
Know in one minute about Secondary battery
|
Introduction
A battery is a device or arrangement which generates electrical energy with the help of chemical reactions between the two electrodes present inside it. There are two types of batteries primary battery and secondary battery. In this article, we will understand secondary batteries.
Secondary batteries are electrochemical batteries that can be recharged by passing a current through them considering the condition that the direction of the current must be opposite to the direction of the current produced by the battery.
The secondary battery is a reusable battery, hence when a secondary battery is discharged, still it can be used by the charging process.
A good secondary cell/battery endures numerous charge and discharge cycles.
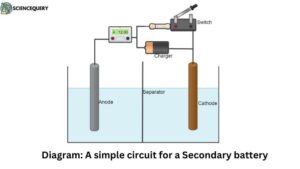
Circuit for the secondary battery: description
In the circuit of a secondary battery, there is a special arrangement for the charging process to commence. As shown in the figure the arrangement consists of two electrodes out of which one acts as a cathode while the other acts as an anode. These electrodes are dipped in an electrolyte and are also separated by a separator.
The arrangement used for charging consists of a switch that is responsible for changing the nature of the circuit from discharging to charging and vice versa.
When the battery is discharging then the circuit is the same as that of any other electrochemical cell. The switch or key is closed and the circuit has an anode as a negative terminal while the cathode behaves like a positive terminal. The current flown in the cell is then drawn by connecting an external load from it.
While the cell is in the charging cycle/ process the switch is open and the electrodes are connected to an external power source (generally known as a charger). The connection is made in such a manner that the anode is now connected to the positive terminal while the cathode is connected to the negative terminal. This makes the external current flow in the opposite direction to the current generated by the cell/battery.
Secondary battery: Types
Based on various designs and functioning of the battery it can be of different types. Some batteries are differentiated by the elements used in them like anode and cathode.
- Lithium-ion battery
- Aluminum-ion battery
- Glass Battery
- Lead acid battery
- Magnesium ion battery
1. Lithium-ion battery

A lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery, invented by M. Stanley Whittingham in the 1970s. It is a battery that stores energy by reverse reduction of lithium ions. A conventional lithium-ion battery contains graphite as the anode while a metal oxide is a cathode. The battery consists of lithium in an organic solvent as its electrolyte.
These types of batteries are widely used in portable electronics and electric vehicles. The reaction taking place in
The cathodic half-cell is
CoO2 + Li+ + e– → LiCoO2
While the anodic half-cell reaction is:
LiC6 → C6 + Li+ + e–
The full reaction is:
LiC6 + CoO2 → C6 + LiCoO2
2. Aluminum-ion battery
This class of rechargeable batteries is based on the intercalation of aluminum ions between the layers of a transition metal oxide cathode. Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, which use lithium as the primary ion, aluminum-ion batteries use aluminum ions, making them a safer and more cost-effective alternative.
An important feature of aluminum ion batteries is their high energy density and low cost. It is much safer than lithium-ion batteries due to their low flammability and lesser chance to cause thermal runaway reactions.
In these batteries, Al3+ acts as charge carriers which are trivalent ions and hence can carry 3 units of charge by one ion. Due to this the energy storage capacity of the battery is more than that of a lithium-ion battery.
3. Glass Battery
These types of batteries are based on one of the newly developed battery technologies. These cells use glass electrolytes instead of liquid or solid electrolytes used in traditional batteries.
In a glass battery, the glass electrolyte allows for the use of a wide range of metal ions as charge carriers, including lithium, sodium, and aluminum. This versatility can lead to higher energy densities and longer cycle life compared to traditional batteries.
Additionally, the solid-state nature of the glass electrolyte can result in improved safety compared to liquid electrolyte batteries, as there is no risk of leakage or explosion.
Moreover, since the glass battery technology is still in the research stage there are a lot more challenges to be resolved before they can be commercialized.
4. Lead Acid Battery
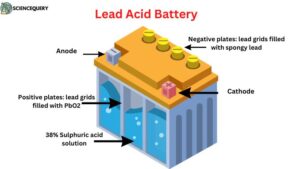
Lead acid batteries are one of the oldest technologies used to manufacture rechargeable batteries. This technology has been in use for about 150 years.
These batteries are widely used in vehicles like cars, and trucks, as well as in backup power supplies for telecoms and computers. These batteries are made up of several cells each of which contains lead plates and lead oxide plates immersed in an electrolytic solution of sulfuric acid.
During the discharge process the lead sulfate reforms back to lead oxide and sulfuric acid releasing electrons in the process generating a flow of current.
This flow of current is used to supply power to various electronic devices.
While the battery is being charged the lead oxide and sulfuric acid react with each other to form lead sulfate releasing electrons in the process this stores energy in the battery.
Diagram
5. Magnesium Ion battery
These batteries use magnesium ions as active charge carriers. The secondary magnesium battery consists of the reversible insertion and removal of Mg2+ ions in anodes and cathodes during the charging and discharging process.
This kind of technology is said to be one of the possible replacements for lithium-ion batteries as the magnesium ions have 50% higher volumetric energy density when compared with lithium ions.
The metallic magnesium anode does not form dendrite structures, while the lithium anode does have dendrite formation. The dendrite-free Mg deposition allows the magnesium metal to be used with elements without intercalation at the anode, thus it increases the volumetric energy density up to 5 times more than the lithium graphite batteries.
Q&A
1. What is the difference between primary battery and secondary battery? What are the benefits of using a secondary battery?
Primary Batteries are also known as disposable batteries they are designed to be used once and then to be discarded. They have a limited lifespan and cannot be recharged. These batteries are often used in low-drained devices. These are suitable for devices where the battery life is longer than the life of the devices.
Secondary Batteries known as rechargeable batteries can be recharged and used multiple times. They have a longer lifespan as compared to primary batteries but are more expensive. These batteries are often used for high-drain devices like smartphones, laptops, etc. They are suitable for devices that have a higher lifespan than that of the battery.
There are several benefits of using Secondary batteries:
- It is less harmful to the environment.
- It is convenient and can be reused easily.
- They provide a consistent and reliable power source.
2. Which is safer to use an Aluminium ion or a Lithium-ion battery and why?
Both the batteries i.e. Lithium ion whereas Aluminium ion batteries are safe to use but when compared aluminum ion batteries are a bit safer than lithium-ion batteries. This is because aluminum batteries have a low chance to cause thermal runaway reactions and are also low flammable.
Reference
https://ncert.nic.in/textbook/pdf/lech103.pdf
Written By: Bharat Awasthi
