help of each other. Lichen is an example of mutualism. In commensalism, two organisms also nourish each other separately from coexistence. Gajpippali is an example of commensalism.
Insectivorous
Plants that absorb nutrients from the insect’s body by absorbing nitrogen-containing protein for food are called insectivorous. Sundews, butterworts, venus flytraps, etc. are examples of insectivorous plants.
Difference between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition
Based on the above information some of the key differences between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition (1) & (2).
Properties |
Autotrophic nutrition |
Heterotrophic nutrition |
|
1. Dependence |
Autotrophic nutrition plants can prepare their own food. |
Heterotrophic nutrition plants are unable to produce their own food. The depends on autotrophs for food |
|
2. Presence of chlorophyll |
They usually have chlorophyll in their body. |
They have no chlorophyll in their body. |
|
3. Photosynthesis |
The photosynthesis process occurs. |
The photosynthesis process does not occur. |
|
4. Presence of sunlight |
In this nutrient system photosynthesis occurs in the presence of sunlight with the help of chlorophyll. |
In this nutrient system, photosynthesis does not occur because they have no chlorophyll. So this nutrition process does not depend on sunlight. |
|
5. Collections of food ingredients |
They collect simple inorganic substances in liquid and gaseous states from the environment for nutrition. |
They can also take solid and complex foods for nutrition. |
|
6. Stage of nutrition |
Photosynthesis and assimilation |
Mainly food intake, digestion, assimilation, and exclusion. |
Similarities between autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition
Autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition- both types of nutrition systems’ purpose is to grow, develop, and nourish the body through food (1).
