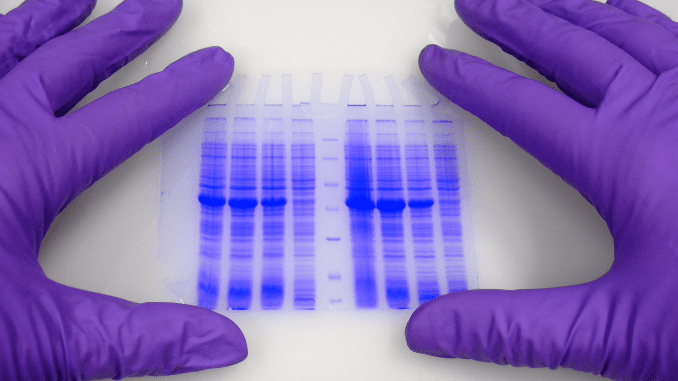
Introduction
2D gels are commonly called two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-DE).
Electrophoresis is technique used to separate the compounds in a cell or used to separate and purify nucleic acids.
The term electrophoresis means the movement of colloidal particles in a medium under the influence of an electric field.
The speed of electrophoretic mobility of a molecule depends on its charge and molecular mass.
Moreover, charge of a molecule can be influenced by:
- pH of buffer
- Temperature
- Strength of an electric field
- Matrix used for mobility
2D gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool to extract complex proteins from several biological specimens such as tissues and cells. It can be referred to as an orthogonal technique as thousands of proteins can be separated in one gel slot.
Principle
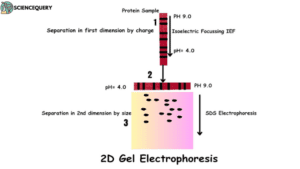
The principle of protein separation in 2D gel electrophoresis is performed in two major steps.
Step 1: First Dimension
- In the first dimension, proteins are resolved according to their isoelectric point.
- It is then separated in a pH gradient.
- The isoelectric point is defined as the value of pH where the molecule carries zero net electric charge on it.
Step 2: Second Dimension
- In the second dimension, proteins are separated according to their molecular weight.
- This separation is done by SDS laemmli buffer.
- Both these separations are carried out in the polyacrylamide gels.
Polyacrylamide gels are most effective in the separation of small DNA fragments and have high resolving power. These gels are cross linked gels formed by the polymerization of acrylamide with a cross linking agent N,N-methylenebisacrylamide.
One advantage of using this gel is they can accommodate large quantities of DNA and produce sharp bands. It is sometimes observed that different molecules may have the same physicochemical properties. In such cases proteins are easily separated by the help of 2D gel electrophoresis method rather than 1D-SDS PAGE.
Instrument diagram
Method or how it works
First Dimension Electrophoresis
The first dimension electrophoresis is carried out by a carrier ampholyte pH gradient. Ampholyte can be defined as an ionic substance that can react either as an acid or base. Today, immobilized pH gradients are used enabling high protein loading capacity with less labour effort.
Immobilized pH gradient strips are used in this process which are usually short length strips being used for fast screening. Long IPG strips are used for comprehensive analysis. Already cast acrylamide gel matrix when copolymerized with pH gradient results in a stable pH value.
Second Dimension Electrophoresis
This step separates proteins based on their molecular weight by the help of a vertical electrophoretic device or Laemmli buffer. Laemmli buffers are used for isolating protein molecules by SDS PAGE electrophoresis technique. The first dimension rehydrated strip is placed on top of SDS-PAGE and sealed with agarose gel instead of loading the protein sample.
Steps 2D gel electrophoresis
Step 1: Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is an important step for obtaining an informative 2-DE result. The addition of SDS, an anionic detergent, is a good surfactant in order to solubilize protein molecules. Later on it was investigated and found that non-ionic detergents like TritonX-100 are the best choice for extracting the proteins.
Step2: Protein Extraction
Several proteins are extracted according to different chaotropes, and non-ionic detergents according to the desired protein of interest. Chaotropes are basically molecules present in solvent such as water that unwind the structure of proteins. They are responsible for breaking the hydrogen bonding between the water molecules and weakens protein stability.
Step 3: Removal of contamination
Non-protein contaminants like nucleic acids, ionic molecules are removed before first-dimensional electrophoresis. This process is important as it may interfere with the protein separation during electrophoresis.
Step 4: Rehydration buffer
The addition of a rehydration buffer can help to improve the resolution and separation of proteins on 2-D gels, leading to more accurate results. It contains protease inhibitors which can prevent protein degradation during the electrophoresis process.
Applications
1. Research Purposes
The 2D gels electrophoresis technique is widely used in the field of biochemistry, cell biology and clinical biology.
2. Biomarker discovery
One major application of 2-D gel electrophoresis is in the discovery of biomarkers.
3. Disease research
2-D gel electrophoresis techniques are used in studying various diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease etc. It is done by identification of changes in protein expression.
4. Agricultural research
Researchers have also utilized 2-D gel electrophoresis techniques to study plant proteins involved in stress responses, and regulation of growth.
Advantages
- Two dimensional gel electrophoresis method is the best technique for the separation of proteins within one gel.
- It provides high resolution and efficiency.
- It has the ability to fractionate proteins for better visual analysis and identification.
- With the help of two dimensional gel electrophoresis, researchers are able to quantify proteins and its isomers.
Disadvantages
- One of the major limitations is its limited capability to resolve the membrane proteins. They are hydrophobic in nature and hence unable to dissolve in rehydration buffers.
- Low abundance protein remains hidden and large protein molecules mask their appearance, leading to faulty results.
- High molecular weight proteins are very difficult to visualize.
- This technique of gel electrophoresis is time consuming and expensive.
Q&A
1. What are 2D gels used for?
Two dimensional gel electrophoresis is used for the detection, analysis and quantification of protein molecules.
2. What is the difference between SDS-PAGE and 2D gel electrophoresis?
SDS page and 2-D gel electrophoresis are two commonly used techniques in biochemistry for separating and analyzing proteins. But they have few differences.
SDS page (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) separates proteins based on their molecular weight. Whereas 2-D gel electrophoresis combines two separation techniques – isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE to achieve higher resolution.
3. What is the difference between 1d gel and 2D gel?
The main difference between 1D and 2-D gel electrophoresis is the number of dimensions involved. In 1D gel electrophoresis, only one dimension is considered while running a sample through a gel matrix. 2-D gel electrophoresis uses two dimensions.
4. What are the steps in 2-D gel electrophoresis?
There are two primary steps in 2D gel electrophoresis:
-
First Dimension Electrophoresis- The first dimension electrophoresis is carried out by a carrier ampholyte pH gradient.
-
Second Dimension Electrophoresis- This step separates proteins based on their molecular weight by the help of a vertical electrophoretic device.
Summary
- 2D gels are commonly called as two dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-DE). Electrophoresis through polyacrylamide gels is a standard method used to separate and purify nucleic acids.
- The term electrophoresis means the movement of colloidal particles in a medium under the influence of an electric field.The speed of electrophoretic mobility of a molecule depends on its charge and molecular mass.
- 2D gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool to extract complex proteins from several biological specimens such as tissues and cells. Polyacrylamide gels are most effective in the separation of small DNA fragments and have high resolving power.
- The 2D gels electrophoresis technique is widely used in the field of biochemistry, cell biology and clinical biology. One major application of 2-D gel electrophoresis is in the discovery of biomarkers.
- Researchers have also utilized 2-D gel electrophoresis techniques to study plant proteins involved in stress responses, and regulation of growth.
- 2-D gel electrophoresis combines two separation techniques – isoelectric focusing and SDS-PAGE to achieve higher resolution.
References
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367593101002757
https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/pmic.200800298
