Introduction
Sometimes the vision becomes blurred due to the refractive defect of the eye. A refractive defect means the inefficiency of the lens of the eye to bend light correctly which results in blurred unclear vision. The current article is about Myopia vs Hyperopia.
There are three common defects of vision
- Myopia near-sightedness or short-sightedness
- Hyperopia or Hypermetropia far-sightedness or Long-sightedness
- Presbyopia
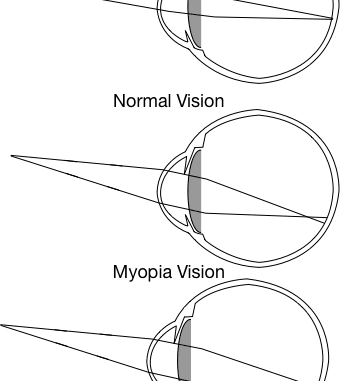
Myopia near-sightedness or short-sightedness
Another name for myopia is nearsightedness. When the eye is too long or the refractive power of the cornea and lens of the eye are too strong it results in the formation of an image in front of the retina. As a result, a blurred image is formed.
Therefore a person with myopia can see near objects clearly but is unable to longer or distant objects distinctly.
Very high levels of myopia are associated with other eye conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, and retinal detachment, which can lead to low vision and even legal blindness.
Hypermetropia or Hyperopia far-sightedness or Long-sightedness
Hyperopia occurs when images are formed behind the retina because the eye is relatively too short or the refractive powers of the cornea and lens of the eye are relatively too weak. The result is a blurred image.
A person with hypermetropia can see distant objects clearly but cannot see nearby objects distinctly. The near point, for the person, is farther away from the normal near point (25 cm).
Presbyopia
With age, the lens gradually hardens and becomes less pliable, making it increasingly difficult to focus on near objects. By about 45 years of age, most people require reading correction. Many people assume that this correction is for hyperopia but actually it is presbyopia.
Myopia vs Hyperopia
| Long-sightedness | Short-sightedness |
| Known as hyperopia | Known as Myopia |
| The focal length of the eye lens is too long, or the eyeball has become too small. | The image of the distant object is formed in front of the retina. |
| In this condition, a person is unable to focus objects at a distance. | In this condition, a person is unable to see nearby objects. |
| The power of cornea and lens becomes insufficient | The cornea becomes too flat or the eye is too short. Excessive curvature of the eye lens or elongation of the eyeball. |
| Convex lenses are used to correct hyperopia | Concave lenses are used to correct myopia. |
| Commonly found in older adults under the age of 50. | Commonly found in 41% adults of age group (20-40) |
References
