Introduction
Soil pH tells us whether the soil is acidic, neutral, or alkaline depending upon the hydrogen ions present in it and this is done by soil pH test. It is an important parameter that influences different soil factors, affecting plant growth. The soil pH test helps us to determine the pH acidity or alkaline level of the soil.
Soil health and significance of soil testing
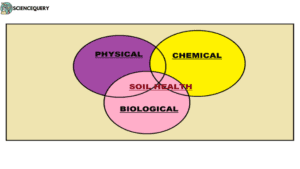
Soil health refers to a balanced condition of soil physical, chemical, and biological processes conducive to high productivity and environmental quality. The health of the soil is very important as it is a vital natural resource for sustainable agricultural production (1).
Owing to rapid industrialization, increasing population, and widespread use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, the quality of soil can deteriorate. And therefore soil must be tested for its quality and fertility.
A soil test is crucial because it will help in the optimization of crop production, diagnosing the nutrient deficiencies in the soil, and consequently working towards improving the lacking nutrients.
Soil testing informs the farmers of the imbalances in the soil and guides them in adopting specific fertilizers or soil conditioners to deal with the diagnosed issues. These tests can equip farmers to take preventive and corrective measures even before sowing the crops, and that results in an uncompromised final yield.
What is Soil pH?
Soil pH is a measure of soil acidity or alkalinity. It is an important indicator of soil health. It affects crop yield, crop sustainability, plant nutrient availability, and soil micro-organism activity which influence key soil processes (7).
Can be balanced by applying the proper amount of nitrogen fertilizer, liming, and cropping practices that improve soil organic matter and overall soil health (2).
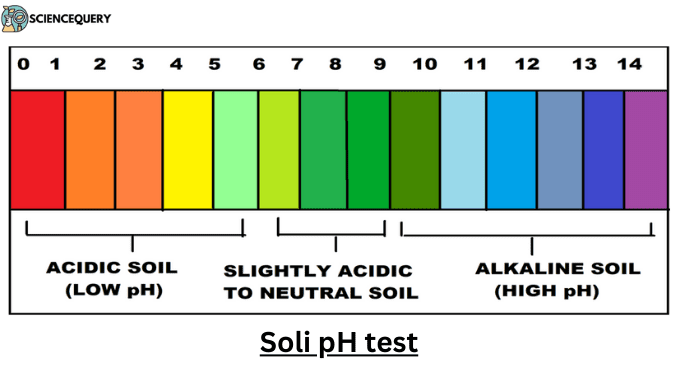
pH Scale
- Soil pH is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+).
- It is a measure of the soil solutions of acidity and alkalinity, on a scale from 0 to 14.
- Acidic solutions have a pH less than 7, while basic or alkaline solutions have a pH greater than 7.
- By definition, pH is measured on a negative scale of hydrogen ion concentration.
- Therefore, as hydrogen ion concentration and acidity go up, the pH value goes down.
- Also, because pH is a function, each unit on the pH scale is 10 times more acidic than the unit above it.
Importance of soil pH
- Soil reaction is of great importance as it influences crop growth both directly and indirectly.
- Most plants do well in neutral soils. Many of them fail to grow properly if the reaction becomes acidic or alkaline.
- The reaction of soil also exerts an important influence on soil structure.
- Soil pH also influences the activity of microorganisms which in turn influence plant growth and crop production.
- Most microorganisms are very active in neutral or slightly alkaline soils.
- Soil pH influences the need for fertilizers. The availability of phosphorus is much less in acid soils, thus a higher application of the fertilizer is needed.
- Soil pH affects the quality of crops also. The quality of tobacco grown in more acid conditions is greatly impaired.
- It influences plant diseases, especially those that are soil-borne.
- Soil pH plays a very important role in governing the relationship between soil condition and crop production.
When and how to do a soil pH test?
Testing the pH value of soil basically depends on the following factors
- While trying a new variety of crop production.
- Shifting the base of agriculture to a new area, soil pH information is needed.
- Growing new plants with specific pH needs.
- A sudden discovery of unproductivity in certain plants.
- A new type of plant disease has been discovered, which makes the testing of soil pH mandatory.
Techniques for measuring the soil pH
1. Electrometric
It is based on measuring the electrical conductivity of the medium, which depends on the soil moisture.
2. Colorimetric
It means to measure color. The colorimetric pH determination method is based on the property of acid-base indicator dyes, which produce color depending on the pH of the sample.
Electrometric method for soil pH testing
1. The glass electrode method
This method is the most suitable for measuring the pH of soils. It measures the potential between the glass electrode membrane and the solution which is closely related to its pH.
2. Quinhydrone method
This method is useful for soils that have a pH of less than 8.5 only.
3. The hydrogen electrode method
Measures the EMF (electromotive force) of the equilibrium of hydrogen.
Method of testing the soil pH
There are various ways to test the pH of the soil, few of them are described briefly-
1: Testing soil pH with a commercial test probe
- Digging a small hole in the soil: Use a trowel or spade for digging a hole 2-5 inches deep. Then breaking up the soil within the hole and removing any foreign objects.
- Filling the hole with water: Use distilled water and fill the hole until a muddy pool is formed at the bottom.
- Inserting test probe into the mud: the test probe must be clean for more exact results. Wiping the probe with a tissue or clean cloth, and inserting it into the mud.
- Holding the test probe there for 60 seconds and taking a reading: pH is usually measured on a scale of 1-14 though the tester may or may not include the entire range. A pH of 7 indicates neutral soil, a pH of above 7 indicates alkaline soil and a pH below 7 indicates acidic soil.
- Taking several measurements in different spots: a single reading may be inaccurate, hence taking the measurements at different areas will give an appropriate reading.
2: Using paper test strips
- Using pH paper test strips: Test strips also known as litmus paper, are a quick and easy way to measure the pH of soil. It can be purchased online.
- Mixing a handful of soil with room temperature distilled water: take a handful of soil and put it in a jar. Then pour some distilled water into the bowl until the dirt is in the consistency of a milkshake.
- Dipping a pH test strip in the mixture for 20-30 seconds: holding the pH test strip at the non-reading end, dip the strip into the dirt mixture for 20-30 seconds. When the time is up, lift the strip from the soil and dip it into distilled water to clean the dirt off.
- Compare the pH strip to the test kit’s key: use the key that is included in the pH test kit to read the pH of the soil (5).
3: Changing the soil pH
- Make the soil less acidic: if the soil pH is below 7, add a cup of dolomite or lime to the soil. Mix well, then retest with a test probe.
- Make the soil less alkaline: if the soil pH is tested above 7, then add a cup of organic matter such as pine needles, peat moss, or decomposed tree leaves. Then, retest the soil to get the new pH level.
- Change soil pH to suit specific plants: for example, add sulfur to a certain part of the soil for planting crops/trees that prefer more acidic soils. The pH of the soil does not need to be uniform in the entire area.
Difference between DIY and professional testing
DIY is basically a testing procedure (3) which means Do It Yourself(DIY) while professional testing is done by experts and technological advancements. Below are a few points to differentiate them
DIY (Do It Yourself) |
Professional testing |
| They are conducted by unskilled individuals | Are conducted by highly skilled professionals. |
| It may or may not involve a team of people. | This type of testing involves a huge team of professionals. |
| The results are not 100% accurate | Results are usually 100% accurate. |
| It is a longer/time-consuming process. | Takes less time to take testing procedures. |
| This process is cheap. | It is quite expensive compared to DIY. |
| It involves little capital investment. | Needs huge capital investment. |
| No professional tools are used. | All professional gadgets and tools are used. |
| Use of technology is negligible. | Use of technology is the prime factor. |
| The results are less durable. | Test results are very durable. |
Testing of different soil types
1. Garden soil
To test the soil pH of garden soil the pantry soil pH test can be taken. It follows
- Place 2 tablespoons of soil in a bowl and add ½ cup vinegar. If the mixture fizzes, we have alkaline soil.
- Place 2 tablespoons of soil in a bowl and moisten it with distilled water. Add ½ cup baking soda. If the mixture fizzes, we have acidic soil
- If it doesn’t react to any test, then that means the garden soil has a neutral pH
2. Potting mixtures
Potting soil or potting mixture is a mixture of materials like bark, moss, etc. They are used for growing plants in containers, also known as indoor plant soil. The adjustment or measurement of soil pH of potting soil can be done by adding sulfur or aluminum to make it acidic or alkaline.
3. Lawn soil
Lawn soil is composed of rocks, silts clay and it is denser and more compact than crustal soil. As it covers a huge area, the soil pantry pH test can be conducted here to check the soil’s pH value.
Adjusting soil pH and techniques
Soil pH is the key factor in agriculture and farming hence it is important to know how to adjust the pH levels in soil during times of need. A few techniques are described below-
- Adding organic matter like compost, straw, and leaf to soil can help to balance the pH levels and improve soil fertility (6).
- Ammonia is a naturally occurring acid that can be added to soil to increase alkalinity.
- Manure or compost can be added to soil to produce acid levels in soil.
- Herbicides containing lime or sulfur dioxide must be applied at the correct rate to achieve the desired pH.
- The usage of compost instead of commercial fertilizers helps in balancing soil pH.
- Mulching plants with organic materials to help keep the ground cooler and reduce erosion.
pH level of different crops
Listed below are a few of the major crops and their pH value.
CROP |
BOTANICAL NAME |
pH RANGE |
| Cereals | ||
| Barley | Hordeum sativum | 6.5-8.2 |
| Oats | Avena sativa | 4.8-7.5 |
| Rice | Oryza sativa | 5.5-6.5 |
| Wheat | Triticum vulgare | 5.5-8.0 |
| Millets- | ||
| Italian millet | Setaria italica | 5.0-7.0 |
| Maize | Zea mays | 5.5-8.0 |
| Sorghum | Sorghum vulgare | 5.5-7.5 |
| Oilseeds | ||
| coconut | Cocos nucifera | 6.0-7.5 |
| groundnut | Arachis hypogaea | 5.3-7.0 |
| linseed | Linium usitatissimum | 5.0-7.0 |
| rape | Brassica napus | 6.0-8.0 |
| soybean | Glycine max | 6.0-7.5 |
| Fiber crops | ||
| Cotton | Gossypium spp. | 5.0-6.5 |
| Sugar crops: | ||
| Sugarcane | Saccharum officinarum | 6.0-8.0 |
| Fodder crops | ||
| Bermuda grass | Cynodon dactylon | 6.0-7.5 |
| Berseem | Trifolium alexandrinum | 6.5-8.5 |
| Johnson grass | Sorghum halepense | 5.0-6.0 |
| Lucerne | Medicago sativa | 6.2-8.2 |
| Sudan grass | Sorghum sudanense | 5.0-6.5 |
| Sunflower | Helianthus annuus | 6.0-8.0 |
| Vegetables | ||
| Cabbage | Brassica oleracea | 5.5-7.5 |
| Cowpea | Vigna sinensis | 5.0-7.0 |
| French bean | Phaseolus vulgaris | 6.0-8.0 |
| Lima bean | Phaseolus limensis | 6.0-8.0 |
| Onion | Allium cepa | 6.0-8.0 |
| Pea | Pisum sativum | 6.5-7.5 |
| Potato | Solanum tuberosum | 4.5-6.5 |
| Sweet potato | Ipomea batatas | 5.8-6.0 |
| Tomato | Lycopersicum esculentum | 5.5-7.0 |
| Turnip | Brassica rapa | 5.5-7.0 |
| Velvet bean | Stizolobium deeringianum | 5.5-7.0 |
| Fruit crops |
| Banana | Musa spp. | 6.0-7.5 |
| Pineapple | Ananas sativa | 5.0-6.5 |
| Plantation crops | ||
| Coffee | Coffea arabica | 4.5-7.0 |
| Rubber | Hevea brasiliensis | 3.5-6.0 |
| Tea | Thea sinensis | 4.0-5.5 |
| Narcotics | ||
| Indian hemp | Cannabis sativa | 6.0-7.5 |
| Tobacco | Nicotiana tabacum | 5.0-5.6 |
Role of soil pH
1. Gardens
- pH is very important in the case of gardens as it helps in plant growth.
- It also helps to determine what type of plants are needed to be planted in a specific garden.
- The soil pH also determines the availability of almost all types of nutrients required for the plants.
- Most plants in garden soil grow in the range of 6.0-7.0
2. Landscaping
- pH value in landscaping is very important as it determines the acidity or alkalinity of the soil.
- It also determines the types of crops to be grown.
- Also determines the areas suitable for horticulture plants like vegetables, medicinal plants, etc.
3. Agriculture
- It determines what type of fertilizer must be used on the crops
- Whether the fertilizer is acidic or alkaline
- It also determines the type of nutrients needed for the plants.
Soil buffering and nutrient uptake
Soil buffering refers to the ability of soil to resist changes in pH. Soils high in clay minerals are more resistant to changes in pH. Sandy soils and highly weathered soils are the least buffered. A well-buffered soil will resist changes in pH if acid is introduced (4).
Plants require at least 14 essential minerals for growth along with water and carbohydrates to complete their life cycle. In most situations, roots do not take up minerals directly from the soil but work in association with soil microbes that make the minerals more available to plants. This is known as nutrient uptake.
Q&A
1. What is the most accurate way to test soil pH?
The most effective way would be a soil pH testing kit.
2. How do I test pH in my soil?
Soil pH can be tested in the following ways
- pH strips
- pH testing kit
- pH test probe
- Adding lime for alkalinity
- Adding sulfur for acidity.
3. How do you test soil pH at home?
Testing soil pH at home is very easy nowadays. The method of pantry soil test must be followed. Here the addition of vinegar and baking soda to the soil determines whether the soil is alkaline or acidic in nature. It’s a do-it-yourself (DIY) technique.
Summary
- Soil pH expresses the activity of the hydrogen ions in the soil solution
- It is an important parameter that influences different soil factors, affecting plant growth.
- Soil health is the state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment
- A soil test is crucial because it will help in the optimization of crop production, diagnosing the nutrient deficiencies in the soil, and consequently working towards improving the lacking nutrients
- Soil pH is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+). It is a measure of the soil solutions of acidity and alkalinity, on a scale from 0 to 14.
- Soil pH also influences the activity of microorganisms which in turn influence plant growth and crop production.
- Several techniques have been proposed for measuring soil pH such as electrometric and colorimetric.
- There are various ways to test the pH of soil like testing with commercial probes, using paper strips, and also by changing the soil pH.
References
- D Biswas, S.K Mukherjee, Soil Science, McGraw Hill Education Private Limited, New Delhi, 2013.
- J.A. Daji, A textbook of soil science, Media Promoters and Publishers PVT.LTD, Bombay, 2005.
