
Introduction
Weather phenomena is a natural phenomenon that occurs as a result of combinations of the water cycle, Coriolis force, and pressure system. Precipitation is one of the most important weather phenomena having different forms. Sleet and hail both are forms of precipitation, the topic of the discussion below is sleet vs hail.
Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, rivers, ponds, canals, etc due to the sun. The water vapor rises as it becomes lighter. When exposed to the extreme cold of the upper atmosphere, condensation causes water vapor to turn into tiny water particles. These water particles float in the dust of the air.
When water particles combine with each other to form large water particles, they can no longer float in the air. Under the influence of the earth’s gravitational force, it falls on the ground in the form of liquid and solid precipitation. Sleet and hail is one such type of solid or frozen form of precipitation. Now let’s see what sleet and hail are and how different they are from each other (1) & (3).
What is Sleet?
Definition
When partially melted snow and rain falls together on the earth’s surface it is called sleet. In the temperate regions, in winter, instead of rainfall, airborne ice particles fall to the ground. These ice particles are quite solid and are known as sleet (2).
Other forms of precipitation are seen in the atmosphere like snow, frost, dew, freezing rain, etc besides rainfall. Sleet is also a form of precipitation in which water is partially frozen but not crystalline (4).
Characteristics
- It is a natural phenomenon that falls on the earth’s surface in the form of precipitation.
- Sleet is a type of precipitation where rain and snow occur at the same time.
- Some parts of this type of precipitation are icy and others form water droplets or small ice crystals.
- In this case, ice crystals are quite solid.
- This type of precipitation occurs from nimbostratus, stratocumulus, and cumulonimbus clouds.
- It can occur when a warm layer of air is above the freezing layer below the surface of the earth.
- Sleet forms mainly during the winter seasons.
- When these types of precipitation occur it covers all outside surfaces.
- It forms from frozen snowflakes.
- When sleet falls on the ground it covers the ground at a depth of one-half inches or more.
- The sleet is small in size.
- It can create an ice layer on the road that is very unsafe for driving (2) & (4).
What is Hail?
Definition
Cumulonimbus clouds enter the coldest parts of the atmosphere as a result of upward winds. Then the water particles slowly turn to ice. At some point, these ice cubes fall to the ground. This type of natural phenomenon is called hail (3).
Hails are made from storm clouds. According to the meteorological departments, if an ice cube is not less than 3/4 inches in diameter, there is no risk of hail damage. It is formed when drops of water freeze together in the cold upper regions of thunderstorm clouds (5).
Characteristics
- Hail is a type of storm that settles on a piece of ice.
- These storms are usually during regular thunderstorms.
- Small clouds forms hail.
- There are some irregular hailstones that grow up to 2 inches and can cause damage.
- The hailstones are of various shapes.
- It consists of small ice with a diameter of about 5 to 150 millimeters.
- In some cases, when hail starts to fall through the clouds, it melts and becomes liquid.
- The actual temperature of a country is not directly related to hail. Hailstones occur during storms.
- Usually, hail lasts no more than 5 minutes.
- There is more hail in the hilly regions than in the temperate countries (2) & (5).
How sleet forms
-
Formation of sleet
Sleet is a type of precipitation where rain and snow occur at the same time. It forms when the snow melts in a warm layer and then refreezes into ice pellets as it falls through a cold layer. Sleet occurs when there is warm air near the base of the cloud, not on the ground. Snow falls through this wedge of warm air, partially melts, and then re-freezes as a small ice ball before hitting the ground (1) & (5).
How hail forms
-
Formation of hail
When the raindrops fall, they are almost always in the middle of the upward pressure of the wind. As a result, as the raindrops go down, some of them start rising again and become colder. The condensed water droplets become heavier and go down again. Some parts of it may go up again due to the upward pressure of the warm air.
During such ups and downs, some of the water droplets turn into small ice cubes. These are heavier so these ice cubes can no longer rise. The force of gravity pulls down with the flow of rain creating hail. The main condition of hail is extreme heat (2) & (4).
Difference between sleet and hail
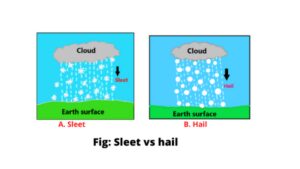
Water vapor is light and rises easily. Upon contact with the cool air above, the water vapor condenses and turns into tiny water droplets or snow particles, sheltering dust, coal particles, etc. floating in the air. These floating water particles or snow particles are called clouds. These cloud-forming water particles or snow particles are very small, with an average diameter of only 0.01 mm. So they float like clouds very easily.
But when these tiny particles floating in the clouds join together and have an average diameter of 0.5 mm, they can no longer float. Under the influence of gravity, the cloud falls down as precipitation. Sleet and hail are two forms of precipitation. Now sleet vs hail are discussed below (3) & (5).
Sleet vs Hail: differences
Content |
Sleet |
Hail |
| 1. Definition | In temperate regions, some snowflakes fall to the ground with rain called sleet. | When thunderstorms clouds enter the coldest parts of the atmosphere as a result of upward winds, the water particles gradually turn to ice. At some point, these ice cubes fall to the ground with rain called hail. |
| 2. Formation process | Many times a layer of cool clouds near the surface of the earth and a layer of warm clouds above it. When rain falls from a warm cloud, it condenses into tiny snowflakes as it passes through the cool clouds below it. Then these condensed snowflakes fall to the ground with rain in the form of sleet. | Clouds or raindrops rise to a very cool place at very high altitudes through strong upward winds in the sky. In extreme colds, those water particles freeze and turn into small ice. As the wind speed decreases, these ice cubes collect more water particles and increase in size and with rain, ice cubes of different sizes fall to the ground. |
| 3. Size | Sleet is smaller than hail. It is a transparent ice pellet that has a diameter of 5 mm. | Hail is larger than sleet. It consists of small ice with a diameter of about 5 to 150 millimeters. |
| 4. Time | It forms mainly during the winter seasons. | This type of precipitation forms mainly during the summer seasons. |
| 5. Location | Sleet is mainly found in temperate countries. | Generally, it is found in continental interiors at mid-latitudes and less common in the tropics. |
| 6. Cloud types | This type of precipitation is mainly caused by nimbostratus, stratocumulus, and cumulonimbus clouds. | Hail is mainly formed from cumulonimbus clouds. |
| 7. Create a thin layer | It can create a thin ice layer on the road. | It cannot create a thin ice layer on the road. |
| 8. Crystalline structure | Here water is partially frozen but not crystalline. | Hail is a form of precipitation in which water is partially frozen and crystalline. |
| 9. Type | Sleet is softer than hail. They are small ice particles. | Hail is quite harder than sleet. It is solid precipitation that can form in very large sizes (4) & (5). |
Sleet vs Hail: Similarities
There are some similarities between sleet and hail. The following are the similarities between the two before discussing sleet vs hail.
- Sleet and hail both are forms of frozen precipitation.
- Both are natural phenomena.
- Sleet and hail both are bounce when they fall to the ground.
- Hail and sleet both fall to the ground with rain.
- Both of these types of precipitation damage the crops.
- These two forms of precipitation both are ice particles (2).
Q&A
1. Is sleet smaller than hail?
Sleet is smaller than hail. Hail is quite large. The sleet is small in size, it is around 5 mm and the hail is 5 to 150 mm.
2. Which is bigger sleet or hail?
Sleet is small ice particles. It consists of small ice with a diameter of about 5 mm. On the other hand, hail is a large ice particle. It is made of ice particles with a diameter of about 5 mm to 150 mm. So a comparison between these two forms of precipitation shows that hail is bigger than sleet.
3. What is frozen snow called?
Graupel is called frozen snow that forms when super condense water droplets are collected.
Written By: Manisha Bharati
Reference
1. Savindra Singh. Climatology. Pravalika Publications, Allahabad. Chapter 9: Fogs, Clouds, and Precipitation. Page No: 174 to 201.
