Know in one minute about the inverted pyramid of biomass
|
Introduction
An ecological pyramid is an important part of an ecosystem. There are three types of ecological pyramids. These are the pyramid of biomass, the pyramid of energy, and the pyramid of numbers. These are an upright pyramid and an inverted pyramid. Below we discussed what the Inverted pyramid of biomass is (1).
Before discussing the inverted pyramid, let’s see what the biomass pyramid is. A biomass pyramid is mainly formed by arranging the biomass of organisms in the ecosystem. This type of ecological pyramid has producers at the bottom and tertiary consumers at the top. So the base of the pyramid of biomass is wide and the top is progressively narrower (1) & (5).
For example in a grassland ecosystem, the biomass of producers (grass) is highest. Then the biomass gradually decreases from the primary consumer (deer) to the secondary consumer (jackal) and from the secondary consumer to the tertiary consumer (tiger).
But some ecosystems do not form a pyramid of biomass like this. The exception is aquatic ecosystems. In this case, the biomass of organisms present in this ecosystem decreases from secondary consumers to producers. As a result, the pyramid appears inverted hence called the inverted pyramid of biomass (3).
Definition
Biomass at a trophic level usually decreases progressively from producers to consumers. But in some cases, this biomass is reduced from consumer to producer. As a result, the pyramid that is formed is inverted in shape. Hence it is called an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Description
- The dry weight of organisms in a trophic level of an ecosystem or a specific habitat is known as biomass.
- The pyramid that is formed by arranging these dry weights of organisms at each level of the food chain is called the pyramid of biomass.
- But in some food chains, these biomass are arranged in reverse. In this case, the pyramid is inverted in shape.
- It has been found that 15 to 25% of biomass from one trophic level in a food chain is transferred to the next trophic level. Because of this primary consumers have less amount of biomass than producers and secondary consumers have less biomass than primary consumers.
- But the biomass is reversed in the aquatic ecosystem. In a trophic level of an aquatic ecosystem primary consumers have the highest amount of biomass than producers and secondary consumers have the highest biomass of primary consumers. So in this way, an inverted pyramid of biomass is formed (2) & (4).
Examples
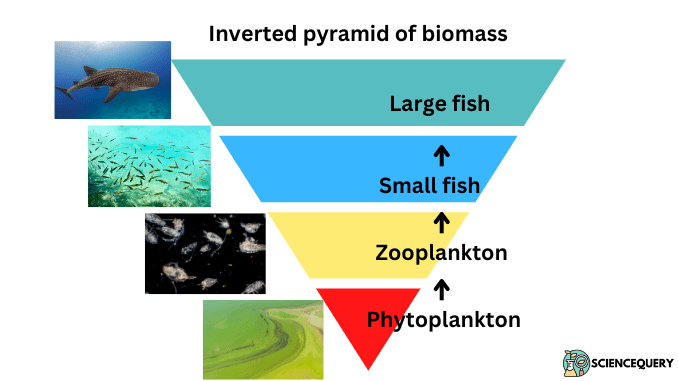
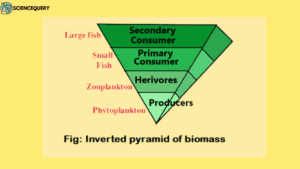
In aquatic ecosystems, the pyramid of biomass is inverted. The biomass of zooplankton (herbivores) is higher than that of phytoplankton (producers), small fish (primary consumers) have higher biomass than zooplankton. And large fishes (secondary consumers) have higher biomass than small fish (1).
Diagram and flow charts
Flow chart
Phytoplankton→ Zooplankton→ Small fish→ large fish
Q&A
1. What does a pyramid of biomass represent?
A pyramid of biomass represents the total living biomass or organic matter that it present at each trophic level of the food chain in an ecosystem.
2. How does a biomass pyramid work?
It shows the total amount of living biomass available at each trophic level/ the area at the bottom to the producer level. In this way, it works.
3. Why would a biomass pyramid be inverted?
The inverted pyramid of biomass is found in many aquatic ecosystems. So it is inverted because the biomass of fish exceeds that of phytoplankton.
4. Short note on the pyramid of biomass?
A pyramid of biomass is a pyramid formed by adding the biomass of organisms present in a food chain of an ecosystem. There are two types of biomass pyramids, upright and inverted. Forest ecosystem biomass pyramids are upright and aquatic ecosystem biomass pyramids are inverted. It indicates the total mass of each nutrient level in a particular food chain in an ecosystem.
5. Why are biomass pyramids inverted?
The biomass of phytoplankton is lower than that of small herbivorous fish. And the biomass of large carnivorous fish is still high. So the biomass pyramids are inverted.
