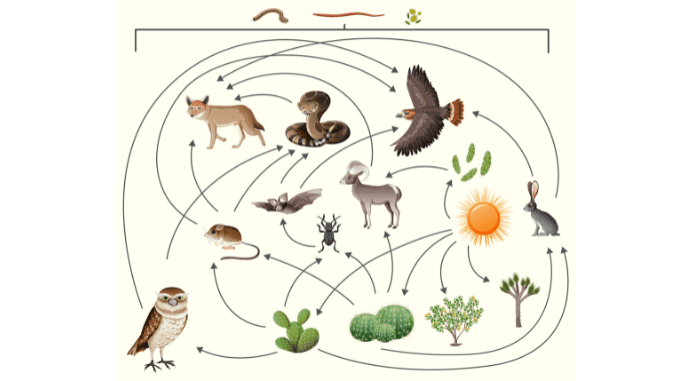
Introduction
All living thing whether it is plants or animals depends on food for their survival. Plants produce their own food with the help of sunlight, water, nutrients from the soil, and carbon dioxide from the air. Therefore plants are the basic layer of all types of tropic levels therefore they are known as the producers. Animals who depend directly on plants for their nutrition are known as primary consumers. This food is absorbed by various plant organisms located at the trophic level. As a result, sometimes complex and sometimes simple chains are formed in the ecosystem based on the relationship between food and consumer. This article is about the food chain vs food web.
A simple sequence of transfer of energy in the form of food from one tropic level to another in a linear fashion is known as a food chain. When two or more than two types of food chains get connected or interlinked with each other then they form a food web. Therefore, the food chain and food web are interrelated (2).
Food chain
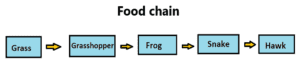
The periodic process by which the food energy of an ecosystem flows from the producer to different groups of organisms based on the food-consumer relationship is called the food chain. There are several layers associated with the food chain, called the trophic level. The food chain is important for the survival of the ecosystem as well as the entire biosphere. Food and energy are transferred from the producer to other organisms in this food chain. So if the food chain is broken, ecological existence is endangered (1) & (4).
Characteristics of the food chain
1. Green plants (producers) are the base layer of almost all food chains.
2. A food chain usually has three to five trophic levels.
3. From the lowest to the highest levels of the food chain, the number of organisms, biomass, and energy decreases.
4. The food chain is not isolated in the ecosystem. These are closely related to each other.
5. If biodiversity is high, the complexity of the food chain increases.
6. Almost no food chain is created without producers. But there are exceptions, there are some food chains that are formed without producers. Such as parasitic food chains (2) & (4).
Food web
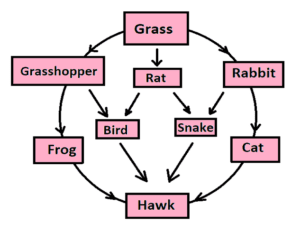
In the ecosystem, food and energy are not only transported through a food chain but also through a number of interrelated food chains. That is, no single food chain is isolated in nature. Food chains are related to each other in many ways.
Relation of the food chain with food web (Food chain vs food web)
This is because the dietary characteristics of organisms are quite diverse. When an animal eats many different types of food, the animal is no longer a member of a single food chain, it becomes a member of several food chains. Not only that, but the animal’s food level also varies in different food chains. The food-consumer relationship of the ecosystem is extremely complex (1) & (3).
The web of unequal food-consumer relationships between organisms that are formed by the interaction of different food chains in an ecosystem is called the food web (4). So a food chain can be considered as a part of the food web.
Food webs are relatively simple in terrestrial ecosystems compared to aquatic ecosystems (2) & (3).
Characteristics of the food web
1. The food web is made up of multiple food chains.
2. The food web interconnects a large number of interrelated food chains.
3. It is shaped like a web.
4. Some groups of animals take food from different food chains at the same time in the food web.
5. An unequal variety of food-consumer relationships can be observed among the living groups in the food web (2) & (4).
Differences and similarities between the food chain and food web
The food chain and food web of the ecosystem are interrelated. The food web is formed by many food chains. So some similarities between them.
Food chain vs food web: Similarities
1. The food chain and the food web, both represent the flow of food and energy from producers to the consumer.
2. Both the food chain and the food web include producers, consumers, and decomposers.
3. The food chain and the food web are arranged like chains.
4. Both the food chain and food web discuss the number of organisms, the amount of energy in organisms, etc. (3).
Food chain vs food web: Differences
Although there are similarities between the food chain and the food web, besides this there are some differences between them which are discussed below (2) & (4).
Content |
Food chain |
Food web |
1. Definition |
The sequential stage at which food energy flows from producer to consumer and to the various animal groups related to the consumer is called a food chain. | The web of unequal food-consumer relationships between organisms that are formed by the interaction of different food chains in an ecosystem is called the food web. |
2. Dependence |
The food chain is not dependent on the food web. | The food web is dependent on the food chain. |
3. Biodiversity |
Simple chains are created in the food chain. Because the number of organisms here is less. So the biodiversity in the food chain is low. | Many food chains come together to form a food web. Food webs are of a complex type. So the number of organisms here is also very high and the biodiversity is very high. |
4. Progress |
It moves in a straight line. | It moves like a polygon. |
5. Relationships |
The food-consumer relationship is specified in the food chain. | The relationship between food and consumers in the food web is indefinite. |
6. Energy flow |
Energy flow of the food chain flows in the same chain. | The energy flow of the food web flows through multiple chains. |
7. Stability |
The stability of the food chain is unsustainable. Because one of the components of the food chain becomes extinct, the food chain is likely to be destroyed. | Food web will be disturbed if more than one food chain is destroyed. So the food web is sustainable. |
8. Number |
An ecosystem has more than one food chain. | An ecosystem usually has a food web. |
9. Biomass |
As the food chain is a single chain, its biomass is less. | Since the food web has multiple chains, the total biomass is higher (2) & (4). |
Q&A
1. Why does the food web not develop without a food chain?
In the ecosystem, the diversity of organisms is highly unequal. This is why energy and nutrition flow through a large number of interrelated food chains. Although an organism is the primary consumer of one food chain, it can be a secondary or tertiary consumer in another food chain. As a result, no single food chain in the ecosystem is isolated. These food chains are connected to each other to form a web system and turn into a food web. So it is impossible to develop a food web without a food chain.
2. What are the producers?
Chlorophyll-containing green plants that produce carbohydrate foods (glucose) by chemically combining CO₂ and H₂O from the environment with sunlight are called producers. Producers are autotrophs because they can make their own food. Green plants are the producers of the ecosystem.
3. What are consumers?
Those who survive by eating the food items that the producers of the ecosystem produce are called consumers. Almost all animals belong to the consumer class. Consumers in the ecosystem are divided into several classes. These are primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, and final consumer or apex.
4. What is the relationship between the producer and consumer?
All green plants depend on the inorganic elements of nature. Some food remains after the plants have been used for their physiological needs. This residual food is taken by the consumer and regulates the biological functions of the body. Thus producers and consumers maintain the balance of CO₂ and O₂, in the atmosphere through their biological actions.
5. What is a decomposer?
Several classes of fungi and bacteria derive nutrients from the dead bodies of producers and consumers. Called decomposers. They decompose the dead bodies of those organisms and turn complex organic compounds into simple organic compounds.
6. What is the difference between the producer and consumer?
Producer |
Consumer |
| Producers can make their own food. They do not depend on others for food. | Consumers are unable to produce food. Depends on producers for food. |
| Have chlorophyll in their body. | Do not have chlorophyll in their body. |
| Can use solar energy directly by binding it to their body. | Cannot bind solar energy to their bodies. |
| Producers absorb carbon dioxide from the environment and release oxygen. | Consumers absorb oxygen from the environment and release carbon dioxide. |
7. Who is the modifier or converter in the ecosystem?
There are some classes of bacteria and decomposers that further decompose modified simple compounds and return them to the environment by converting them into inorganic compounds or elements. Hence, called modifiers or converters.
